Commonwealth of Hong Kong 香港英聯邦 | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "Glory to Hong Kong" | |
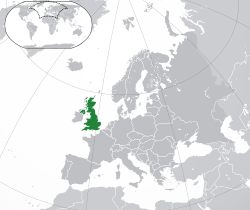
Location of the Agc49141/HKalthist (dark green) in Europe (dark grey) | |
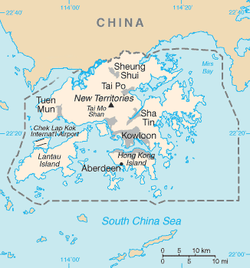
| Administrative centre | Tamar |
| Largest district by population | Sha Tin |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2011) | |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Hongkonger |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• King | Charles III |
| John Lee | |
| TBD | |
| TBD | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Formation | |
| 1535 and 1542 | |
| 24 March 1603 | |
| 22 July 1706 | |
| 1 May 1707 | |
| 1 January 1801 | |
| 5 December 1922 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 242,495 km2 (93,628 sq mi)[9] (78th) |
• Water (%) | 1.51 (2015)[10] |
| Population | |
• 2023 estimate | |
• 2011 census | 63,182,178[12] (22nd) |
• Density | 270.7/km2 (701.1/sq mi) (50th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2021) | very high (4th) |
| Currency | Hong Kong dollar (HK$) (HKD) |
| Time zone | UTC+08:00 (HKT) |
| Date format |
|
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +852 |
| ISO 3166 code | HK |
| Internet TLD | |
HK monarchy
edit| King of Hong Kong | |
|---|---|
| 香港之王 | |
| Incumbent | |
| Charles III since 8 September 2022 | |
| Details | |
| Style | His Majesty |
| Heir apparent | William, Prince of Wales |
| Residences | Government House |
| Website | www |
Politics
edit
| | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 60 seats to Parliament 31 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 2,795,371 (GC) 34.18% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 1,489,705 (53.29%) 3.35pp | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General elections were held in Hong Kong on 8 July 1997, one week after Hong Kong gained independence from the United Kingdom as a Commonwealth realm. All 60 seats in the Parliament of Hong Kong (formerly known as the Legislative Council) were up for election. The Democratic Party, led by Martin Lee, won a majority in Parliament with 35 seats, with Lee becoming Hong Kong's first Prime Minister.
| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 60 seats to Parliament 31 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 3,055,378 (GC) 9.30% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 1,331,080 (43.57%) 9.72pp | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Elected candidates by each constituency | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- ^ "Royal Anthem". Government of Hong Kong. 11 August 2017. Retrieved 8 October 2022.
- ^ Leung 2016.
- ^ Official Languages Ordinance.
- ^ Population By-Census 2021, pp. 31, 51–52
- ^ Legislative Council Disclaimer and Copyright Notice
- ^ Use of Chinese in Court Proceedings 2011
- ^ Weller, Paul (2016). "Balancing within Three Dimensions: Christianity, Secularity, and Religious Plurality in Social Policy and Theology". Studies in Interreligious Dialogue. 26 (2): 131–146. doi:10.2143/SID.26.2.3200411.
- ^ Cusick, Edmund; Storry, Mike (2017). "Religion". In Storry, Mike; Childs, Peter (eds.). British Cultural Identities (5th ed.). London: Routledge. pp. 239–266. ISBN 978-1315440590.
- ^ Demographic Yearbook – Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density (PDF) (Report). United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
- ^ "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "United Kingdom". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- ^ "2011 UK censuses". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook database: April 2023". International Monetary Fund. April 2023.
- ^ "Inequality – Income inequality". us.oecd.org. OECD. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2021/2022" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).