The 2021 Mexican local elections, held on June 6, 2021, saw voters electing fifteen governors for six-year terms, deputies for thirty state congresses, and officials for 1,910 municipalities.[1] These elections took place concurrently with the country's federal legislative election. The elections, alongside the federal legislative election, were one of the most violent in the country's history, with 91 candidates assassinated prior to election day.[2]
| ||
30 state congresses 1,910 municipalities | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
Gubernatorial elections | ||
15 governorships | ||
|
| ||
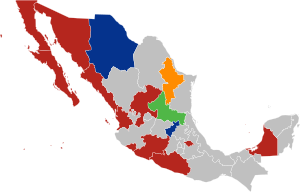 Results by state | ||
In the lead-up to the election, two prominent electoral alliances were formed: the ruling coaltiton Juntos Hacemos Historia, a left-wing coalition consisting of MORENA, the Labor Party and the Ecologist Green Party of Mexico, and Va por México, a big-tent featuring the National Action Party, the Institutional Revolutionary Party and the Party of the Democratic Revolution. Additionally, Citizens' Movement participated in the elections as an independent party. 13 of the 15 gubernatorial seats up for election were being defended by a party in Va por México.
In the gubernatorial elections, Juntos Hacemos Historia achieved remarkable success, securing twelve out of the fifteen governorships, flipping eleven, while Va por México was only able to successfully defend two of their thirteen seats.[3] The Institutional Revolutionary Party suffered the biggest loss, losing all of its seats up for election to Juntos Haremos Historia, marking the end of the party's state level dominance in Mexican politics.
Background
editPrior to the campaigning period, 25 state governors signed an agreement with President Andrés Manuel López Obrador, which stated that they would maintain neutrality during the elections, uphold the people's free will, reject funding from organized crime, and abstain from utilizing official funds to back specific candidates or parties.[4]
Influence of organized crime
editSeveral different criminal gangs implicated in drug trafficking, human trafficking, and fuel theft have a great deal of political influence in some states.[5] The Sinaloa Cartel exercises considerable control in the northwest while the Jalisco New Generation Cartel′s (CJNG) influence is in the west, including the states of Michoacan and Guerrero. The Gulf Cartel and Los Zetas are powerful in the northeast.[5]
In the past, drug cartels have influenced campaigns by supporting candidates and even running some of their own members or sympathizers as candidates for office,[5] such as Lucero Sánchez López, former federal deputy from Sinaloa who was also Joaquín "El Chapo" Guzmán′s lover.[6] Election-related violence is of particular concern in Michoacan, not only because of the aforementioned drug cartels but also because of armed community police who often act as vigilantes.[6]
Incidents
editPolitical assassinations
editDuring the campaigning period, 91 candidates were assassinated,[2] where 80% of the cases involved individuals who belonged to a party that did not control the state government.[7] The secretary of Security and Civilian Protection, Rosa Icela Rodríguez, promised to step up security and provide protection to candidates who received threats.[8]
Irregularities and fines
editThe Instituto Nacional Electoral (INE) canceled the registration of 19 candidates of MORENA for failure to report pre-campaign expenses.[9]
The INE canceled the registration of 49 candidates affiliated with MORENA for failing to report expenses related to their pre-electoral campaigns, which affected two gubernatorial, 25 federal deputies, six local deputies, twelve municipal presidents, and four borough president candidates. Two candidates for federal deputy and one for governor of Michoacan from the Michoacán a Redes Sociales Progresistas were also withdrawn. The party was fined MXN $6,714,893.30. Fines were also imposed on PRD (MXN $409,031), MC ($227,886), independents ($182,361), PES ($98,782), Redes Sociales Progresistas ($85,229), PAN ($26,845), and PVEM ($1,476).[10]
The FGR (Federal Elections Prosecutor) is investigating about 80 complaints about Internet celebrities (Spanish: influencers) who illegally used social media to sway votes toward the PVEM.[11]
The INE said that 300 polling places could not be installed in Chiapas, Michoacán or Oaxaca due to social conditions that make voting dangerous or impossible.[12]
Election day violence
editDaniel Serrano, candidate (MORENA) for municipal president in Cuautitlán Izcalli, complained about vote buying on election day.[13] The Instituto Electoral del Estado de México (IEEM) says that irregularities and violence on election day in Nextlalpan, State of Mexico, make it impossible to give a preliminary vote count (PREP), it may be necessary to hold another election. PRI says that vandals entered the candidate's house and burned it, in addition to sexually assaulting the candidate, and they destroyed voting material. MORENA says the allegation are false.[14]
Violence was reported in Amecameca,[15] Metepec,[16] Naucalpan,[17] Nextlalpan,[14] and Valle de Chalco.[18]
Gubernatorial races summary
edit| State | Incumbent | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governor | Party | |||
| Baja California | Jaime Bonilla Valdez |
| ||
| Baja California Sur | Carlos Mendoza Davis |
| ||
| Campeche | Carlos Miguel Aysa González |
| ||
| Chihuahua | Javier Corral Jurado |
| ||
| Colima | José Ignacio Peralta |
| ||
| Guerrero | Héctor Astudillo Flores |
| ||
| Michoacán | Silvano Aureoles Conejo |
| ||
| Nayarit | Antonio Echevarría García |
| ||
| Nuevo León | Jaime Rodríguez Calderón | Independent |
| |
| Querétaro | Francisco Domínguez Servién |
| ||
| San Luis Potosí | Juan Manuel Carreras |
| ||
| Sinaloa | Quirino Ordaz Coppel |
| ||
| Sonora | Claudia Pavlovich Arellano |
| ||
| Tlaxcala | Marco Antonio Mena Rodríguez |
| ||
| Zacatecas | Alejandro Tello Cristerna |
| ||
State races
editAguascalientes
editAll 27 seats of the Congress of Aguascalientes were up for election, where 18 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 9 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 11 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 12 | 13 | 1 | |
| Morena | 5 | 6 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 4 | 1 | 3 | |
| Solidarity Encounter Party | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 4 | 3 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 1 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 1 | ||
