The Kingdom of Pergamon, Pergamene Kingdom, or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (/ˈætəlɪd/; Greek: Δυναστεία των Ατταλιδών, romanized: Dynasteía ton Attalidón).
Kingdom of Pergamon | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| approx. 282 BC–129 BC | |||||||||||
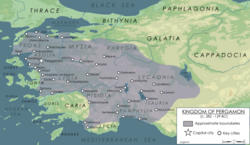 Pergamon in 188 BC | |||||||||||
| Capital | Pergamon (modern-day Bergama, İzmir, Turkey) | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Greek Lycian, Carian, Lydian | ||||||||||
| Religion | Greek Polytheism, Hellenistic Religion | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Basileus | |||||||||||
• 282–263 BC | Philetaerus | ||||||||||
• 263–241 BC | Eumenes I | ||||||||||
• 241–197 BC | Attalus I | ||||||||||
• 197–159 BC | Eumenes II | ||||||||||
• 160–138 BC | Attalus II | ||||||||||
• 138–133 BC | Attalus III | ||||||||||
• 133–129 BC | Eumenes III | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Hellenistic period | ||||||||||
• Philetaerus takes control of the city of Pergamon | approx. 282 BC | ||||||||||
• Attalus III bequeathed the kingdom to the Roman Republic | 133 BC | ||||||||||
• Incorporated into Roman province of Asia after the defeat of Eumenes III Aristonicus | 129 BC | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||


The kingdom was a rump state that was created from the territory ruled by Lysimachus, a general of Alexander the Great. Philetaerus, one of Lysimachus' lieutenants, rebelled and took the city of Pergamon and its environs with him; Lysimachus died soon after in 281 BC. The new kingdom was initially in a vassal-like relationship of nominal fealty to the Seleucid Empire, but exercised considerable autonomy and soon became entirely independent. It was a monarchy ruled by Philetaerus's extended family and their descendants. It lasted around 150 years before being eventually absorbed by the Roman Republic during the period from 133–129 BC.
History edit
From autonomy to independence (282–241 BC) edit
Philetaerus rose from humble origins to become a lieutenant of Lysimachus, one of Alexander the Great's generals (diadochi), who ruled a large state centered around Byzantium.[1] Philetaerus was trusted to manage the fortress of Pergamon and guard much of Lysimachus's treasury, and had 9,000 talents under his purview. At some point prior to 281 BC, Philetaerus deserted Lysimachus and rebelled, allegedly over fears of Arsinoe, Lysimachus's wife, who was accused of arranging the death of Agathocles, Lysimachus's son. In 281 BC, Seleucus I Nicator, another of Alexander's generals, defeated and killed Lysimachus at the Battle of Corupedium, while Seleucus himself was killed a few months later. Philetaerus offered his services to Seleucus and his successors of the Seleucid Empire, but enjoyed considerable autonomy.[2] He extended his power and influence beyond just the city of Pergamon, making allies with neighboring city states. He contributed troops, money, and food to the city of Cyzicus, in Mysia, for its defense against the invading Gauls, thus gaining prestige and goodwill for him and his family.[3] He built the sanctuary of Demeter on the acropolis of Pergamon, the temple of Athena (Pergamon's patron deity), and Pergamon's first palace. He added considerably to the city's fortifications.[3]
Philetaerus' nephew and adopted son, Eumenes I, succeeded him upon his death in 263 BC. He rebelled and defeated the Seleucid king Antiochus I Soter near the Lydian capital of Sardis in 261 BC. He created an outright independent Pergamese state, and greatly increased its territories. He established garrisons, such as Philetaireia, in the north at the foot of Mount Ida, which was named after his adoptive father, and Attaleia, in the east, to the northeast of Thyatira near the sources of the river Lycus, which was named after his grandfather. He also extended his control to the south of the river Caïcus, reaching the Gulf of Cyme. Eumenes I minted coins with the portrait of Philetaerus, who during his reign had still been depicting the Seleucid king Seleucus I Nicator on his coins.[4]
Reign of Attalus I Soter (241–197 BC) edit
Attalus I (r. 241–197 BC) succeeded Eumenes I after being adopted as his son.[5] Early in his reign, he won a battlefield victory against the Galatians of Asia Minor (called Gauls by Pausanias) at the Battle of the Caecus River.[6] This victory was a key to the legitimacy of Hellenistic kings, who styled themselves after Alexander the Great's legacy of military glories, and improved the standing and prestige of the kingdom.[4] Attalus took the name Soter, "Savior", afterward, and explicitly took the title of basileus, king.[7] Several years later, the "War of the Brothers" broke out in the Seleucid Empire between Seleucus II Callinicus and Antiochus Hierax. Antiochus Hierax made alliances with other kings in Asia Minor, his base of power, including both the Galatians and the Cappadocians. Around 230 BC, Hireax attacked Pergamon with the help of the Galatians. Attalus defeated the Gauls and Antiochus in the Battle of Aphrodisium and in a second battle in the east. He then fought Antiochus alone in a battle near Sardis and in the Battle of the Harpasus in Caria in 229 BC. After this Antiochus left to start a campaign in Mesopotamia, and then pivoted toward Thrace in 227 BC. He was killed in battle against the Gauls and the Kingdom of Tylis.[8] With Antiochus Hierax's death, Attalus gained control over all Seleucid territories in Asia Minor north of the Taurus Mountains. He repulsed several attempts by Seleucus III Ceraunus, who had succeeded Seleucus II, to recover the lost territory. The newly expanded kingdom stretched over 143,000 square kilometres (55,000 sq mi).[8]
The expansion was not to last long. In 223 BC, Seleucus III crossed the Taurus, but was assassinated, and the general Achaeus assumed control of the Seleucid army. Antiochus III the Great made Achaeus governor of the Seleucid territories north of the Taurus. Achaeus embarked upon a remarkably successful military campaign. Within two years, he had recovered the lost territories, taken parts of the traditional Pergamese heartland, and forced Attalus to retreat within the walls of Pergamon. However, Achaeus himself turned on Antiochus III and proclaimed himself a king, perhaps because he was accused of intending to revolt anyway, or perhaps simply drunk with success. By 220/219 BC, Achaeus and Attalus seem to have made peace.[9][10]
In 218 BC, Achaeus undertook an expedition to Selge, south of the Taurus. Attalus recaptured his former territories with the help of some Thracian Gauls. Achaeus returned from his victorious campaign in 217 BC and hostilities between the two resumed. Attalus made an alliance with Antiochus III, who besieged Achaeus in Sardis in 214 BC. Antiochus captured the city and put Achaeus to death in the next year. Attalus regained control over his territories.[9]
The Attalids became allies of the Roman Republic during the First Macedonian War (214–205 BC), although their participation was rather ineffective and insignificant.[11][12] They would go on to support Rome in many subsequent wars. Attalus I, who had helped the Romans in the first war, also provided them with assistance in the Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC).[13]
Expansion after the Treaty of Apamea (197–138 BC) edit
King Antiochus III of the Seleucids seem to have conquered or at least cowed into neutrality much of Pergamese territory in 198 BC; by 196 BC, at least, it seems that Antiochus III was able to march his armies through the area without opposition, and important putatively Attalid cities such as Phocaea and Thyatira were in Seleucid possession.[14] The authority of the Pergamese state was hanging by a thread when Eumenes II (r. 197–159 BC)[15] came to the throne in 197 BC. Eumenes II sought alliances with the Achaean League, rejected an offer of marriage and alliance with the Seleucids, and supported Rome in the Roman–Seleucid War of 192–188 BC.[16] In 188 BC, after the war's end by the Treaty of Apamea, the Romans seized the possessions of the defeated Antiochus III in Asia Minor and gave Mysia, Lydia, Phrygia, and Pamphylia to the kingdom of Pergamon and Caria, Lycia and Pisidia, in the southwestern corner of Asia Minor, to Rhodes, another Roman ally. Later the Romans gave these possessions of Rhodes to Pergamon. These acquisitions were an enormous increase in the size and influence of Pergamon. During the reign of Eumenes II, the Pergamese would also fight the Galatian War, Prusias I of Bithynia (around 188–184 BC?), Pharnaces I of Pontus (around 183-179 BC?), and would aid the Romans again in the Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC).[16] Eumenes II also successfully intervened in Seleucid politics, aiding Antiochus IV Epiphanes in his quest to take the throne from Heliodorus.[16]
