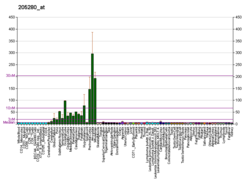
Glycine receptor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLRB gene.[5][6][7]
The inhibitory glycine receptor mediates postsynaptic inhibition in the spinal cord and other regions of the central nervous system. It is a pentameric receptor composed of alpha (GLRA1, MIM 138491; GLRA2, MIM 305990) and beta subunits.[supplied by OMIM][7]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000109738 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028020 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Milani N, Mulhardt C, Weber RG, Lichter P, Kioschis P, Poustka A, Becker CM (Oct 1998). "The human glycine receptor beta subunit gene (GLRB): structure, refined chromosomal localization, and population polymorphism". Genomics. 50 (3): 341–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5324. PMID 9676428.
- ^ Handford CA, Lynch JW, Baker E, Webb GC, Ford JH, Sutherland GR, Schofield PR (Oct 1996). "The human glycine receptor beta subunit: primary structure, functional characterisation and chromosomal localisation of the human and murine genes". Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 35 (1–2): 211–9. doi:10.1016/0169-328x(95)00218-h. PMID 8717357.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: GLRB glycine receptor, beta".
Further reading
edit- Meyer G, Kirsch J, Betz H, Langosch D (1995). "Identification of a gephyrin binding motif on the glycine receptor beta subunit". Neuron. 15 (3): 563–72. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(95)90145-0. PMID 7546736. S2CID 10164739.
- Sarang SS, Miller GW, Grant DF, Schnellmann RG (1999). "Expression and localization of the neuronal glycine receptor beta-subunit in human, rabbit and rat kidneys". Nephron. 82 (3): 254–60. doi:10.1159/000045410. PMID 10395998. S2CID 382638.
- Rees MI, Lewis TM, Kwok JB, et al. (2002). "Hyperekplexia associated with compound heterozygote mutations in the beta-subunit of the human inhibitory glycine receptor (GLRB)". Hum. Mol. Genet. 11 (7): 853–60. doi:10.1093/hmg/11.7.853. PMID 11929858.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Chen Z, Dillon GH, Huang R (2004). "Molecular determinants of proton modulation of glycine receptors". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (2): 876–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307684200. PMID 14563849.
- Burzomato V, Groot-Kormelink PJ, Sivilotti LG, Beato M (2004). "Stoichiometry of recombinant heteromeric glycine receptors revealed by a pore-lining region point mutation". Recept. Channels. 9 (6): 353–61. doi:10.3109/714041016. PMID 14698963.
- Harvey K, Duguid IC, Alldred MJ, et al. (2004). "The GDP-GTP exchange factor collybistin: an essential determinant of neuronal gephyrin clustering" (PDF). J. Neurosci. 24 (25): 5816–26. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1184-04.2004. PMC 6729214. PMID 15215304.
- Grudzinska J, Schemm R, Haeger S, et al. (2005). "The beta subunit determines the ligand binding properties of synaptic glycine receptors". Neuron. 45 (5): 727–39. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.028. PMID 15748848. S2CID 2778607.
External links
edit- GLRB+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.