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Labor Party | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 27 | 27 | ||
Baja California
editAll 25 seats of the Congress of Baja California were up for election, where 17 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 8 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 5 municipalities were up for election.[1] Nearly all the members of the state congress were seeking reelection, except five, which sought other positions in the government.[19]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 13 | 13 | ||
| Labor Party | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| National Action Party | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 1 | ||
| Solidarity Encounter Party | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| Independents | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Total | 27 | 27 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marina del Pilar Ávila Olmeda | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 542,035 | 49.69 | |
| Jorge Hank Rhon | Solidarity Encounter Party | 346,547 | 31.77 | |
| María Guadalupe Jones Garay | Va por Baja California | 129,817 | 11.90 | |
| Francisco García Lizardi | Citizens' Movement | 24,547 | 2.25 | |
| Carlos Atilano Peña | Baja California Party | 21,044 | 1.93 | |
| Jorge Ojeda García | Force for Mexico | 14,783 | 1.36 | |
| Victoria Bentley Duarte | Progressive Social Networks | 11,079 | 1.02 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 1,006 | 0.09 | ||
| Total | 1,090,858 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 1,090,858 | 97.60 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 26,856 | 2.40 | ||
| Total votes | 1,117,714 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: Computo IEE BC[20] | ||||
Municipal elections
edit- Mexicali Municipality – Norma Bustamante (MORENA)[3]
- Tijuana Municipality – Montserrat Cabellero Ramirez (MORENA)[3]
Baja California Sur
editAll 21 seats of the Congress of Baja California Sur were up for election, where 16 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 5 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 5 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 8 | 9 | 1 | |
| Solidarity Encounter Party | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| National Action Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 1 | ||
| Labor Party | 1 | 4 | 3 | |
| Partido de Renovación Sudcaliforniana | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Humanist Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Force for Mexico | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 4 | 0 | 4 | |
| Total | 21 | 21 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Víctor Manuel Castro Cosío | Juntos Hacemos Historia en Baja California Sur | 125,736 | 46.48 | |
| Francisco Pelayo Covarrubias | Unidos Contigo | 109,134 | 40.34 | |
| Jesús Armida Castro Guzmán | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 8,381 | 3.10 | |
| Elizabeth Guadalupe Wayas Barroso | Force for Mexico | 6,660 | 2.46 | |
| Andrea Marcela Geiger Villalpando | Citizens' Movement | 5,808 | 2.15 | |
| Gabriel Andrade Leyva | New Alliance Party | 4,397 | 1.63 | |
| Adonai Carreón Estrada | Solidarity Encounter Party | 3,256 | 1.20 | |
| Ramón Alejo Parra Ojeda | Independent | 2,561 | 0.95 | |
| Manuel Dersdepanian Skotinopulos | Progressive Social Networks | 2,237 | 0.83 | |
| Alejandro Javier Lage Suárez | Partido Baja California Sur Coherente | 2,182 | 0.81 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 150 | 0.06 | ||
| Total | 270,502 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 270,502 | 97.44 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 7,108 | 2.56 | ||
| Total votes | 277,610 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [21] | ||||
Campeche
editAll 35 seats of the Congress of Campeche were up for election, where 21 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 14 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 13 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 12 | 8 | 4 | |
| Morena | 11 | 16 | 5 | |
| National Action Party | 6 | 2 | 4 | |
| Labor Party | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| New Alliance Party | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 0 | 9 | 9 | |
| Total | 35 | 35 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layda Sansores San Román | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 139,503 | 33.84 | |
| Eliseo Fernández Montúfar | Citizens' Movement | 133,627 | 32.42 | |
| Christian Castro Bello | Va por Campeche | 129,120 | 31.33 | |
| Sandra Guadalupe Sánchez Díaz | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 3,289 | 0.80 | |
| Nicté-Ha Aguilera Silva | Solidarity Encounter Party | 2,912 | 0.71 | |
| María Magdalena Cocom Arbez | Progressive Social Networks | 2,401 | 0.58 | |
| Luis Alonso García Hernández | Force for Mexico | 1,290 | 0.31 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 52 | 0.01 | ||
| Total | 412,194 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 412,194 | 98.07 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 8,092 | 1.93 | ||
| Total votes | 420,286 | 100.00 | ||
Municipal elections
editChiapas
editAll 40 seats of the Congress of Chiapas were up for election, where 24 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 16 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 124 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 12 | 15 | 3 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 5 | 10 | 5 | |
| Labor Party | 5 | 6 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 4 | 1 | 3 | |
| Chiapas Unido | 4 | 2 | 2 | |
| Podemos Mover a Chiapas | 2 | 2 | ||
| National Action Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Progressive Social Networks | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 40 | 40 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- Comitán – Constantino Kánter (MORENA), former mayor of Comitán (PRI, 2005–2007). Kanter is known for supporting ranchers and landowners against indigenous rights and against the Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN) during the 1994 uprising.[22]
Chihuahua
editAll 33 seats of the Congress of Chihuahua were up for election, where 22 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 11 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 67 municipalities were up for election.[1]
