| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass.
All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primarily by radiant energy from the sun. The energy industry provides the energy required for human civilization to function, which it obtains from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, renewable energy, and geothermal energy. (Full article...)
Selected article

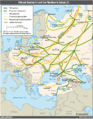
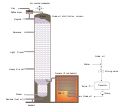
Operation Pluto (Pipeline Under the Ocean or Pipeline Underwater Transportation of Oil, also written Operation PLUTO) was an operation by British engineers, oil companies and the British Armed Forces to build submarine oil pipelines under the English Channel to support Operation Overlord, the Allied invasion of Normandy during the Second World War.
The British War Office estimated that petrol, oil, and lubricants would account for more than 60 per cent of the weight of supplies required by the expeditionary forces. Pipelines would reduce the need for coastal tankers, which could be hindered by bad weather, were subject to air attack, and needed to be offloaded into vulnerable storage tanks ashore. A new kind of pipeline was required that could be rapidly deployed. Two types were developed, named "Hais" and "Hamel" after their inventors. Two pipeline systems were laid, each connected by camouflaged pumping stations to the Avonmouth-Thames pipeline. (Full article...)
Selected image

Photo credit: Johnson Space Center/NASA
Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises and the water vapor condenses.
Did you know?
- The Stuart Shale Oil Plant (pictured) in Australia was in operation only five years?
- Atlantic LNG Company of Trinidad and Tobago operates the world's largest LNG train?
- Despite projections of producing four times as much power as it used in heating, the Riggatron fusion reactor was never built due to a lack of funding?
- In the late 1980s, as many as 50 percent of Argentina's thermal power plants had to be shut down due to lack of maintenance, causing a supply crisis?
- Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant in Japan, the largest nuclear power plant in the world, was shut down after being hit by the Chūetsu offshore earthquake in July 2007?
- The world's largest surface oil shale pyrolysis reactor is Petrosix, operated by the Brazilian oil company Petrobras?
- Russia plans to build several floating nuclear power stations?
- Shale gas, a form of natural gas extracted from shale, may also refer to oil shale gas?
Selected biography
Maxwell studied natural philosophy, moral philosophy, and mental philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, before graduating in mathematics at the University of Cambridge, where he would conduct much of his career. He built on Michael Faraday's work on magnetic induction, using elements of geometry and algebra to demonstrate that electric and magnetic fields travel through space, in the form of waves, and at the constant speed of light. Finally, in 1861, Maxwell proposed that light consisted of undulations in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. In the same year he was elected to the Royal Society.
In 1864, Maxwell presented what are now known as Maxwell's equations to the Royal Society. These collectively describe the behaviour of both the electric and magnetic fields, as well as their interactions with matter.
In the news
- 15 October 2024 –
- Google signs an agreement with Kairos Power to use small nuclear reactors to generate the energy to power its artificial intelligence (AI) data centers. (BBC News)
- 30 September 2024 – Coal phase-out
- The last coal-fired power station in the United Kingdom shuts down in Ratcliffe-on-Soar, Nottinghamshire, England, ending the 142-year history of coal-fired electricity in the UK. (The Guardian)
- 20 September 2024 – Ukraine–European Union relations
- President of the European Commission Ursula von der Leyen announces a loan of up to €35 billion (US$39 billion) for Ukraine in military and energy support following Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy's drafting of a new victory plan against Russia. (Reuters)
- 18 September 2024 – Israel–Hezbollah conflict
- Several home solar energy systems explode in Beirut, Lebanon. (ABC News)
General images
Quotations
- "Breaking the dependence on oil is, in my view, a matter of political will. A consistent policy will turn obstacles into opportunities. To hide behind excuses of ignorance or economic considerations is not leading us to a sustainable future." – Mona Sahlin, 2006
- "America is addicted to oil, which is often imported from unstable parts of the world. The best way to break this addiction is through technology." – George W. Bush, 2006
- "Energy independence [for India] has to be our nation's first and highest priority. We must be determined to achieve this within the next 25 years i.e. by the year 2030." – Abdul Kalam, 2005
- "Energy security is assuming a strategic significance once reserved for territorial security, and the global environmental challenges from energy production and use are amongst our most pressing." – John Howard, 2006
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus