The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is a positive real number that, when multiplied by itself or squared, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as or . It is an algebraic number, and therefore not a transcendental number. Technically, it should be called the principal square root of 2, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property.
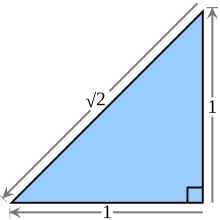 The square root of 2 is equal to the length of the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle with legs of length 1. | |
| Representations | |
|---|---|
| Decimal | 1.4142135623730950488... |
| Continued fraction | |
Geometrically, the square root of 2 is the length of a diagonal across a square with sides of one unit of length; this follows from the Pythagorean theorem. It was probably the first number known to be irrational.[1] The fraction 99/70 (≈ 1.4142857) is sometimes used as a good rational approximation with a reasonably small denominator.
Sequence A002193 in the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences consists of the digits in the decimal expansion of the square root of 2, here truncated to 65 decimal places:[2]
- 1.41421356237309504880168872420969807856967187537694807317667973799
History edit
The Babylonian clay tablet YBC 7289 (c. 1800–1600 BC) gives an approximation of in four sexagesimal figures, 1 24 51 10, which is accurate to about six decimal digits,[3] and is the closest possible three-place sexagesimal representation of :
Another early approximation is given in ancient Indian mathematical texts, the Sulbasutras (c. 800–200 BC), as follows: Increase the length [of the side] by its third and this third by its own fourth less the thirty-fourth part of that fourth.[4] That is,
This approximation is the seventh in a sequence of increasingly accurate approximations based on the sequence of Pell numbers, which can be derived from the continued fraction expansion of . Despite having a smaller denominator, it is only slightly less accurate than the Babylonian approximation.
Pythagoreans discovered that the diagonal of a square is incommensurable with its side, or in modern language, that the square root of two is irrational. Little is known with certainty about the time or circumstances of this discovery, but the name of Hippasus of Metapontum is often mentioned. For a while, the Pythagoreans treated as an official secret the discovery that the square root of two is irrational, and, according to legend, Hippasus was murdered for divulging it.[5][6] The square root of two is occasionally called Pythagoras's number or Pythagoras's constant, for example by Conway & Guy (1996).[7]
Ancient Roman architecture edit
In ancient Roman architecture, Vitruvius describes the use of the square root of 2 progression or ad quadratum technique. It consists basically in a geometric, rather than arithmetic, method to double a square, in which the diagonal of the original square is equal to the side of the resulting square. Vitruvius attributes the idea to Plato. The system was employed to build pavements by creating a square tangent to the corners of the original square at 45 degrees of it. The proportion was also used to design atria by giving them a length equal to a diagonal taken from a square, whose sides are equivalent to the intended atrium's width.[8]
Decimal value edit
Computation algorithms edit
There are many algorithms for approximating as a ratio of integers or as a decimal. The most common algorithm for this, which is used as a basis in many computers and calculators, is the Babylonian method[9] for computing square roots, an example of Newton's method for computing roots of arbitrary functions. It goes as follows:
First, pick a guess, ; the value of the guess affects only how many iterations are required to reach an approximation of a certain accuracy. Then, using that guess, iterate through the following recursive computation:
Each iteration improves the approximation, roughly doubling the number of correct digits. Starting with , the subsequent iterations yield:
Rational approximations edit
A simple rational approximation 99/70 (≈ 1.4142857) is sometimes used. Despite having a denominator of only 70, it differs from the correct value by less than 1/10,000 (approx. +0.72×10−4).
The next two better rational approximations are 140/99 (≈ 1.4141414...) with a marginally smaller error (approx. −0.72×10−4), and 239/169 (≈ 1.4142012) with an error of approx −0.12×10−4.
The rational approximation of the square root of two derived from four iterations of the Babylonian method after starting with a0 = 1 (665,857/470,832) is too large by about 1.6×10−12; its square is ≈ 2.0000000000045.
Records in computation edit
In 1997, the value of was calculated to 137,438,953,444 decimal places by Yasumasa Kanada's team. In February 2006, the record for the calculation of was eclipsed with the use of a home computer. Shigeru Kondo calculated one trillion decimal places in 2010.[10] Among mathematical constants with computationally challenging decimal expansions, only π, e, and the golden ratio have been calculated more precisely as of March 2022[update].[11] Such computations aim to check empirically whether such numbers are normal.
This is a table of recent records in calculating the digits of .[11]
| Date | Name | Number of digits |
|---|---|---|
| January 5, 2022 | Tizian Hanselmann | 10000000001000 |
| June 28, 2016 | Ron Watkins | 10000000000000 |
| April 3, 2016 | Ron Watkins | 5000000000000 |
| January 20, 2016 | Ron Watkins | 2000000000100 |
| February 9, 2012 | Alexander Yee | 2000000000050 |
| March 22, 2010 | Shigeru Kondo | 1000000000000 |
Proofs of irrationality edit
A short proof of the irrationality of can be obtained from the rational root theorem, that is, if is a monic polynomial with integer coefficients, then any rational root of is necessarily an integer. Applying this to the polynomial , it follows that is either an integer or irrational. Because is not an integer (2 is not a perfect square), must therefore be irrational. This proof can be generalized to show that any square root of any natural number that is not a perfect square is irrational.
For other proofs that the square root of any non-square natural number is irrational, see Quadratic irrational number or Infinite descent.
Proof by infinite descent edit
One proof of the number's irrationality is the following proof by infinite descent. It is also a proof of a negation by refutation: it proves the statement " is not rational" by assuming that it is rational and then deriving a falsehood.
- Assume that is a rational number, meaning that there exists a pair of integers whose ratio is exactly .
- If the two integers have a common factor, it can be eliminated using the Euclidean algorithm.
- Then can be written as an irreducible fraction such that a and b are coprime integers (having no common factor) which additionally means that at least one of a or b must be odd.
- It follows that and . ( (a/b)n = an/bn ) ( a2 and b2 are integers)
- Therefore, a2 is even because it is equal to 2b2. (2b2 is necessarily even because it is 2 times another whole number.)
- It follows that a must be even (as squares of odd integers are never even).
- Because a is even, there exists an integer k that fulfills .
- Substituting 2k from step 7 for a in the second equation of step 4: , which is equivalent to .
- Because 2k2 is divisible by two and therefore even, and because , it follows that b2 is also even which means that b is even.
- By steps 5 and 8, a and b are both even, which contradicts step 3 (that is irreducible).
Since we have derived a falsehood, the assumption (1) that is a rational number must be false. This means that is not a rational number; that is to say, is irrational.
This proof was hinted at by Aristotle, in his Analytica Priora, §I.23.[12] It appeared first as a full proof in Euclid's Elements, as proposition 117 of Book X. However, since the early 19th century, historians have agreed that this proof is an interpolation and not attributable to Euclid.[13]
Proof by unique factorization edit
As with the proof by infinite descent, we obtain . Being the same quantity, each side has the same prime factorization by the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, and in particular, would have to have the factor 2 occur the same number of times. However, the factor 2 appears an odd number of times on the right, but an even number of times on the left—a contradiction.
Geometric proof edit
A simple proof is attributed to Stanley Tennenbaum when he was a student in the early 1950s.[14][15] Given two squares with integer sides respectively a and b, one of which has twice the area of the other, place two copies of the smaller square in the larger as shown in Figure 1. The square overlap region in the middle ( ) must equal the sum of the two uncovered squares ( ). However, these squares on the diagonal have positive integer sides that are smaller than the original squares. Repeating this process, there are arbitrarily small squares one twice the area of the other, yet both having positive integer sides, which is impossible since positive integers cannot be less than 1.
Tom M. Apostol made another geometric reductio ad absurdum argument showing that is irrational.[16] It is also an example of proof by infinite descent. It makes use of classic compass and straightedge construction, proving the theorem by a method similar to that employed by ancient Greek geometers. It is essentially the same algebraic proof as in the previous paragraph, viewed geometrically in another way.
Let △ ABC be a right isosceles triangle with hypotenuse length m and legs n as shown in Figure 2. By the Pythagorean theorem, . Suppose m and n are integers. Let m:n be a ratio given in its lowest terms.
Draw the arcs BD and CE with centre A. Join DE. It follows that AB = AD, AC = AE and ∠BAC and ∠DAE coincide. Therefore, the triangles ABC and ADE are congruent by SAS.
Because ∠EBF is a right angle and ∠BEF is half a right angle, △ BEF is also a right isosceles triangle. Hence BE = m − n implies BF = m − n. By symmetry, DF = m − n, and △ FDC is also a right isosceles triangle. It also follows that FC = n − (m − n) = 2n − m.
Hence, there is an even smaller right isosceles triangle, with hypotenuse length 2n − m and legs m − n. These values are integers even smaller than m and n and in the same ratio, contradicting the hypothesis that m:n is in lowest terms. Therefore, m and n cannot be both integers; hence, is irrational.
Constructive proof edit
While the proofs by infinite descent are constructively valid when "irrational" is defined to mean "not rational", we can obtain a constructively stronger statement by using a positive definition of "irrational" as "quantifiably apart from every rational". Let a and b be positive integers such that 1<a/b< 3/2 (as 1<2< 9/4 satisfies these bounds). Now 2b2 and a2 cannot be equal, since the first has an odd number of factors 2 whereas the second has an even number of factors 2. Thus |2b2 − a2| ≥ 1. Multiplying the absolute difference |√2 − a/b| by b2(√2 + a/b) in the numerator and denominator, we get[17]
the latter inequality being true because it is assumed that 1<a/b< 3/2, giving a/b + √2 ≤ 3 (otherwise the quantitative apartness can be trivially established). This gives a lower bound of 1/3b2 for the difference |√2 − a/b|, yielding a direct proof of irrationality in its constructively stronger form, not relying on the law of excluded middle; see Errett Bishop (1985, p. 18). This proof constructively exhibits an explicit discrepancy between and any rational.
Proof by Pythagorean triples edit
This proof uses the following property of primitive Pythagorean triples:
- If a, b, and c are coprime positive integers such that a2 + b2 = c2, then c is never even.[18]
This lemma can be used to show that two identical perfect squares can never be added to produce another perfect square.
Suppose the contrary that is rational. Therefore,
- where and
- Squaring both sides,
Here, (b, b, a) is a primitive Pythagorean triple, and from the lemma a is never even. However, this contradicts the equation 2b2 = a2 which implies that a must be even.
Multiplicative inverse edit
The multiplicative inverse (reciprocal) of the square root of two (i.e., the square root of 1/2) is a widely used constant.
One-half of , also the reciprocal of , is a common quantity in geometry and trigonometry because the unit vector that makes a 45° angle with the axes in a plane has the coordinates
This number satisfies
Properties edit
One interesting property of is
since
This is related to the property of silver ratios.
can also be expressed in terms of copies of the imaginary unit i using only the square root and arithmetic operations, if the square root symbol is interpreted suitably for the complex numbers i and −i:
is also the only real number other than 1 whose infinite tetrate (i.e., infinite exponential tower) is equal to its square. In other words: if for c > 1, x1 = c and xn+1 = cxn for n > 1, the limit of xn as n → ∞ will be called (if this limit exists) f(c). Then is the only number c > 1 for which f(c) = c2. Or symbolically:
appears in Viète's formula for π,
which is related to the formula[19]
Similar in appearance but with a finite number of terms, appears in various trigonometric constants:[20]
It is not known whether is a normal number, which is a stronger property than irrationality, but statistical analyses of its binary expansion are consistent with the hypothesis that it is normal to base two.[21]
Representations edit
Series and product edit
The identity cos π/4 = sin π/4 = 1/√2, along with the infinite product representations for the sine and cosine, leads to products such as
and
or equivalently,
The number can also be expressed by taking the Taylor series of a trigonometric function. For example, the series for cos π/4 gives
The Taylor series of √1 + x with x = 1 and using the double factorial n!! gives
The convergence of this series can be accelerated with an Euler transform, producing