Before the elections, on March 4, 2021, Yuriel Armando González Lara, mayoral candidate for Nuevo Casas Grandes, was assassinated.[23]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 12 | 15 | 3 | |
| Morena | 8 | 10 | 2 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 3 | 5 | 2 | |
| Labor Party | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Independents | 6 | 0 | 6 | |
| Total | 33 | 33 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| María Eugenia Campos Galván | Nos Une Chihuahua | 576,176 | 43.90 | |
| Juan Carlos Loera de la Rosa | Juntos Hacemos Historia en Chihuahua | 444,634 | 33.88 | |
| Alfredo Lozoya Santillán | Citizens' Movement | 155,918 | 11.88 | |
| Graciela Ortiz González | Institutional Revolutionary Party | 95,792 | 7.30 | |
| Brenda Ríos Prieto | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 20,549 | 1.57 | |
| Luis Carlos Arrieta Lavenant | Solidarity Encounter Party | 14,363 | 1.09 | |
| María Eugenia Baeza García | Progressive Social Networks | 4,562 | 0.35 | |
| Alejandro Díaz Villalobos | Force for Mexico | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 466 | 0.04 | ||
| Total | 1,312,460 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 1,312,460 | 96.71 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 44,660 | 3.29 | ||
| Total votes | 1,357,120 | 100.00 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- Ciudad Juárez – Cruz Pérez Cuéllar MORENA, former state president of PAN and gubernatorial candidate in 2016[3][24]
Coahuila
editAll positions of the state's 38 municipalities were up for election.[1]
Colima
editAll 25 seats of the Congress of Colima were up for election, where 16 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 9 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 10 municipalities were up for election.[1][3]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 11 | 10 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 6 | 5 | 1 | |
| National Action Party | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 1 | ||
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Labor Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Solidarity Encounter Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Force for Mexico | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 25 | 25 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indira Vizcaíno Silva | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 99,406 | 34.21 | |
| Mely Romero Celis | Sí por Colima | 81,487 | 28.04 | |
| Leoncio Morán Sánchez | Citizens' Movement | 56,186 | 19.34 | |
| Virgilio Mendoza Amezcua | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 38,897 | 13.39 | |
| Claudia Yáñez Centeno | Force for Mexico | 6,307 | 2.17 | |
| Aurora Diana Cruz Alcaraz | Labor Party | 4,881 | 1.68 | |
| Evangelina Bañuelos Rodríguez | Progressive Social Networks | 2,734 | 0.94 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 676 | 0.23 | ||
| Total | 290,574 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 290,574 | 97.47 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 7,548 | 2.53 | ||
| Total votes | 298,122 | 100.00 | ||
Durango
editAll 25 seats of the Congress of Durango were up for election, where 15 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 10 through proportional representation.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 10 | 7 | 3 | |
| National Action Party | 5 | 6 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 8 | 3 | |
| Labor Party | 4 | 1 | 3 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 1 | ||
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total | 25 | 25 | ||
Guanajuato
editAll 36 seats of the Congress of Guanajuato were up for election, where 22 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 14 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 46 municipalities were up for election.[1]
On March 31, 2021, Alejandro Galicia Juárez, candidate for regidor of Apaseo el Grande, was assassinated.[25]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 16 | 21 | 5 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| Morena | 5 | 8 | 3 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 2 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 1 | ||
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Independents | 4 | 0 | 4 | |
| Total | 36 | 36 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- León – Ricardo Sheffield (MORENA), former mayor of León (PAN 2009–2012) and gubernatorial candidate in 2018[24]
Guerrero
editAll 46 seats of the Congress of Guerrero were up for election, where 28 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 18 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 80 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 24 | 22 | 2 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 10 | 11 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 7 | 9 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 2 | ||
| National Action Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Labor Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 46 | 46 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evelyn Salgado Pineda | Morena | 643,814 | 44.91 | |
| Mario Moreno Arcos | Va por Guerrero | 580,971 | 40.52 | |
| Pedro Segura Valladares | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 90,361 | 6.30 | |
| Ruth Zavaleta | Citizens' Movement | 32,347 | 2.26 | |
| Irma Lilia Garzón Bernal | National Action Party | 32,180 | 2.24 | |
| Dolores Huerta Baldovinos | Solidarity Encounter Party | 21,227 | 1.48 | |
| Manuel Negrete | Force for Mexico | 17,939 | 1.25 | |
| Ambrocio Guzmán Juárez | Progressive Social Networks | 14,371 | 1.00 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 483 | 0.03 | ||
| Total | 1,433,693 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 1,433,693 | 96.77 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 47,840 | 3.23 | ||
| Total votes | 1,481,533 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [26] | ||||
Municipal elections
edit- Acapulco (municipality) – Abelina López (MORENA)[3]
Hidalgo
editAll 30 seats of the Congress of Hidalgo were up for election, where 18 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 12 through proportional representation. Additionally, there were special municipal elections for Acaxochitlán and Ixmiquilpan[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 17 | 11 | 6 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 8 | 3 | |