Eumenes II was ill for the last decade of his life, and was succeeded by his brother Attalus II as king in 159 BC, although Attalus II had already assumed many key responsibilities by then. Before he became king, he was a military commander. In 190 BC he took part in the Battle of Magnesia, which was the final victory of the Romans in the war against the Seleucids. In 189 BC he led the Pergamene troops which flanked the Roman army under Gnaeus Manlius Vulso in the Galatian War. He was the lead commander in the war with Pontus, as well. After becoming king in his own right, he made war against Prusias II of Bithynia in 156–154 BC with the help of the Romans.[17] He also made an alliance and received troops from Ariarathes V of Cappadocia, led by his son Demetrius. Attalus expanded his kingdom and founded the cities of Philadelphia and Attalea-in-Pamphylia. In 152 BC the two kings and Rome helped and funded Alexander Balas in his successful bid to start a civil war in the Seleucid Empire and to seize the Seleucid throne from Demetrius I Soter. In 149 BC, Attalus helped Nicomedes II Epiphanes to seize the Bithynian throne from his father Prusias II.[18] Attalus II also aided the Romans in the Fourth Macedonian War, the final war that destroyed Macedonia as a political force.[19]
Final years (138–129 BC) edit
Not that much has survived in ancient sources of the reign of the last Attalid king, Attalus III; they tend to focus on his personal character rather than describe events during his reign. He seems to have continued to defend his kingdom militarily and to have funded various cults and religious works. He did not have any children, and bequeathed his realm to the Roman Republic in his will with his death in 133 BC.[20][21] The Romans were reluctant to take on territory in Asia Minor and did not take charge of the kingdom. A man named Aristonicus, claiming to be the illegitimate son of Eumenes II, assumed the dynastic name of Eumenes III, attempted to overturn Attalus III's will, and apparently acquired authority at least in the core Pergamese cities. In 131 or 130 BC Rome sent an army against him which was defeated. Scandalously for the time, Eumenes III was apparently willing to recruit slaves for his army and arm them. However, a second force defeated Eumenes III in 129 BC. They annexed the former kingdom of Pergamon, which became the Roman province of Asia.[22]
Art, religion, and culture edit
Two notable cults in early Pergamon were the cult of the Cabiri, a pantheon likely of original Phrygian or Thracian origin that became syncretized with Greek beliefs and mythology, and the Corybantes, worshippers of the mother goddess Cybele (possibly the Asia Minor equivalent of the Greek goddess Rhea). Various art and statues were built to them. The worship of Cybele would later intersect with Roman history. According to Livy, during the Second Punic War between Rome and Carthage (205 BC), the Sibylline Oracle told the Senate that Carthage would be defeated if the cult of the Mater Deum Magna Idaea (Magna Mater = "Great Mother") was imported into Rome. At the time, Pergamon was Rome's closest ally in the region of the Greek Eastern Mediterranean, and they sought out artifacts from the region that matched the request, where the closest equivalent goddess was Cybele. A sacred stone dedicated to Cybele under Pergamese stewardship was sent to Rome within a year (and possibly other relics), and the new cult in Rome took credit for Rome's eventual victory in 201 BC.[12][23]
Another cult of importance, if more common in the Hellenistic world, was to the goddess Athena. A temple to Athena seems to have been built around the beginning of the third century BC, while Lysimachus still acknowledged Seleucid suzerainty, and portraits of Athena appeared on coinage. A festival was also held called Panathenaia, but nothing is known of it. By 220 BC, Attalus I is recorded as holding important games in Athena's honor, and likely expanding the precincts of Athena's temple. At some point at either the end of Attalus I's rule or near the start of Eumenes II's rule, Athena was given the local title Nikephoros, "bestower of victory." Eumenes II would create a magnificent new two-story temple to Athena, refounded the festival in her honor as the festival of Nikephoria in 181 BC, and dedicated a site outside the city with the name Nikephorion. The Nikephoria would be the most important religious celebration in Pergamum in the 2nd century BC.[24]
After the Pergamese expansion in size and prestige after the Treaty of Apamea, King Eumenes II embarked upon a vast building program in Pergamon to suit the capital's new prominence. He expanded the Library of Pergamon that had probably been started by his father Attalus I, which adjoined the newly created Temple to Athena noted above. He also began construction of the great Pergamon Altar in the late 180s BC. In its interior there is a frieze depicting the life of Telephus, son of the demigod Herakles. The ruling dynasty associated Telephus with its city and claimed him as its legendary forefather and the ancestor of the Attalids. Pergamon, having entered the Greek world much later than its counterparts to the west, could not boast the same divine heritage as older city-states and so had to cultivate its place in Greek mythology retroactively. Telephus defeating the giants in the Gigantomachy was likely allegorical to the modern Attalids defeating the Galatians and Gauls in a similar battle of good vs. evil, to burnish the legitimacy of the dynasty. Similarly, the Attalids implausibly claimed a link to Alexander the Great via Pergamus, a very marginal figure who was a son of Andromache and Neoptolemus. According to the Attalids, Pergamus had founded the city of Pergamon and named it after himself, while they claimed Andromache was a distant ancestor of Olympias, Alexander's mother.[25]
Territory edit
-
Territory after the death of Lysimachus in 281 BC. Philetaerus holds just the city of Pergamon and its immediate environs.
-
Pergamon's territory in 200 BC, before the outbreak of war with the Seleucids.
-
Pergamon's expansion after Roman victory in the Roman–Seleucid War. Rome was eager to weaken the Seleucids by awarding territory to the weaker and Roman-allied Pergamon.
-
Another map of Pergamon after 188 BC, showing specific cities in Asia Minor
Dynasty of Pergamon edit
| Attalid dynasty Δυναστεία των Ατταλιδών | |
|---|---|
| Country | Kingdom of Pergamon |
| Current region | Western Asia Minor |
| Place of origin | Paphlagonia |
| Founder | Philetaerus |
| Final ruler | Attalus III |
| Final head | Eumenes III |
| Deposition | 133 BC |
Knowledge of the dates of the reigns of the Attalid kings are largely based on Strabo's Geography, with a few minor corrections by modern historians for apparent slips of the pen.[26][27]
- Philetaerus (282–263 BC)
- Eumenes I (263–241 BC)
- Attalus I Soter (241–197 BC)
- Eumenes II (197–159 BC)
- Attalus II Philadelphus (159–138 BC)
- Attalus III (138–133 BC)
- Eumenes III Aristonicus (pretender, 133–129 BC)
A notable aspect of Attalid dynastic propaganda was the unity of the family and the avoiding of petty royal squabbles between siblings that consumed their neighbors in civil wars and assassinations. Perhaps spurred by the precariousness of their royal claim, the Attalids displayed remarkable cooperation between each other. Polybius has Philip V of Macedon praise the Attalids, his enemies, for their unity as instrumental to their success as he mourns the hatred between his own sons that brought down the Antigonid Macedonian kingdom. While this dialogue was surely a literary invention, it seems accurate that the Attalid royal court avoided scandal and appealed well to the common citizenry.[28]
Attalid genealogy edit
| Attalus ∞ Boa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Philetaerus ruler of Pergamon 282–263 BC | Eumenes ∞ Satyra | Attalus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eumenes I ruler of Pergamon 263–241 BC | Philetaerus (?) | Attalus ∞ Antiochis | Eumenes (?) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Attalus I Soter king of Pergamon 241–197 BC | Apollonis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (?) | Eumenes II Soter king of Pergamon 197–159 BC | Stratonice daughter of Ariarathes IV of Cappadocia | Attalus II Philadelphos king of Pergamon 159–138 BC | Philetaerus | Athenaeus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eumenes III Aristonikos king of Pergamon 133–129 BC | Attalus III Philometor king of Pergamon 138–133 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Namesakes edit
- Attalea in Lydia, Roman city, former diocese and present Latin Catholic titular bishopric; now Yanantepe
- Attalea in Pamphylia, Roman city, former diocese and present Latin Catholic titular bishopric; now Antalya
References edit
- ^ Kosmetatou 2003, pp. 159–160.
- ^ Kosmetatou 2003, pp. 160–161.
- ^ a b Hansen 1971, pp. 17–19.
- ^ a b Kosmetatou 2003, p. 161.
- ^ Hansen 1971, pp. 28–29.
- ^ Pausanias, Description of Greece, 1.8.1
- ^ Hansen 1971, pp. 30–31.
- ^ a b Hansen 1971, pp. 34–36.
- ^ a b Hansen 1971, pp. 36–43.
- ^ Green, P., "The Road to Sellasia". Alexander to Actium, pp. 264-265
- ^ Hansen 1971, pp. 46–50.
- ^ a b Kosmetatou 2003, p. 163.
- ^ Hansen 1971, pp. 57–60.
- ^ Allen 1983, pp. 77, 86.
- ^ Attalus, Eumenes II Soter
- ^ a b c Allen 1983, pp. 76–81.
- ^ Hansen 1971, pp. 133–135.
- ^ Hansen 1971, pp. 136–139.
- ^ Allen 1983, pp. 81–83.
- ^ Allen 1983, pp. 84–85.
- ^ Shipley 2000, pp. 318–319.
- ^ Kosmetatou 2003, pp. 165–166.
- ^ Hansen 1971, pp. 50–51, 434–436.
- ^ Allen 1983, pp. 122–129.
- ^ Kosmetatou 2003, pp. 164–165, 167–168.
- ^ Allen 1983, pp. 9–11, 181–183.
- ^ Strabo, Geography, 13.4.1-2; 623-624
- ^ Kosmetatou 2003, pp. 168–170.
Bibliography edit
- Modern sources
- Allen, Reginald E. (1983). The Attalid Kingdom: A Constitutional History. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-814845-3.
- Austin, M. M., "The Attalids of Pergamum", The Hellenistic World from Alexander to the Roman Conquest: A Selection of Ancient Sources in Translation, Cambridge University Press, 2006; ISBN 978-0521535618.
- Dignas B., "Rituals and the Construction of Identity in Attalid Pergamon" in Dignas B, Smith RRR (eds.), Historical and Religious Memory in the Ancient World, Oxford University Press, 2012; ISBN 978-0199572069.
- Hansen, Esther V. (1971) [1947]. The Attalids of Pergamon. Cornell Studies in Classical Philology, Volume 36 (Second ed.). Ithaca and London: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0-8014-0615-3. LCCN 71-142284.
- Kosmetatou, Elizabeth (2003). "The Attalids of Pergamon". In Erskine, Andrew (ed.). A Companion to the Hellenistic World. Blackwell. pp. 159–174. ISBN 0-631-22537-4.
- Shipley (2000). The Greek World After Alexander, 323–30 BC (The Routledge History of the Ancient World), Routledge, first edition, 1999; ASIN: B017PNSW7M
- Ancient sources
- Livy, From the Founding of the City, Books 33–35, 42–45
- Livy, Periochae, 42.3
- Pausanias, Description of Greece. See 10.15.3
- Polybius, The Histories. See Polybius, Histories, 4.48, 5.77, 7.15 .
External links edit
- Media related to Pergamon at Wikimedia Commons