It is not known whether can be represented with a BBP-type formula. BBP-type formulas are known for π√2 and √2 ln(1+√2), however.[22]
The number can be represented by an infinite series of Egyptian fractions, with denominators defined by 2n th terms of a Fibonacci-like recurrence relation a(n) = 34a(n−1) − a(n−2), a(0) = 0, a(1) = 6.[23]
Continued fraction edit
The square root of two has the following continued fraction representation:
The convergents p/q formed by truncating this representation form a sequence of fractions that approximate the square root of two to increasing accuracy, and that are described by the Pell numbers (i.e., p2 − 2q2 = ±1). The first convergents are: 1/1, 3/2, 7/5, 17/12, 41/29, 99/70, 239/169, 577/408 and the convergent following p/q is p + 2q/p + q. The convergent p/q differs from by almost exactly 1/2√2q2, which follows from:
Nested square edit
The following nested square expressions converge to :
Applications edit
Paper size edit
In 1786, German physics professor Georg Christoph Lichtenberg[24] found that any sheet of paper whose long edge is times longer than its short edge could be folded in half and aligned with its shorter side to produce a sheet with exactly the same proportions as the original. This ratio of lengths of the longer over the shorter side guarantees that cutting a sheet in half along a line results in the smaller sheets having the same (approximate) ratio as the original sheet. When Germany standardised paper sizes at the beginning of the 20th century, they used Lichtenberg's ratio to create the "A" series of paper sizes.[24] Today, the (approximate) aspect ratio of paper sizes under ISO 216 (A4, A0, etc.) is 1: .
Proof:
Let shorter length and longer length of the sides of a sheet of paper, with
- as required by ISO 216.
Let be the analogous ratio of the halved sheet, then
- .
Physical sciences edit
There are some interesting properties involving the square root of 2 in the physical sciences:
- The square root of two is the frequency ratio of a tritone interval in twelve-tone equal temperament music.
- The square root of two forms the relationship of f-stops in photographic lenses, which in turn means that the ratio of areas between two successive apertures is 2.
- The celestial latitude (declination) of the Sun during a planet's astronomical cross-quarter day points equals the tilt of the planet's axis divided by .
- In the brain there are lattice cells, discovered in 2005 by a group led by May-Britt and Edvard Moser. "The grid cells were found in the cortical area located right next to the hippocampus [...] At one end of this cortical area the mesh size is small and at the other it is very large. However, the increase in mesh size is not left to chance, but increases by the squareroot of two from one area to the next."[25]
See also edit
- List of mathematical constants
- Square root of 3, √3
- Square root of 5, √5
- Gelfond–Schneider constant, 2√2
- Silver ratio, 1 + √2
Notes edit
- ^ Fowler, David H. (2001), "The story of the discovery of incommensurability, revisited", Neusis (10): 45–61, MR 1891736
- ^ "A002193 - OEIS". oeis.org. Retrieved 2020-08-10.
- ^ Fowler and Robson, p. 368.
Photograph, illustration, and description of the root(2) tablet from the Yale Babylonian Collection Archived 2012-08-13 at the Wayback Machine
High resolution photographs, descriptions, and analysis of the root(2) tablet (YBC 7289) from the Yale Babylonian Collection - ^ Henderson.
- ^ "The Dangerous Ratio". nrich.maths.org. Retrieved 2023-09-18.
- ^ Von Fritz, Kurt (1945). "The Discovery of Incommensurability by Hippasus of Metapontum". Annals of Mathematics. 46 (2): 242–264. doi:10.2307/1969021. ISSN 0003-486X.
- ^ Conway, John H.; Guy, Richard K. (1996), The Book of Numbers, Copernicus, p. 25
- ^ Williams, Kim; Ostwald, Michael (2015). Architecture and Mathematics from Antiquity to the Future: Volume I: Antiquity to the 1500s. Birkhäuser. p. 204. ISBN 9783319001371.
- ^ Although the term "Babylonian method" is common in modern usage, there is no direct evidence showing how the Babylonians computed the approximation of seen on tablet YBC 7289. Fowler and Robson offer informed and detailed conjectures.
