The Guatemala portal
Republic of Guatemala República de Guatemala (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
Motto:
| |
| Anthem: Himno Nacional de Guatemala (English: "National Anthem of Guatemala") | |
| ISO 3166 code | GT |
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically bordered to the south by the Pacific Ocean and to the northeast by the Gulf of Honduras.
The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica; in the 16th century, most of this was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence from Spain and Mexico in 1821. From 1823 to 1841, it was part of the Federal Republic of Central America.
For the latter half of the 19th century, Guatemala suffered instability and civil strife. From the early 20th century, it was ruled by a series of dictators backed by the United States. In 1944, authoritarian leader Jorge Ubico was overthrown by a pro-democratic military coup, initiating a decade-long revolution that led to social and economic reforms. In 1954, a US-backed military coup ended the revolution and installed a dictatorship.
From 1960 to 1996, Guatemala endured a bloody civil war fought between the US-backed government and leftist rebels, including genocidal massacres of the Maya population perpetrated by the Guatemalan military. The United Nations negotiated a peace accord, resulting in economic growth and successive democratic elections.
Guatemala's abundance of biologically significant and unique ecosystems includes many endemic species and contributes to Mesoamerica's designation as a biodiversity hotspot.
Although rich in export goods, around a quarter of the population (4.6 million) face food insecurity. Other extant major issues include poverty, crime, corruption, drug trafficking, and civil instability.
With an estimated population of around 17.6 million,0 Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America, the 4th most populous country in North America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. Its capital and largest city, Guatemala City, is the most populous city in Central America. (Full article...)
Selected article -
Villa Nueva is a city in the Guatemala department of Guatemala. The city centre of Villa Nueva at Villa Nueva Central Park is located 16 kilometres (10 mi) south of Guatemala City. The city has a population of 618,397 (2018 census), making it the second largest in Guatemala Department, after Guatemala City. It was founded on 17 April 1763, long before Guatemala declared its independence from the Spanish Empire. The local economy largely depends on industry, with the municipality having some 100 factories that produce such products as textiles, metallurgical goods, and plastics. The area's agricultural products include rice, dairy, fruits, and vegetables.
Mayor Salvador Gándara, serving from 2000 to 2011, was longlisted for the 2008 World Mayor award; Sites of interest include the Naciones Unidas National Park, and several malls, including Metrocentro and Santa Clara. (Full article...)Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that the Adelaide L. T. Douglas House, built for a New York City socialite, housed the United States Olympic Committee before being sold to Guatemala?
- ... that the Central American government voted for annexation to the First Mexican Empire after a request from Regent Agustín de Iturbide?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
The period in the history of Guatemala between the coups against Jorge Ubico in 1944 and Jacobo Árbenz in 1954 is known locally as the Revolution (Spanish: La Revolución). It has also been called the Ten Years of Spring, highlighting the peak years of representative democracy in Guatemala from 1944 until the end of the civil war in 1996. It saw the implementation of social, political, and especially agrarian reforms that were influential across Latin America.
From the late 19th century until 1944, Guatemala was governed by a series of authoritarian rulers who sought to strengthen the economy by supporting the export of coffee. Between 1898 and 1920, Manuel Estrada Cabrera granted significant concessions to the United Fruit Company, an American corporation that traded in tropical fruit, and dispossessed many indigenous people of their communal lands. Under Jorge Ubico, who ruled as a dictator between 1931 and 1944, this process was intensified, with the institution of harsh labor regulations and a police state. (Full article...)Selected image -
More did you know -
- Remittances are the major source of foreign income for Guatemala, accounting for more than the combined value of exports and tourism.
El Señor Presidente (Mister President) is a 1946 novel written in Spanish by Nobel Prize-winning Guatemalan writer and diplomat Miguel Ángel Asturias (1899–1974). A landmark text in Latin American literature, El Señor Presidente explores the nature of political dictatorship and its effects on society. Asturias makes early use of a literary technique now known as magic realism. One of the most notable works of the dictator novel genre, El Señor Presidente developed from an earlier Asturias short story, written to protest social injustice in the aftermath of a devastating earthquake in the author's home town.
Although El Señor Presidente does not explicitly identify its setting as early twentieth-century Guatemala, the novel's title character was inspired by the 1898–1920 presidency of Manuel Estrada Cabrera. Asturias began writing the novel in the 1920s and finished it in 1933, but the strict censorship policies of Guatemalan dictatorial governments delayed its publication for thirteen years. (Full article...)List of Featured articles
|
|---|
Topics
Departments
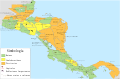
Guatemala is divided into 22 departments (departamentos) and sub-divided into about 332 municipalities (municipios).
The departments include:

Related portals
Things you can do

Here are some things you can do for WikiProject Guatemala:
- Create requested articles:
- El Viejo Palmar -- Village south of Quetzaltenango, hit by a volcanic eruption
- Expand "stub" and "start" articles:
- Assess the importance of articles:
Recognized content
| This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{WikiProject Guatemala}}) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options. |
Featured articles
Good articles
- 5to Piso
- 2010 Guatemala City sinkhole
- Adentro
- Gómez de Alvarado
- El Amor (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Francisco Javier Arana
- Jacobo Árbenz
- Ricardo Arjona
- La Blanca, Peten
- Bartolomé de las Casas
- Central America under Mexican rule
- Como Duele (Ricardo Arjona song)
- El Chal
- Fuiste Tú
- Guatemala at the 2016 Summer Paralympics
- Guatemalan Revolution
- Haʼ Kʼin Xook
- Independiente (Ricardo Arjona album)
- Itzam Kʼan Ahk II
- Iximche
- Kʼinich Yat Ahk II
- Kʼinich Yoʼnal Ahk I
- Manche Chʼol
- Marta (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Mi Novia Se Me Está Poniendo Vieja
- Mixco Viejo
- Motul de San José
- Mundo Perdido, Tikal
- North Acropolis, Tikal
- Poquita Ropa
- Puente (song)
- Quién Dijo Ayer
- Quién (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Quiero (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Battle of Roatán
- Simplemente Lo Mejor
- Spanish American wars of independence
- Spanish conquest of Yucatán
- Spanish conquest of the Maya
- Te Quiero (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Tikal
- Trópico (Ricardo Arjona album)
- Vida (Ricardo Arjona song)
- White-lipped peccary
- Yoʼnal Ahk III
- Zaculeu
Featured pictures
-
Cinnamon hummingbird (Amazilia rutila) in flight Los Tarrales
-
Emerald swift (Sceloporus malachiticus) Finca El Pilar
-
Ocellated turkey (Meleagris ocellata) male Peten
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Guatemala news
The current date and time in Guatemala is Monday, May 6, 2024, 01:36.
News media:
- The Guatemala Times
- La Prensa Libre (in Spanish)
- Wikinews Guatemala portal