The North America Portal
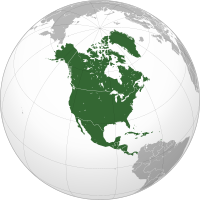
North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Greater North America includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
Continental North America covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), representing approximately 16.5% of the Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography, the terms "North America" and "North American" sometimes refer to just Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Greenland.
It is unknown with certainty how and when first human populations first reached North America. People were known to live in the Americas at least 20,000 years ago but various evidence points to possibly earlier dates. The Paleo-Indian period in North America followed the Last Glacial Period, and lasted until about 10,000 years ago when the Archaic period began. The classic stage followed the Archaic period, and lasted from approximately the 6th to 13th centuries. Beginning in 1000 AD, the Norse were the first Europeans to begin exploring and ultimately colonizing areas of North America.
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, African slaves, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups. (Full article...)
Wood Badge is a Scouting leadership programme and the related award for adult leaders in the programmes of Scout associations throughout the world. Wood Badge courses aim to make Scouters better leaders by teaching advanced leadership skills, and by creating a bond and commitment to the Scout movement. Courses generally have a combined classroom and practical outdoors-based phase followed by a Wood Badge ticket, also known as the project phase. By "working the ticket", participants put their newly gained experience into practice to attain ticket goals aiding the Scouting movement. The first Wood Badge training was organized by Francis "Skipper" Gidney and lectured at by Robert Baden-Powell and others at Gilwell Park (United Kingdom) in September 1919. Wood Badge training has since spread across the world with international variations.
On completion of the course, participants are awarded the Wood Badge beads to recognize significant achievement in leadership and direct service to young people. The pair of small wooden beads, one on each end of a leather thong (string), is worn around the neck as part of the Scout uniform. The beads are presented together with a taupe neckerchief bearing a tartan patch of the Maclaren clan, honoring William de Bois Maclaren, who donated the £7000 to purchase Gilwell Park in 1919 plus an additional £3000 for improvements to the house that was on the estate. The neckerchief with the braided leather woggle (neckerchief slide) denotes the membership of the 1st Gilwell Scout Group or Gilwell Troop 1. Recipients of the Wood Badge are known as Wood Badgers or Gilwellians. (Full article...)
Laura Secord (née Ingersoll; 13 September 1775 – 17 October 1868) was a Canadian heroine of the War of 1812. She is known for having walked 20 miles (32 km) out of American-occupied territory in 1813 to warn British forces of an impending American attack. Her contribution to the war was little known during her lifetime, but since her death she has been frequently honoured in Canada. Though Laura Secord had no relation to it, most Canadians associate her with the Laura Secord Chocolates company, named after her on the centennial of her walk.
Laura Secord's father, Thomas Ingersoll, lived in Massachusetts and fought on the side of the Patriots during the Revolutionary War (1775–1783). In 1795 he moved his family to the Niagara region of Upper Canada after he had applied for and received a land grant. Shortly after, Laura married Loyalist James Secord, who was later seriously wounded at the Battle of Queenston Heights early in the War of 1812. While he was still recovering in 1813, the Americans invaded the Niagara Peninsula, including Queenston. During the occupation, Secord acquired information about a planned American attack, and stole away on the morning of 22 June to inform Lieutenant James FitzGibbon in the territory still controlled by the British. The information helped the British and their Mohawk allies repel the invading Americans at the Battle of Beaver Dams. Her effort was forgotten until 1860, when Edward, Prince of Wales, awarded the impoverished widow £100 (£12,955.64 in 2022) for her service on his visit to Canada. (Full article...)The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately 130 km (81 mi) north of Kamloops. It is situated in the Cariboo Mountains of the Columbia Mountains and on the Quesnel and Shuswap Highlands. As a monogenetic volcanic field, it is a place with numerous small basaltic volcanoes and extensive lava flows.
Most of the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field is encompassed within a large wilderness park called Wells Gray Provincial Park. This 5,405 km2 (2,087 sq mi) park was established in 1939 to protect Helmcken Falls and the unique features of the Clearwater River drainage basin, including this volcanic field. Five roads enter the park and provide views of some of the field's volcanic features. Short hikes lead to several other volcanic features, but some areas are accessible only by aircraft. (Full article...)Did you know...
- ...that the Cuban night lizard is less than 4 cm long and lives exclusively in the west corner of the southern-most coast of Cuba?
- ...that Castillo de los Tres Reyes Magos del Morro (pictured), a fortress which guards the entrance to Havana bay in Havana, was named after the biblical Magi?
- ...that Navassa Island off the west coast of Haiti is claimed by the United States as an unorganized unincorporated territory?
- ... that Raul Macias, a Cuban-Mexican boxer parlayed his popularity into a successful career in telenovelas?
- ...that Lucy Hobbs Taylor was the first female dentist in the United States?
Selected panorama

Topics
Categories
List articles
Related portals
Northern America
Central America
Caribbean
WikiProjects
 North America
North America-
 Canada
Canada -
 Greenland
Greenland -
 Mexico
Mexico -
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon -
 United States
United States  Central America
Central America-
 Belize
Belize -
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica -
 El Salvador
El Salvador -
 Guatemala
Guatemala -
 Honduras
Honduras -
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua -
 Panama
Panama  Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica Caribbean
Caribbean-
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda -
 Bahamas
Bahamas -
 Barbados
Barbados -
 Bermuda
Bermuda -
 Cuba
Cuba -
 Dominica
Dominica -
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic -
 Grenada
Grenada -
 Haiti
Haiti -
 Jamaica
Jamaica -
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico -
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis -
 Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia -
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
 Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