Fowler and Robson, p. 376. Flannery, p. 32, 158. - ^ "Constants and Records of Computation". Numbers.computation.free.fr. 2010-08-12. Archived from the original on 2012-03-01. Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ^ a b "Records set by y-cruncher". Archived from the original on 2022-04-07. Retrieved 2022-04-07.
- ^ All that Aristotle says, while writing about proofs by contradiction, is that "the diagonal of the square is incommensurate with the side, because odd numbers are equal to evens if it is supposed to be commensurate".
- ^ The edition of the Greek text of the Elements published by E. F. August in Berlin in 1826–1829 already relegates this proof to an Appendix. The same thing occurs with J. L. Heiberg's edition (1883–1888).
- ^ Proof 8‴ Archived 2016-04-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Yanofsky, N. (2016). "Paradoxes, Contradictions, and the Limits of Science". Archived from the original on 2016-06-30.
- ^ Tom M. Apostol (Nov 2000), "Irrationality of The Square Root of Two -- A Geometric Proof", The American Mathematical Monthly, 107 (9): 841–842, doi:10.2307/2695741, JSTOR 2695741
- ^ See Katz, Karin Usadi; Katz, Mikhail G. (2011), "Meaning in Classical Mathematics: Is it at Odds with Intuitionism?", Intellectica, 56 (2): 223–302 (see esp. Section 2.3, footnote 15), arXiv:1110.5456, Bibcode:2011arXiv1110.5456U
- ^ Sierpiński, Wacław (2003), Pythagorean Triangles, Dover, pp. 4–6, ISBN 978-0-486-43278-6
- ^ Courant, Richard; Robbins, Herbert (1941), What is mathematics? An Elementary Approach to Ideas and Methods, London: Oxford University Press, p. 124
- ^ Julian D. A. Wiseman Sin and cos in surds Archived 2009-05-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Good & Gover (1967).
- ^ Bailey, David H. (13 February 2011). "A Compendium of BBP-Type Formulas for Mathematical Constants" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-06-10. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A082405 (a(n) = 34*a(n-1) - a(n-2); a(0)=0, a(1)=6)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2016-09-05.
- ^ a b Houston, Keith (2016). The Book: A Cover-to-Cover Exploration of the Most Powerful Object of Our Time. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 324. ISBN 978-0393244809.
- ^ Nordengen, Kaja (2016). The Book: Hjernen er sternen. 2016 Kagge Forlag AS. p. 81. ISBN 978-82-489-2018-2.
References edit
- Apostol, Tom M. (2000), "Irrationality of the square root of two – A geometric proof", American Mathematical Monthly, 107 (9): 841–842, doi:10.2307/2695741, JSTOR 2695741.
- Aristotle (2007), Analytica priora, eBooks@Adelaide
- Bishop, Errett (1985), Schizophrenia in contemporary mathematics. Errett Bishop: reflections on him and his research (San Diego, Calif., 1983), 1–32, Contemp. Math. 39, Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI.
- Flannery, David (2005), The Square Root of Two, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 0-387-20220-X.
- Fowler, David; Robson, Eleanor (1998), "Square Root Approximations in Old Babylonian Mathematics: YBC 7289 in Context", Historia Mathematica, 25 (4): 366–378, doi:10.1006/hmat.1998.2209.
- Good, I. J.; Gover, T. N. (1967), "The generalized serial test and the binary expansion of ", Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A, 130 (1): 102–107, doi:10.2307/2344040, JSTOR 2344040.
- Henderson, David W. (2000), "Square roots in the Śulba Sūtras", in Gorini, Catherine A. (ed.), Geometry At Work: Papers in Applied Geometry, Cambridge University Press, pp. 39–45, ISBN 978-0-88385-164-7.
External links edit
- Gourdon, X.; Sebah, P. (2001), "Pythagoras' Constant: ", Numbers, Constants and Computation.
- The Square Root of Two to 5 million digits by Jerry Bonnell and Robert J. Nemiroff. May, 1994.
- Square root of 2 is irrational, a collection of proofs
- Grime, James; Bowley, Roger. "The Square Root of Two". Numberphile. Brady Haran.
- √2 Search Engine 2 billion searchable digits of √2, π and e


