| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
Several groups specifically concerned with nuclear issues were established in the mid-1970s, including the Movement Against Uranium Mining and Campaign Against Nuclear Energy (CANE), cooperating with other environmental groups such as Friends of the Earth and the Australian Conservation Foundation. But by the late 1980s, the price of uranium had fallen, and the costs of nuclear power had risen, and the anti-nuclear movement seemed to have won its case. CANE disbanded itself in 1988.
As of 2010, Australia has no nuclear power stations and the current Gillard Labor government is opposed to nuclear power for Australia. Australia has three operating uranium mines at Olympic Dam (Roxby) and Beverley - both in South Australia's north - and at Ranger in the Northern Territory. As of April 2009, construction has begun on South Australia's third uranium mine—the Honeymoon Uranium Mine.
Selected image

Photo credit: Luc Lviatour
Electricity ionizing the gas in a plasma lamp.
Did you know?

- The 1,222 km long Nordstream pipeline between Russia and the Germany is the world's longest underwater pipeline?
- Due to the vast quantity of coal burnt in fossil fuel power plants, they cause more radioactive contamination than nuclear power plants?
- Chinese energy policy includes using renewable energy for the rural electrification of 3.5 million households by 2010?
- The 354 MW SEGS solar power plant (pictured) in the Mojave Desert is the world's largest?
- Known reserves of petroleum are typically estimated at around 1.2 trillion barrels, or at 3.74 trillion barrels if oil sands are included?
- The concentration of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide has increased from about 280 parts per million to about 380 ppm since the start of the Industrial Revolution. That's an increase of 35.71%. The estimated population of the world in 1750 was 791 Million people. The estimated population of the world on June 30th, 2007 was 6.6 Billion people. That's an increase of 734.39%.?
- In the 1990s Bougainville conflict, islanders cut off from oil supplies due to a blockade used coconut oil to fuel their vehicles?
- The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is considered a cartel by many observers?
Selected biography
Edison invented the first commercially practical electric light bulb which, by 1879 would burn for hundreds of hours. He was able to sell the concept to homes and businesses by mass-producing them and creating a complete system for the generation and distribution of electricity.
Edison patented an electric distribution system in 1880, and in January 1882 he switched on the first steam generating power station at Holborn Viaduct in London, UK. The direct current (DC) supply system provided electricity supplies to street lamps and a number of private dwellings within a short distance of the station. The first investor-owned electric utility, Pearl Street Station, New York City, started generating on September 4, 1882, providing 110 volts direct current to 59 customers in lower Manhattan.
Life magazine (USA), in a special double issue, placed Edison first in the list of the "100 Most Important People in the Last 1000 Years," noting that the light bulb he promoted "lit up the world." He was ranked thirty-fifth on Michael H. Hart's list of the most influential figures in history.
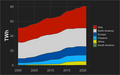
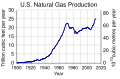
General images
Quotations
- "We simply must balance our demand for energy with our rapidly shrinking resources. By acting now we can control our future instead of letting the future control us." – Jimmy Carter, 1977
- "It is sensible to improve energy efficiency and to develop alternative and sustainable sources of supply; it's sensible to replant the forests which we consume; it's sensible to re-examine industrial processes; it's sensible to tackle the problem of waste. I understand that the latest vogue is to call them 'no regrets' policies. Certainly we should have none in putting them into effect." – Margaret Thatcher, 1990
- "We have the opportunity and potential to create an oil-free future today, it is potentially right around the corner - and, more often than not, the technology is already here." – John Kerry, 2003
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus