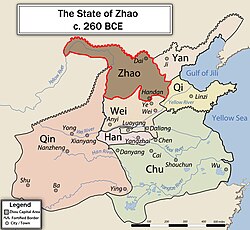
Zhao (traditional Chinese: 趙; simplified Chinese: 赵) was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It emerged from the tripartite division of Jin, along with Han and Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained considerable strength from the military reforms initiated during the reign of King Wuling, but suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Qin at the Battle of Changping. Its territory included areas in the modern provinces of Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi. It bordered the states of Qin, Wei, and Yan, as well as various nomadic peoples including the Hu and Xiongnu. Its capital was Handan, in modern Hebei province.
State of Zhao 趙 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 403 BC–222 BC | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Status | State → Kingdom | ||||||||
| Capital | Jinyang, Handan | ||||||||
| Religion | |||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
• 423 BCE - 409 BCE (first) | Marquess Xian of Zhao | ||||||||
• 403 BCE - 400 BCE | Marquess Lie of Zhao | ||||||||
• 386 BCE - 375 BCE | Marquess Jing of Zhao | ||||||||
• 374 BCE - 350 BCE | Marquess Cheng of Zhao | ||||||||
• 349 BCE - 326 BCE | Marquess Su of Zhao | ||||||||
• 325 BCE - 299 BCE | King Wuling of Zhao | ||||||||
• 298 BCE - 266 BCE | King Huiwen of Zhao | ||||||||
• 265 BCE - 245 BCE | King Xiaocheng of Zhao | ||||||||
• 244 BCE - 236 BCE | King Daoxiang of Zhao | ||||||||
• 235 BCE - 228 BCE | King Youmiu of Zhao | ||||||||
• 227 BCE - 223 BCE (last) | King Jia of Zhao | ||||||||
| Historical era | Warring States period | ||||||||
| 403 BC | |||||||||
• Conquered by Qin | 222 BC | ||||||||
| Currency | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Zhao | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Zhao" in seal script (top), Traditional (middle), and Simplified (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 趙 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 赵 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Zhao was home to the administrative philosopher Shen Dao, Confucian Xun Kuang, and Gonsun Long, who is affiliated to the school of names.[1]
Origins and ascendancy edit
The Zhao clan within Jin had been accumulating power for centuries, including annexing the Baidi state of Dai in the mid-5th century BC.
At the end of the Spring and Autumn period, Jin was divided between three powerful ministers, one of whom was Zhao Xiangzi, patriarch of the Zhao family. In 403 BC, the Zhou king formally recognised the existence of the Zhao state along with two other states, Han and Wei. Some historians, beginning with Sima Guang, take this recognition to mark the beginning of the Warring States Period.
At the beginning of the Warring States period, Zhao was one of the weaker states. Despite its extensive territory, its northern border was frequently harassed by the Eastern Hu, Forest Hu, Loufan, Xiongnu, and other northern nomadic peoples. Zhao lacked the military might of Wei or the wealth of Qi, and became a pawn in the struggle between them. This struggle came to a head in 354 BC when Wei invaded Zhao, forcing Zhao to seek help from Qi. The resulting Battle of Guiling was a major victory for Qi, reducing the threat to Zhao's southern border.
Zhao remained relatively weak until the military reforms of King Wuling of Zhao (325–299 BC). Zhao soldiers were ordered to dress like their Hu neighbours and to replace war chariots with cavalry archers (胡服骑射; 胡服騎射; húfúqíshè). This reform proved to be a brilliant strategy. With the advanced technology of the Chinese states and tactics of the steppe nomads, Zhao's cavalry became a powerful force. As a result, the newly empowered Zhao were more evenly matched with their greatest threat, Qi.
Zhao demonstrated its increased military prowess by conquering the state of Zhongshan in 295 BC after a protracted war and annexing territory from the neighbouring states of Wei, Yan, and Qin. During this time, Zhao cavalry also occasionally intruded into Qi during campaigns against Chu.
