The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Polio, also called poliomyelitis or infantile paralysis, was one of the most feared childhood diseases of the 20th century. Poliovirus, the causative agent, only naturally infects humans and spreads via the faecal–oral route. Most infections cause no or minor symptoms. In around 1% of cases, the virus enters the central nervous system, causing aseptic meningitis. There it can preferentially infect and destroy motor neurons, leading in 0.1–0.5% of cases to muscle weakness and acute flaccid paralysis. Spinal polio accounts for nearly 80% of paralytic cases, with asymmetric paralysis of the legs being typical; in a quarter of these cases permanent severe disability results. Bulbar involvement is rare, but in severe cases the virus can prevent breathing by affecting the phrenic nerve, so that patients require mechanical ventilation with an iron lung or similar device.
Depictions in ancient art show that the disease has existed for thousands of years. The virus was an endemic pathogen until the 1880s, when major epidemics began to occur in Europe and later the United States. Polio vaccines were developed in the 1950s and a global eradication campaign started in 1988. The annual incidence of wild-type disease fell from many hundreds of thousands to 22 in 2017, but has since resurged to a few hundreds.
Selected image
The castor bean tick, Ixodes ricinus, can transmit the tick-borne encephalitis virus. Ticks are common vectors for viruses, and other tick-borne diseases include Colorado tick fever and Crimean–Congo haemorrhagic fever.
Credit: Richard Bartz (24 April 2009)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
The history of virology is usually considered to begin in the late 19th century, when the first evidence for the existence of viruses came from experiments using filters with pores small enough to retain bacteria. Dmitry Ivanovsky showed in 1892 that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious despite having been filtered; this agent, later known as tobacco mosaic virus, was the first virus to be demonstrated. In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch showed that foot-and-mouth, an animal disease, was caused by a filterable agent. That year, Martinus Beijerinck (pictured) called the filtered infectious substance a "virus" – often considered to mark the beginning of virology.
Bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, were characterised by Frederick Twort and Félix d'Herelle in the early 20th century. In 1926, Thomas Milton Rivers defined viruses as obligate parasites. Viruses were demonstrated to be particles, rather than a fluid, by Wendell Meredith Stanley, and the invention of the electron microscope in 1931 allowed them to be visualised.
Selected outbreak
The 2001 foot-and-mouth outbreak included 2,000 cases of the disease in cattle and sheep across the UK. The source was a Northumberland farm where pigs had been fed infected meat that had not been adequately sterilised. The initial cases were reported in February. The disease was concentrated in western and northern England, southern Scotland and Wales, with Cumbria being the worst-affected area. A small outbreak occurred in the Netherlands, and there were a few cases elsewhere in Europe.
The UK outbreak was controlled by the beginning of October. Control measures included stopping livestock movement and slaughtering over 6 million cows and sheep. Public access to farmland and moorland was also restricted (pictured), greatly reducing tourism in affected areas, particularly in the Lake District. Vaccination was used in the Netherlands, but not in the UK due to concerns that vaccinated livestock could not be exported. The outbreak cost an estimated £8 billion in the UK.
Selected quotation
| “ | ...getting rid of the last 1 percent has been like trying to squeeze Jell-O to death. As the vaccination fist closes in one country, the virus bursts out in another... | ” |
—Donald McNeil on the campaign to eradicate polio
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
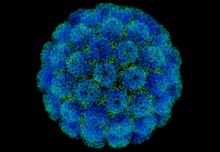
Adenoviruses are a group of non-enveloped DNA viruses that make up the Adenoviridae family. At 90–100 nm in diameter, they are the largest known viruses to lack an envelope. Unique spikes or fibres protrude from the icosahedral capsid, with knobs that bind to the receptor on the host cell. The linear double-stranded genome is 26 to 48 kb long, encodes 23 to 46 proteins, and has a 55 kDa protein attached to each end.
Adenoviruses infect a broad range of vertebrates, including humans, livestock, horses, dogs, bats and other mammals, as well as birds and reptiles, and usually cause infections of the upper respiratory tract. The virus is very stable. Transmission can occur by respiratory droplets or via faeces, with swimming pools being a common source of infection. A total of 57 serotypes, grouped into 7 species, have been found in humans; they cause a wide range of illnesses including mild respiratory infections, conjunctivitis and gastroenteritis. Some types have been associated with obesity. In people with an immunodeficiency they can cause life-threatening multi-organ disease. No antiviral treatment or vaccine is generally available; hand washing is the best way to prevent infection. Adenoviruses are an important viral vector for gene therapy. An oncolytic adenovirus has been approved in China for the treatment of head and neck cancer.
Did you know?
- ...that the elegant rice rat (pictured; top) sometimes carries a hantavirus that can cause a fatal disease in humans?
- ...that a quaranjavirus that can infect humans was discovered in 1953, but it took 60 years to classify it?
- ...that in 1918, infected crew members aboard HMS Mantua inadvertently spread the Spanish flu to Africa?
- ...that in the mid-1980s, some HIV patients pinned their hopes for survival on an experimental drug called HPA-23?
- ...that Li Zaiping and his research group were the first to sequence a viral genome in China?
Selected biography
Walter Reed (13 September 1851 – 22 November 1902) was an American physician in the U.S. Army medical corps who is known for his research on the epidemiology of yellow fever, at a time when viruses had only just been discovered.
Reed started to study yellow fever in the USA in the 1890s, showing that walking through swampy woods at night was associated with the disease, while drinking water from the Potomac River was not. In 1900, he led an army commission under the direction of George Miller Sternberg to investigate yellow fever in Cuba, where the disease was endemic. Building on Carlos Finlay's work suggesting that yellow fever was transmitted by a particular species of mosquito acting as a vector, Reed and co-workers confirmed Finlay's results, and also disproved the popular idea that the disease was transmitted by contaminated objects, such as clothing or bedding. The experiments involved the deliberate infection of human volunteers, several of whom died of yellow fever, and Reed pioneered the concept of medical consent.
In this month
May 1955: First issue of Virology; first English-language journal dedicated to virology
4 May 1984: HTLV-III, later HIV, identified as the cause of AIDS by Robert Gallo and coworkers
5 May 1939: First electron micrographs of tobacco mosaic virus taken by Helmut Ruska and coworkers
5 May 1983: Structure of influenza neuraminidase solved by Jose Varghese, Graeme Laver and Peter Colman
8 May 1980: WHO announced formally the global eradication of smallpox
11 May 1978: SV40 sequenced by Walter Fiers and coworkers
12 May 1972: Gene for bacteriophage MS2 coat protein is sequenced by Walter Fiers and coworkers, the first gene to be completely sequenced
13 May 2011: Boceprevir approved for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, the first direct-acting antiviral for HCV
14 May 1796: Edward Jenner inoculated James Phipps (pictured) with cowpox
15/16 May 1969: Death of Robert Rayford, the earliest confirmed case of AIDS outside Africa
18 May 1998: First World AIDS Vaccine Day
20 May 1983: Isolation of the retrovirus LAV, later HIV, by Luc Montagnier, Françoise Barré-Sinoussi and coworkers
23 May 2011: Telaprevir approved for the treatment of chronic HCV infection
25 May 2011: WHO declared rinderpest eradicated
31 May 1937: First results in humans from the 17D vaccine for yellow fever published by Max Theiler and Hugh H. Smith
Selected intervention
Influenza vaccines include live attenuated and inactivated forms. Inactivated vaccines contain three or four different viral strains selected by the World Health Organization to cover influenza A H1N1 and H3N2, as well as influenza B, and are usually administered by intramuscular injection. The live attenuated influenza vaccine contains a cold-adapted strain and is given as a nasal spray. Most influenza vaccine strains are cultivated in fertilised chicken eggs (pictured), a technique developed in the 1950s; others are grown in cell cultures, and some vaccines contain recombinant proteins. Annual vaccination is recommended for high-risk groups and, in some countries, for all those over six months. As the influenza virus changes rapidly by antigenic drift, new versions of the vaccine are developed twice a year, which differ in effectiveness depending on how well they match the circulating strains. Despite considerable research effort for decades, no effective universal influenza vaccine has been identified. A 2018 meta-analysis found that vaccination in healthy adults decreased confirmed cases of influenza from about 2.4% to 1.1%. However, the effectiveness is uncertain in those over 65 years old, one of the groups at highest risk of serious complications.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus