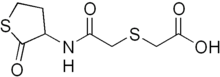 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | oral, inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 65% |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 1-3 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H11NO4S2 |
| Molar mass | 249.309 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Erdosteine is a mucolytic. Specifically it is a thiol derivative developed for the treatment of chronic obstructive bronchitis, including acute infective exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. Erdosteine contains two blocked sulfhydryl groups which are released following first-pass metabolism. The three active metabolites exhibit mucolytic and free radical scavenging activity. Erdosteine modulates mucus production and viscosity and increases mucociliary transport, thereby improving expectoration. It also exhibits inhibitory activity against the effects of free radicals produced by cigarette smoke.
Clinical studies in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease have demonstrated the efficacy and tolerability of erdosteine.[citation needed] Erdosteine 300 mg twice daily reduced cough (both frequency and severity) and sputum viscosity more quickly and more effectively than placebo and reduced the adhesivity of sputum more effectively than bromhexine 30 mg twice daily.
Co-administration of erdosteine and amoxicillin in patients with acute infective exacerbation of chronic bronchitis resulted in higher concentrations of the antibiotic in the sputum, leading to earlier and more pronounced amelioration of clinical symptoms compared with placebo.
The LD50 ranges between 3,500-5,000 mg/kg.
Adverse effects
editAdverse effects most commonly associated with Erdosteine are headache, epigastralia, nausea, and diarrhea.[1][2]
Category:Antitussives Category:Carboxylic acids Category:Thioethers Category:Thiolactones Category:Amides
- ^ Marchioni CF, Polu JM, Taytard A et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of erdosteine in patients affected by chronic bronchitis during an infective exacerbation phase and receiving amoxycillin as basic treatment (ECOBES, European Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Erdosteine Study). Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 1995;33:612-618.
- ^ Mohanty KC, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of erdosteine in patients affected by exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and receiving ciprofloxacin as basic treatment. J Clin Res 2001;4:35-39