Several brilliant military commanders of the period served Zhao contemporaneously, including Lian Po, Zhao She, and Li Mu. Lian Po was instrumental in defending Zhao against Qin. Zhao She was most active in the east, leading the invasion of Yan. Li Mu defended Zhao against the Xiongnu in the Zhao–Xiongnu War and later against Qin.
Fall of Zhao edit
By the end of the Warring States period, Zhao was the only state strong enough to oppose the mighty Qin. An alliance with Wei against Qin began in 287 BC, but ended in defeat at Huayang in 273 BC. The struggle then culminated in the bloodiest battle of the entire period, the Battle of Changping in 260 BC. Zhao's forces were utterly defeated by Qin. Although the forces of Wei and Chu saved Handan from a subsequent siege by the victorious Qin, Zhao would never recover from the enormous loss of troops in the battle.
In 229 BC, invasions led by the Qin general Wang Jian were resisted by Li Mu and his subordinate officer Sima Shang (司馬尚) until 228 BC. Li Mu was one of the finest generals of the Warring States period, and although he was unable to defeat Wang Jian (also one of the best generals of the period), Wang Jian was unable to make any headway. The invasion ended in a stalemate. The Qin emperor, Qin Shihuang, realised that he needed to get rid of Li Mu in order to conquer Zhao, and tried to sow discord among the Zhao leadership. The Zhao king Youmiu fell for the plot: on the false advice of disloyal court officials and Qin infiltrators, he ordered Li Mu's execution and relieved Sima Shang of his duties. Li Mu's replacement, Zhao Cong, was promptly defeated by Wang Jian. Qin captured King Youmiu and defeated Zhao in 228 BC. Prince Jia, half-brother of King Qian, was proclaimed King Jia at Dai and led the last Zhao forces against the Qin. This regime lasted until 222 BC, when the Qin army captured him and defeated his forces at Dai.
A rebel named Wu Chen, following the example of Chen Sheng and Wu Guang in Chu, proclaimed himself King of Zhao. Wu was later killed by his subordinate Li Liang (李良). Zhang Er (張耳) and Chen Yu (陳餘), former officials of Zhao, created the Zhao royal Zhao Xie (趙歇) as King of Zhao. In 206 BC, the rebel lord Xiang Yu of Chu defeated the Qin dynasty and made himself and seventeen other lords kings, appointing Zhao Xie the king of Dai. Chen Yu helped Zhao Xie reclaim the land of Zhao from Zhang Er, so Zhao Xie created Chen Yu as Prince of Dai. In 205 BC, Chen Yu's subordinate in Dai, Xia Yue (夏說), was defeated by Liu Bang's generals Han Xin and Zhang Er. Chen Yu was defeated by Han Xin in 204 BC, and later Zhao Xie was killed by Han forces. Liu Bang gave the state of Zhao to Zhang Er.
In 154 BC, an unrelated Zhao, led by Prince of Zhao Liu Sui (劉遂), participated in the unsuccessful Rebellion of the Seven States (Chinese: 七國之亂) against the newly installed second emperor of the Han dynasty.
Culture and society edit
Before Qin Shi Huang unified China in 221 BC, each region had its own customs and culture, although elite culture was identical throughout. In the Yu Gong (Tribute of Yu) chapter of the Book of Documents – probably written in the 4th century BC – China is described as divided into nine regions, each with its own distinctive peoples and products. The central theme of this section is that these nine regions are unified into one state through the travels of the eponymous sage, Yu the Great, and the sending of each region's unique goods to the capital as tribute. Other texts also discussed these regional differences in culture and physical environment.[2]
One such text was Wuzi (The Book of Master Wu), a military treatise of the Warring States, written in response to a request from Marquis Wu of Wei for advice on how to deal with the other states. Wu Qi, to whom work is attributed, explained that the government and nature of the people are linked to the physical environment and territory in which they live.[2]
Of Zhao, he said:
The two states of Han and Zhao train their troops rigorously but have difficulty in applying their skills to the battlefield.