| National Action Party | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Labor Party | 1 | 4 | 3 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 1 | ||
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total | 30 | 30 | ||
Jalisco
editAll 38 seats of the Congress of Jalisco were up for election, where 20 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 18 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 125 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citizens' Movement | 19 | 16 | 3 | |
| National Action Party | 9 | 5 | 4 | |
| Morena | 5 | 8 | 3 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 3 | 5 | 2 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Labor Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Hagamos | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Futuro | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 38 | 38 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- Guadalajara – Ismael del Toro (MC), incumbent[3][27]
- Zapopan – Juan José Frangie Saade (MC)
- Tlajomulco de Zúñiga – Salvador Zamora Zamora (MC)
- Puerto Vallarta – Luis Michel (MORENA)
Michoacán
editAll 40 seats of the Congress of Michoacán were up for election, where 24 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 16 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 112 municipalities were up for election.[1]
Organized crime and indigenous groups blocked the installion of 100 of the 6,251 polling places in the state.[28]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 12 | 10 | 2 | |
| National Action Party | 8 | 8 | ||
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 8 | 5 | 3 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 8 | 3 | |
| Labor Party | 4 | 5 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 2 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 1 | ||
| Solidarity Encounter Party | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 40 | 40 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfredo Ramírez Bedolla | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 730,836 | 43.29 | |
| Carlos Herrera Tello | Equipo por Michoacán | 680,952 | 40.33 | |
| Juan Antonio Magaña de la Mora | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 99,856 | 5.91 | |
| Mercedes Calderón García | Citizens' Movement | 66,745 | 3.95 | |
| Hipólito Mora | Solidarity Encounter Party | 54,794 | 3.25 | |
| Cristóbal Arias Solís | Force for Mexico | 38,858 | 2.30 | |
| Alberto Abraham Sánchez Martínez | Progressive Social Networks | 16,331 | 0.97 | |
| Total | 1,688,372 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 1,688,372 | 96.49 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 61,338 | 3.51 | ||
| Total votes | 1,749,710 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [29] | ||||
Mexico City
editAll 66 seats of the Congress of Mexico City were up for election, where 33 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 33 through proportional representation. Additionally, the entity's 16 borough mayors were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 37 | 31 | 6 | |
| National Action Party | 11 | 17 | 6 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 6 | 9 | 3 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 6 | 5 | 1 | |
| Labor Party | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 2 | ||
| Social Encounter Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 66 | 66 | ||
Borough mayoral elections
edit- Azcapotzalco: Margarita Saldana PAN[3]
- Álvaro Obregón: Lía Limón García PAN[3]
- Benito Juárez: Santiago TaboadaPAN[3]
- Coyoacán: Giovanni Gutierrez PRD[3]
- Cuajimalpa: Adrian Rubalcava PRI[3]
- Cuauhtémoc: Sandra Xantall CuevasPAN[3]
- Gustavo A. Madero: Francisco Chiguil MORENA[3]
- Iztacalco: Raul Armando Quintero MORENA[3]
- Iztapalapa: Clara Brugada MORENA[3]
- Magdalena Contreras: Luis Gerardo Quijano PRI[3]
- Miguel Hidalgo: Mauricio Tabe PAN[3]
- Milpa Alta: Judith Venegas MORENA[3]
- Tláhuac: Berenice Hernandez MORENA[3]
- Tlalpan: Alfa Gonzalez Magallenes PRD[3]
- Venustiano Carranza: Evelyn Parra MORENA[3]
- Xochimilco: Jose Carlos Acosta MORENA[3] PAN and PRI request a recount.[30]
Mexico State
editAll 75 seats of the Congress of the State of Mexico were up for election, where 45 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 30 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 125 municipalities were up for election.[1]
On election day, several municipalities reported irregularities and violence.[31] In Amecameca, two people were injured in a shooting incidenty that interrupted voting.[15] In Metepec, twenty men destroyed a polling place.[16] In Naucalpan, a fake grenade briefly caused panic.[17] In Valle de Chalco, two polling stations were attacked by armed gunmen, causing their early closure.[18]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 38 | 25 | 13 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 12 | 22 | 10 | |
| National Action Party | 9 | 11 | 2 | |
| Labor Party | 7 | 4 | 3 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 5 | 0 | 5 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 2 | 4 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 2 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| New Alliance Party | 0 | 5 | 5 | |
| Total | 75 | 75 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- Tepotzotlán: Ángeles Zuppa Villegas (MC), daughter of three-time mayor Ángel Zuppa Núñez.[32]
Morelos
editAll 20 seats of the Congress of Morelos were up for election, where 12 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 8 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 33 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 6 | 7 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 5 | 0 | 5 | |
| Labor Party | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| National Action Party | 1 | 5 | 4 | |
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Humanist Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Partido Socialdemócrata de Morelos | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Progressive Social Networks | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Morelos Progresa | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 20 | 20 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- Jojutla – Juan Ángel Flores Bustamante (MORENA), incumbent
- Jiutepec – Rafael Reyes (MORENA), incumbent
- Puente de Ixtla – Claudia Mazari (MORENA)
- Cuautla – Rodrigo Arredondo (MORENA)
- Axochiapan – Félix Sánchez (MORENA)
- Tlaltizapán – Gabriel Moreno (MORENA)
- Tlaquiltenango – Carlos Franco (MORENA)
Nayarit
editAll 30 seats of the Congress of Nayarit were up for election, where 18 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 12 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 20 municipalities were up for election.[1]
The National Electoral Institute (INE) warned that Governor Antonio Echevarria was evading his responsibilities, claiming that he lied about the state not having MXN $200 million needed to organize the elections.[24]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 9 | 2 | 7 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 8 | 1 | 7 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| Labor Party | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| Morena | 2 | 12 | 10 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 4 | 3 | |
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| Progressive Social Networks | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Total | 30 | 30 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miguel Ángel Navarro Quintero | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 234,742 | 50.56 | |
| Ignacio Flores Medina | Citizens' Movement | 97,723 | 21.05 | |
| Gloria Núñez Sánchez | Va por Nayarit | 84,228 | 18.14 | |
| Águeda Galicia Jiménez | Movimiento Levántate para Nayarit | 20,546 | 4.43 | |
| Nayar Mayorquín Carrillo | Progressive Social Networks | 14,169 | 3.05 | |
| Víctor Manuel Chávez Vázquez | Visión y Valores en Acción | 4,549 | 0.98 | |
| Natalia Rojas Iñiguez | Solidarity Encounter Party | 4,195 | 0.90 | |
| Natalia Rojas Iñiguez | Force for Mexico | 3,985 | 0.86 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 179 | 0.04 | ||
| Total | 464,316 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 464,316 | 97.51 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 11,872 | 2.49 | ||
| Total votes | 476,188 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [26] | ||||
Nuevo León
editAll 42 seats of the Congress of Nuevo León were up for election, where 26 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 16 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 51 municipalities were up for election.[1]
Mayco Fabián Tapia Quiñones, state deputy candidate, was murdered on March 24, 2021.[33]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 15 | 16 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 10 | 14 | 4 | |
| Morena | 8 | 2 | 6 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 3 | 6 | 3 | |
| Labor Party | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Independents | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 42 | 42 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samuel García | Citizens' Movement | 786,808 | 37.35 | |
| Adrián de la Garza | Va fuerte por Nuevo León | 598,052 | 28.39 | |
| Fernando Larrazábal | National Action Party | 392,901 | 18.65 | |
| Clara Luz Flores | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 300,588 | 14.27 | |
| Emilio Jacques Rivera | Force for Mexico | 13,863 | 0.66 | |
| Carolina Garza Guerra | Solidarity Encounter Party | 7,042 | 0.33 | |
| Daney Siller Tristán | Progressive Social Networks | 6,629 | 0.31 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 702 | 0.03 | ||
| Total | 2,106,585 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 2,106,585 | 98.30 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 36,420 | 1.70 | ||
| Total votes | 2,143,005 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [34] | ||||
Municipal elections
edit- Monterrey – Luis Donaldo Colosio Riojas (MC), deputy of the Congress of Nuevo León (2018–2021) and son of former presidential candidate Luis Donaldo Colosio Murrieta[35]
- Apodaca – César Garza Villarreal (PRI)
- Guadalupe – María Cristina Díaz Salazar (PRI)
- Escobedo – Andrés Mijes Llovera, (MORENA)
- Juárez – Francisco Héctor Treviño Cantú (PRI)
- San Nicolás de los Garza – Daniel Carrillo Martínez (PAN)
- Santa Catarina – Jesús Ángel Nava Rivera (PAN)
- San Pedro – Miguel Treviño de Hoyos (independent), incumbent
- Cadereyta – Cosme Julián Leal Cantú, (PAN)
- General Terán – David Jonathan Sánchez Quintanilla (MC)
- Linares – Sergio Eduardo Elizondo Guzmán (PAN)
Oaxaca
editAll 42 seats of the Congress of Oaxaca were up for election, where 25 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 17 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 153 municipalities were up for election.[1]
Polling places could not be installed due to social-political conflicts in seven communities. Additionally, 800 ballots were stolen in “El Ocote” y San José Llano Grande, Miahuatlán de Porfirio Díaz.[36]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 26 | 23 | 3 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 6 | 8 | 2 | |
| Labor Party | 3 | 3 | ||
| Social Encounter Party | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| National Action Party | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| New Alliance Party | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Partido Unidad Popular | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Total | 42 | 42 | ||
Puebla
editAll 41 seats of the Congress of Puebla were up for election, where 26 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 15 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 217 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 15 | 16 | 1 | |
| National Action Party | 6 | 9 | 3 | |
| Labor Party | 5 | 5 | ||
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 6 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 1 | ||
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Compromiso por Puebla | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Pacto Social de Integración | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total | 41 | 41 | ||
Querétaro
editAll 25 seats of the Legislature of Querétaro were up for election, where 15 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 10 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 18 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 11 | 13 | 2 | |
| Morena | 6 | 5 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 1 | ||
| Partido Querétaro Independiente | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| Independents | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 25 | 25 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mauricio Kuri | ¡Contigo y con todo! | 491,550 | 55.36 | |
| Celia Maya García | Morena | 218,310 | 24.59 | |
