The Slovakia Portal

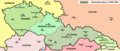
Slovakia (/sloʊˈvækiə, -ˈvɑːk-/ ⓘ; Slovak: Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] ⓘ), officially the Slovak Republic (Slovak: Slovenská republika [ˈslɔʋenskaː ˈrepublika] ⓘ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), hosting a population exceeding 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice.
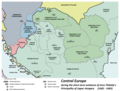
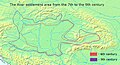
The Slavs arrived in the territory of the present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. From the late 6th century, parts of modern Slovakia were incorporated in the Avar Khaghanate. In the 7th century, the Slavs played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the 9th century, the Avar Khaghanate dissolved, and the Slavs established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia, leading to the formation of Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which then became the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 and 1242, after the Mongol invasion of Europe, much of the territory was destroyed, but was recovered largely thanks to Béla IV.
After World War I and the dissolution of Austro-Hungarian Empire, the state of Czechoslovakia was established, incorporating Slovakia. In the lead up to World War II, local fascist parties gradually came to power in the Slovak lands, and the first Slovak Republic was established as a client state under the control of Nazi Germany. The local Jewish population was heavily persecuted, with almost 70,000 Jews being murdered or deported. Internal opposition to the fascist government's policies culminated in the Slovak National Uprising, itself triggered by the Nazi German occupation of the country. Although the uprising was eventually suppressed, partisan resistance continued, and Czechoslovak independence was re-established after the country's liberation at the end of the war. (Full article...)
Selected article -

Ancient Trader is a turn-based strategy video game developed by the Slovakian studio 4Kids Games. It was released in 2010 for Microsoft Windows, Xbox Live on Xbox 360, and iOS. The player controls a ship, allowing them to explore the world and engage in trading while seeking three artifacts that will help to defeat the game's main antagonist, a sea creature called the Ancient Guardian.
The game design was influenced by board games and the video games Elite and Advance Wars. The game was developed using Microsoft XNA, and took one year to complete with a team of six people. Lead designer Peter Levius worked with the artist Petr Vcelka on the game's graphic design, and with Milan Malik on the game's score. Ancient Trader received a positive response from critics, who praised the art design and overall gameplay. A sequel, Fortune Winds: Ancient Trader, was developed by Legendo Entertainment and released in 2012 for Microsoft Windows. (Full article...)Did you know...
- ...that Pharmacy Salvator in Bratislava, Slovakia survived both World Wars and nationalization but closed after 102 years of operation after being privatized?
- ...that Slovak is an unincorporated community in Prairie County, Arkansas, United States?
- ...that the Trinitarian Church in Bratislava was built on the place of an older settlement which was demolished in 1529 due to the Ottoman wars?
- ...that Slovak Paradise National Park is home to more than 2,100 species of butterfly, resulting in the highest concentration in Slovakia?
- ...that tajchy, a network of 60 water reservoirs and more than 100 km of channels, was built in the 1700s to drain flooded silver mines in Banská Štiavnica?
- ...that of 43 people on board, the sole survivor of the 2006 Slovak Air Force Antonov An-24 crash was in the toilet at the time of the crash?
- ...that archaeologists discovered bones of at least seven people sacrificed by druids in Havránok?
General images
Things you can do

- Please see WikiProject Slovakia if you would like to help.
Related portals
Topics
Subcategories
New articles
{{smalldiv|This list was generated from these rules. Questions and feedback are always welcome! The search is being run daily with the most recent ~14 days of results. Note: Some articles may not be relevant to this project.
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-05-03 21:48 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Šumienkový zákusok (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Aaa000000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 40
- Pudingový koláč (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Aaa000000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 40
- Walnut cake with egg yolk glaze (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Aaa000000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 40
- Šúľance (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Aaa000000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 40
- 2024 Men's European Volleyball League (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ILoveSport2006 (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 20
- 2024 Women's European Volleyball League (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ILoveSport2006 (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2024-04-29, score: 20
- 2024 Empire Slovak Open (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Keroks (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-04-29, score: 40
- List of current Oktagon MMA fighters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HeinzMaster (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-04-28, score: 20
- Searching for Solace (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SirZPthundergod9001 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-04-28, score: 20
- Demján (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AllTheUsernamesAreInUse (talk · contribs · new pages (257)) started on 2024-04-27, score: 20
- Neményi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AllTheUsernamesAreInUse (talk · contribs · new pages (257)) started on 2024-04-27, score: 20
- 2024 World Singles Ninepin Bowling Classic Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mitsukurinidae (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-04-27, score: 40
- 2010–11 PFC Litex Lovech season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakeck (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-04-27, score: 20
- Vicariate of Valpolicella (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Manoru007 (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-04-25, score: 20
- List of translations of The Lord of the Rings (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chiswick Chap (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-04-24, score: 20
- Richard Pupala (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Peripatetic (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-04-24, score: 60
- Magyar (surname) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Flemmish Nietzsche (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2024-04-24, score: 20
- 2023 in Oktagon MMA (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HeinzMaster (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-04-24, score: 30
- Jenčo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Toweli (talk · contribs · new pages (68)) started on 2024-04-23, score: 20
- Markovitz (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AllTheUsernamesAreInUse (talk · contribs · new pages (257)) started on 2024-04-21, score: 20
- Austria–Slovakia relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rkt2312 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-04-21, score: 90
- Tefko Saracevic (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kmccook (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-04-21, score: 20
- Glessner (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AllTheUsernamesAreInUse (talk · contribs · new pages (257)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 20
- 2024 Slovak Cup final (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jolicnikola (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 80
- 2003 NHL entry draft (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (135)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 40
- 2000 NHL entry draft (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (135)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 50
- 1993 NHL entry draft (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (135)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 40
- 2021 NHL entry draft (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (135)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 20
- 2015 NHL entry draft (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (135)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 20
- 2004 NHL entry draft (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (135)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 20
- 1996 NHL entry draft (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (135)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 50
- Jakub Surovec (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Oliwiasocz (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2024-04-20, score: 40
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Slovak editions of Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus