The Orinoco piculet (Picumnus pumilus) is a species of bird in subfamily Picumninae of the woodpecker family Picidae.[2][3] It is found in Brazil, Colombia, and possibly Venezuela.[4][5]
| Orinoco piculet | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Piciformes |
| Family: | Picidae |
| Genus: | Picumnus |
| Species: | P. pumilus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Picumnus pumilus | |
| |
Taxonomy and systematics
editThe Orinoco piculet was for a time considered a subspecies of Lafresnaye's piculet (P. lafresnayi), and they are now thought to form a superspecies.[3] It is monotypic.[2]
Description
editThe Orinoco piculet is about 9 cm (3.5 in) long and weighs 9 to 10 g (0.32 to 0.35 oz). Adult males have a dark brown cap with yellow spots on the forehead and whiter ones on the rest of it. Their face is blackish with white spots, bare gray-blue skin around the eye, and a pale stripe behind the eye. Their upperparts are brownish green. Their primaries and secondaries are brown with greenish edges and tips. The upper side of their tail is black; the innermost pair of feathers have white inner webs and the outer three pairs have a white patch near the tip. Their chin, throat, and underparts are pale yellowish to buffy white with dark brown bars except in the center of the belly. The beak is blackish and the legs gray. Adult females are identical but for whitish spots on their entire crown. Juveniles are similar to adults but duller overall, greener above, and less evenly barred below.[6]
Distribution and habitat
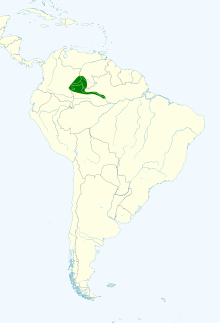
editAccording to the Clements taxonomy the Orinoco piculet is found in eastern Colombia, northwestern Brazil, and adjacent southern Venezuela's Amazonas state.[4] However, the South American Classification Committee of the American Ornithological Society has no records from Venezuela.[5] The species inhabits the edges of humid mature forest, the edges of gallery forest, and dense thickets. In elevation it mostly ranges up to 300 m (980 ft) but occurs locally as high as 500 m (1,600 ft).[6][7]
Behavior
editMovement
editAs far as is known, the Orinoco piculet is a year-round resident throughout its range.[6]
Feeding
editThe Orinoco piculet forages from the forest's lower strata to the canopy. Its diet has not been detailed but is assumed to be ants and other small insects.[6]
Breeding
editThe Orinoco piculet's breeding season is thought to include November and December but nothing else is known about its breeding biology.[6]
Vocalization
editThe Orinoco piculet's vocalizations have not been transcribed.[6][7]
Status
editThe IUCN has assessed the Orinoco piculet as being of Least Concern. It has a restricted range and its population size is not known and is believed to be decreasing. No immeditate threats have been identified.[1] It is "[p]oorly known and probably uncommon."[6]
References
edit- ^ a b BirdLife International (2016). "Orinoco Piculet Picumnus pumilus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22680700A92873502. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22680700A92873502.en. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ a b Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. (August 2022). "Woodpeckers". IOC World Bird List. v 12.2. Retrieved August 8, 2022.
- ^ a b Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 July 2022. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved July 24, 2022
- ^ a b Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, S. M. Billerman, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2022. The eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: v2022. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ retrieved November 10, 2022
- ^ a b Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 July 2022. Species Lists of Birds for South American Countries and Territories. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCCountryLists.htm retrieved July 24, 2022
- ^ a b c d e f g Winkler, H. and D. A. Christie (2020). Orinoco Piculet (Picumnus pumilus), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.oripic1.01 retrieved January 9, 2023
- ^ a b van Perlo, Ber (2009). A Field Guide to the Birds of Brazil. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 190. ISBN 978-0-19-530155-7.
Further reading
edit- Gorman, Gerard (2014). Woodpeckers of the World: A Photographic Guide. Firefly Books. pp. 46–47. ISBN 177085309X.