| Abigail Arredondo Ramos | Institutional Revolutionary Party | 106,301 | 11.97 | |
| Katia Reséndiz Jaime | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 21,865 | 2.46 | |
| Beatriz León Sotelo | Citizens' Movement | 14,940 | 1.68 | |
| Juan Carlos Martínez | Force for Mexico | 8,946 | 1.01 | |
| Miguel Nava Alvarado | Progressive Social Networks | 8,628 | 0.97 | |
| Raquel Ruiz de Santiago Álvarez | Party of the Democratic Revolution | 6,473 | 0.73 | |
| María de Jesús Ibarra Pérez | Solidarity Encounter Party | 5,334 | 0.60 | |
| Penélope Ramírez Manríquez | Labor Party | 4,859 | 0.55 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 639 | 0.07 | ||
| Total | 887,845 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 887,845 | 97.69 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 20,981 | 2.31 | ||
| Total votes | 908,826 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [37] | ||||
Municipal elections
editQuintana Roo
editAll positions of the state's 11 municipalities were up for election.[1]
Municipal elections
edit- Benito Juárez – Mara Lezama Espinosa (MORENA)
- Tulum – Marciano Dzul Caamal (MORENA)
- Solidaridad – Lili Campos Miranda (PAN)
- José María Morelos – Erik Noé Borges Yam (MORENA)[39]
San Luis Potosí
editAll 27 seats of the Congress of San Luis Potosí were up for election, where 15 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 12 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 58 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 6 | 6 | ||
| Morena | 6 | 4 | 2 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| Labor Party | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 6 | 4 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 1 | ||
| Social Encounter Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Partido Conciencia Popular | 1 | 1 | ||
| Progressive Social Networks | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 27 | 27 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ricardo Gallardo Cardona | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 458,156 | 39.14 | |
| Octavio Pedroza Gaitán | Sí por San Luis Potosí | 400,273 | 34.19 | |
| Mónica Rangel Martínez | Morena | 139,243 | 11.90 | |
| José Luis Romero Calzada | Progressive Social Networks | 105,870 | 9.04 | |
| Marvelly Costanzo Rangel | Citizens' Movement | 31,527 | 2.69 | |
| Adrián Esper Cárdenas | Solidarity Encounter Party | 12,889 | 1.10 | |
| Francisco Javier Rico Ávalos | New Alliance Party | 12,199 | 1.04 | |
| Juan Carlos Machinena Morales | Force for Mexico | 6,093 | 0.52 | |
| Arturo Segoviano | Independent | 4,330 | 0.37 | |
| Total | 1,170,580 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 1,170,580 | 96.32 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 44,776 | 3.68 | ||
| Total votes | 1,215,356 | 100.00 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- San Luis Potosí City – Enrique Francisco Galindo Ceballos (PRI)
Sinaloa
editAll 40 seats of the Congress of Sinaloa were up for election, where 24 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 16 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 18 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 21 | 20 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 8 | 8 | ||
| Labor Party | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| National Action Party | 2 | 2 | ||
| Partido Sinaloense | 1 | 8 | 7 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Total | 40 | 40 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubén Rocha Moya | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 624,225 | 57.94 | |
| Mario Zamora Gastélum | Va por Sinaloa | 358,313 | 33.26 | |
| Sergio Torres Félix | Citizens' Movement | 31,897 | 2.96 | |
| Gloria González Burboa | Labor Party | 19,982 | 1.85 | |
| Rosa Elena Millán | Force for Mexico | 12,396 | 1.15 | |
| Ricardo Arnulfo Mendoza Sauceda | Solidarity Encounter Party | 11,285 | 1.05 | |
| Misael Sánchez Sánchez | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 10,536 | 0.98 | |
| Yolanda Cabrera Peraza | Progressive Social Networks | 8,386 | 0.78 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 422 | 0.04 | ||
| Total | 1,077,442 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 1,077,442 | 97.70 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 25,380 | 2.30 | ||
| Total votes | 1,102,822 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [40] | ||||
Sonora
editAll 33 seats of the Congress of Sonora were up for election, where 21 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 12 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 72 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 12 | 14 | 2 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 5 | 0 | 5 | |
| Labor Party | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| National Action Party | 3 | 4 | 1 | |
| New Alliance Party | 2 | 2 | ||
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Solidarity Encounter Party | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 33 | 33 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfonso Durazo | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 496,651 | 53.37 | |
| Ernesto Gándara Camou | Va por Sonora | 339,139 | 36.44 | |
| Manuel Scott Sánchez | Citizens' Movement | 45,539 | 4.89 | |
| María del Rosario Robles Robles | Force for Mexico | 19,426 | 2.09 | |
| Carlos Zatarain González | Solidarity Encounter Party | 18,071 | 1.94 | |
| David Cuahutémoc Galindo Delgado | Progressive Social Networks | 11,729 | 1.26 | |
| Total | 930,555 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 930,555 | 97.08 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 27,971 | 2.92 | ||
| Total votes | 958,526 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [41] | ||||
Municipal elections
edit- Hermosillo Municipality – Antonio Astiazarán Gutiérrez (PAN)
Tabasco
editAll 35 seats of the Congress of Tabasco were up for election, where 21 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 14 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 17 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 21 | 21 | ||
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 6 | 6 | ||
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 6 | 4 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Independents | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 35 | 35 | ||
Municipal elections
edit- Centro Municipality (Villahermosa) – Yolanda Osuna Huerta (MORENA)
Tamaulipas
editAll 36 seats of the Congress of Tamaulipas were up for election, where 22 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 14 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 43 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Action Party | 23 | 13 | 10 | |
| Morena | 10 | 18 | 8 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 2 | 2 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 1 | ||
| Labor Party | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total | 36 | 36 | ||
Tlaxcala
editAll 25 seats of the Congress of Tlaxcala were up for election, where 15 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 10 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 60 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 11 | 8 | 3 | |
| Labor Party | 4 | 4 | ||
| National Action Party | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 2 | 2 | ||
| Social Encounter Party | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Partido Alianza Ciudadana | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Force for Mexico | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 25 | 25 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lorena Cuéllar Cisneros | Juntos Hacemos Historia | 305,468 | 49.93 | |
| Anabell Ávalos Zempoalteca | Unidos por Tlaxcala | 231,424 | 37.83 | |
| Juan Carlos Sánchez García | Progressive Social Networks | 38,771 | 6.34 | |
| Eréndira Jiménez Montiel | Citizens' Movement | 14,660 | 2.40 | |
| Viviana Barbosa Bonola | Force for Mexico | 11,867 | 1.94 | |
| Liliana Becerril Rojas | Solidarity Encounter Party | 5,357 | 0.88 | |
| Evangelina Paredes Zamora | Partido Impacto Social Si | 4,116 | 0.67 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 100 | 0.02 | ||
| Total | 611,763 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 611,763 | 97.47 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 15,901 | 2.53 | ||
| Total votes | 627,664 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [42] | ||||
Veracruz
editAll 50 seats of the Congress of Veracruz were up for election, where 30 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 20 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 212 municipalities were up for election.[1]
On March 4, 2021, Melquiades Vázquez Lucas, mayoral candidate for La Perla, was assassinated.[43]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 21 | 28 | 7 | |
| National Action Party | 13 | 8 | 5 | |
| Labor Party | 4 | 4 | ||
| Social Encounter Party | 4 | 0 | 4 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 2 | 2 | ||
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 4 | 3 | |
| Force for Mexico | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 50 | 50 | ||
Yucatan
editAll 25 seats of the Congress of Yucatan were up for election, where 15 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 10 through proportional representation. Additionally, all positions of the state's 106 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 10 | 3 | 7 | |
| National Action Party | 6 | 14 | 8 | |
| Morena | 4 | 4 | ||
| Citizens' Movement | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 1 | 1 | ||
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 1 | 1 | ||
| New Alliance Party | 1 | 1 | ||
| Total | 27 | 27 | ||
Zacatecas
editAll 30 seats of the Congress of Zacatacas were up for election, where 18 were elected through first-past-the-post voting and 12 through proportional representation. Additionally, the governorship and all positions of the state's 58 municipalities were up for election.[1]
| Party | Before | After | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morena | 8 | 12 | 4 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 7 | 7 | ||
| National Action Party | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Labor Party | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| New Alliance Party | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| Solidarity Encounter Party | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 30 | 30 | ||
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| David Monreal Ávila | Juntos Haremos Historia en Zacatecas | 340,934 | 50.67 | |
| Claudia Anaya Mota | Va por Zacatecas | 265,557 | 39.46 | |
| Ana María Romo Fonseca | Citizens' Movement | 19,428 | 2.89 | |
| María Guadalupe Medina Padilla | Solidarity Encounter Party | 13,400 | 1.99 | |
| Miriam García Zamora | Force for Mexico | 11,483 | 1.71 | |
| Flavio Campos Miramontes | Paz para Desarrollar Zacatecas | 11,377 | 1.69 | |
| Javier Valadez Becerra | Partido del Pueblo | 5,741 | 0.85 | |
| Fernanda Salomé Perera Trejo | Progressive Social Networks | 2,659 | 0.40 | |
| Bibiana Lizardo | Movimiento Dignidad Zacatecas | 1,946 | 0.29 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 368 | 0.05 | ||
| Total | 672,893 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 672,893 | 97.37 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 18,174 | 2.63 | ||
| Total votes | 691,067 | 100.00 | ||
| Source: [44] | ||||
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag "En qué estados habrá elecciones en 2021 y qué cargos se eligen". milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio Digital. December 12, 2020. Retrieved February 12, 2021.
- ^ a b Badillo, Diego (June 6, 2021). "Violencia electoral dejó 91 políticos asesinados durante el proceso". El Economista. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Sevillano, Luis; Galindo, Jorge; Clemente, Yolanda; Alonso, Antonio (June 7, 2021). "Resultados de las elecciones de México". EL PAÍS (in Mexican Spanish). Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ Garduño, Roberto; Vargas, Rosa Elvira (March 1, 2021). "La Jornada – Apoyan 25 gobernadores acuerdo por la democracia: AMLO". jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). La Jornada. Retrieved March 1, 2021.
- ^ a b c (www.dw.com). "Narcos en las elecciones federales de México de 2021: mapa de riesgos | DW | 06.01.2021". DW.COM (in European Spanish). Deutsche Welle. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- ^ a b "La sombra del narco amenaza las próximas elecciones: este es el mapa de las zonas con más riesgo". infobae (in European Spanish). Infobae. January 9, 2021. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- ^ Morán, Raphael (March 18, 2021). "Crece la lista de candidatos y precandidatos asesinados". Aristegui Noticias (in Spanish). Retrieved March 18, 2021.
- ^ "Mexico to raise security for candidates ahead of elections". AP NEWS. March 4, 2021. Retrieved March 4, 2021.