— Wuzi, Master Wu
Han and Zhao are states of the Central Plain. Theirs are a gentle people, weary from war and experienced in arms, but have little regard for their generals. The soldiers' salaries are meager and their officers have no strong commitment to their countries. Although their troops are experienced, they cannot be expected to fight to the death. To defeat them, we must concentrate large numbers of troops in our attacks to present them with certain peril. When they counterattack, we must be prepared to defend our positions vigorously and make them pay dearly. When they retreat, we must pursue and give them no rest. This will grind them down.
— Wuzi, Master Wu
List of Zhao rulers edit
Before the partition of Jin edit
- Chengzi of Zhao
- Xuanzi of Zhao
- Zhuangzi of Zhao
- Wenzi of Zhao
- Jingzi of Zhao (趙景子)
- Jianzi of Zhao (趙簡子)
- Xiangzi of Zhao (趙襄子)
- Huanzi of Zhao (趙桓子)
After the partition of Jin edit
- Marquess Xian (獻侯), personal name Huan (浣), ruled 424 BC–409 BC
- Marquess Lie (烈侯), personal name Ji (籍), son of previous, ruled 409 BC–387 BC, noted for several reforms
- Marquess Jing (敬侯), personal name Zhang (章), son of previous, ruled 387 BC–375 BC
- Marquess Cheng (成侯), personal name Zhong (種), son of previous, ruled 375 BC–350 BC
- Marquess Su (肅侯), personal name Yu (語), son of previous, ruled 350 BC–326 BC
- King Wuling (武靈王), personal name Yong (雍), son of previous, ruled 326 BC–Spring 299 BC
- King Huiwen (惠文王), personal name He (何), son of previous, ruled Spring 299 BC–266 BC
- King Xiaocheng (孝成王), personal name Dan (丹), son of previous, ruled 266 BC–245 BC
- King Daoxiang (悼襄王), personal name Yan (偃), son of previous, ruled 245 BC–236 BC
- King Youmiu (幽繆王), personal name Qian (遷), son of previous, ruled 236 BC–228 BC
- Jia, King of Zhao (代王), personal name Jia (嘉), half-brother of previous, ruled 228 BC–222 BC
- Xie, King of Zhao (趙王歇), ruled 209 BC–205 BC. Also known as Zhao Xie. A reinstalled king of Zhao by rioting peasants during the reign of Qin Er Shi. Defeated and killed by Liu Bang.
Zhao in astronomy edit
There are two opinions about the representing star of Zhao in Chinese astronomy. The opinions are :
- Zhao is represented with the star Lambda Herculis in asterism Left Wall, Heavenly Market enclosure,[3] and also represented with two stars 26 Capricorni (趙一 Zhao yī, English: the First Star of Zhao) and 27 Capricorni (趙二 Zhao èr, English: the Second Star of Zhao) in asterism Twelve States, Girl mansion.[4] (see Chinese constellation).
- Zhao is represented with the star Lambda Herculis,[5] and also represented with star "m Capricorni".[6]
See also edit
References edit
- ^ Huang Kejian (2016) [2010]. From Destiny to Dao: A Survey of Pre-Qin Philosophy in China. Silkroad Press. p. 185. ISBN 978-1-62320-070-1.
- ^ a b Lewis, Mark Edward (2009). The Early Chinese Empires : Qin and Han. Cambridge, Mass: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. pp. 11 - 16. ISBN 9780674024779.
- ^ Chen Huihua (陳輝樺), ed. (23 June 2006). "中國古代的星象系統 (54): 天市左垣、市樓". Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy 天文教育資訊網 (in Chinese).
- ^ zh:北方中西星名對照表
- ^ Richard Hinckley Allen (2021) [1963]. "Hercules". Star Names – Their Lore and Meaning.
- ^ Richard Hinckley Allen (2021) [1963]. "Capricornus". Star Names – Their Lore and Meaning.