- ^ Varela, Micaela (March 26, 2021). "Morena pierde 19 candidaturas por irregularidades en los gastos electorales de la precampaña". EL PAÍS (in Mexican Spanish). Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Quita INE a Morena 49 candidaturas". El Universal (in Spanish). March 26, 2021. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ "FGR abrió investigación contra influencers por apoyo al Verde Ecologista en la veda electoral". infobae (in European Spanish). Infoabae. June 10, 2021. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "INE calcula que 300 casillas no se instalarán en el país por 'falta de condiciones'". www.proceso.com.mx (in Spanish). Proceso. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Daniel Serrano denuncia irregularidades en la jornada electoral en Cuautitlán Izcalli". heraldodemexico.com.mx (in Spanish). Heraldo de Mexico. June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ a b "La única opción en Nextlalpan es irse a extraordinarias, analiza IEEM". www.milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ a b "Balacera en Amecameca deja dos lesionados. Elecciones 2021". www.milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio. June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ a b "Destrozan casillas y golpean a ciudadanos en votaciones de Metepec". www.milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio. June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ a b "Lanzan granada de utilería en casilla de Naucalpan". www.milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio. June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ a b "En Valle de Chalco cierran casillas por balacera". www.milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio. June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Protesta Claudia Anaya como candidata de PRI, PAN y PRD en Zacatecas". jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). La Jornada. March 8, 2021. Retrieved March 8, 2021.
- ^ "AFN POLÍTICO: Marina será declarada gobernadora electa". afntijuana.info. June 14, 2021. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "IEEBCS – Resultados Oficiales 2020/2021". computos2021.ieebcs.org.mx. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "Represor de indígenas, candidato de Morena a la alcaldía de Comitán". jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). La Jornada. April 1, 2021. Retrieved April 1, 2021.
- ^ Villalpando, Rubén (March 5, 2021). "La Jornada – Asesinan a candidato a alcaldía en Nuevo Casas Grandes, Chihuahua". jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c Navarro, Myriam; Villalpando, Rubén; Ocampo, Sergio; García, Carlos (March 5, 2021). "La Jornada – Peligran comicios en Nayarit; el INE responsabiliza a Echevarría". jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). La Jornada. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ García, Carlos (March 31, 2021). "La Jornada – Asesinan a abanderado del PRD a regidor de Apaseo el Grande y hieren a dirigente". jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). La Jornada. Retrieved March 31, 2021.
- ^ a b https://iepcgro.mx/proceso2021/repositorio/Resultados_Gubernatura_2020-2021.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ "Bárbara Trigueros se quedacomo alcaldesa de Guadalajara". El Informador :: Noticias de Jalisco, México, Deportes & Entretenimiento (in European Spanish). March 1, 2021. Retrieved March 1, 2021.
- ^ "Crimen organizado y pueblos indígenas impiden la instalación de 100 casillas en Michoacán". www.proceso.com.mx (in Spanish). Proceso. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Resultado de Cómputos por Casilla". www.iem.org.mx. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Hernández García, Sandra. "La Jornada – Gana Xochimilco Morena; la alianza pedirá el recuento". www.jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). La Jornada. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Partidos reportan irregularidades ante IEEM y piden fuerza pública". www.milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio. June 6, 2021. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Matan a Ricardo Almaraz, candidato a síndico suplente en Tepotzotlán". www.milenio.com (in Mexican Spanish). Milenio. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ Robledo, Raúl (March 26, 2021). "Mata asaltante a aspirante a diputado en NL". jornada.com.mx (in Spanish). La Jornada. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ "Elecciones Nuevo León 2021". computos2021.ieepcnl.mx (in Spanish). Retrieved January 7, 2024.
- ^ Campos Garza, Luciano (January 25, 2021). "Luis Donaldo Colosio Riojas será el candidato de MC a la alcaldía de Monterrey". proceso.com.mx (in Spanish). Proceso. Retrieved February 12, 2021.
- ^ "INE no instala casillas en siete comunidades de Oaxaca por conflictos sociales". www.proceso.com.mx (in Spanish). Proceso. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Resultados Electorales Locales IEEQ – 2021". rel2021qro.ieeq.mx. Retrieved January 7, 2024.
- ^ "Artistas y deportistas dan el salto a la política mexicana en elecciones 2021". San Diego Union-Tribune en Español (in Spanish). January 27, 2021. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- ^ "Elecciones 2021 | Habrá recuento de votos en casillas de Playa del Carmen; Morena alega fraude". Aristegui Noticias (in Spanish). Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ Bojorquez, Jórge (June 13, 2021). "APRUEBAN CÓMPUTOS ESTATALES DE ELECCIÓN A GUBERNATURA Y ASIGNAN DIPUTADOS DE REPRESENTACIÓN PROPORCIONAL". Instituto Electoral del Estado de Sinaloa. Retrieved January 7, 2024.
- ^ "Entrega CG del IEE Sonora constancia de mayoría de elección de gubernatura". www.ieesonora.org.mx. Retrieved January 7, 2024.
- ^ "ITE" (PDF). www.itetlax.org.mx. Retrieved January 7, 2024.
- ^ "Fue asesinado Melquiades Vázquez, candidato del PRI a edil de La Perla". infobae (in European Spanish). March 5, 2021. Retrieved January 7, 2024.
- ^ https://www.ieez.org.mx/PE2021/Doc/Computos%20Gubernatura.pdf [bare URL PDF]