
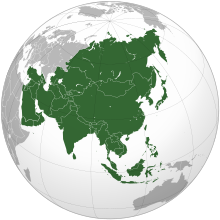
 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleQuneitra (also Al Qunaytirah, Qunaitira, or Kuneitra; Arabic: ٱلْقُنَيْطِرَة or ٱلْقُنَيطْرَة, al-Qunayṭrah or al-Qunayṭirah pronounced [æl qʊˈneɪ̯tˁ(ɨ)rɑ]) is the largely destroyed and abandoned capital of the Quneitra Governorate in south-western Syria. It is situated in a high valley in the Golan Heights at 1,010 metres (3,313 feet) above sea level. Since 1974, pursuant to United Nations Security Council Resolution 350 and the Agreement on Disengagement between Israel and Syria, the city is inside the UN-patrolled buffer zone. Quneitra was founded in the Ottoman era as a way station on the caravan route to Damascus and subsequently became a garrison town of some 20,000 people. In 1946, it became part of the independent Syrian Republic within the Riff Dimashq Governorate and in 1964 became the capital of the split Quneitra Governorate. On 10 June 1967, the last day of the Six-Day War, Quneitra came under Israeli control. It was briefly recaptured by Syria during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, but Israel regained control in its subsequent counter-offensive. The city was almost completely destroyed by Israel before it withdrew in June 1974. Syria later refused to rebuild the city and actively discouraged resettlement in the area. Israel was heavily criticized by the United Nations for the city's destruction, while Israel has also criticized Syria for not rebuilding Quneitra. (Full article...)Selected Country East Timor, also known as Timor-Leste, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor - of which the western half is administered by Indonesia - the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-western half, and the minor islands of Atauro and Jaco. Australia is the country's southern neighbour, separated by the Timor Sea. The country's size is 14,950 square kilometres (5,770 sq mi). Dili, on the north coast of Timor, is its capital and largest city. East Timor was settled by waves of Austronesian and Papuan peoples, which are reflected in the country's diverse mix of cultures and languages reflecting its links to Southeast Asia and Melanesia despite its small area. East Timor came under Portuguese influence in the sixteenth century, remaining a Portuguese colony until 1975. Internal conflict preceded a unilateral declaration of independence and an Indonesian invasion and annexation. Resistance continued throughout Indonesian rule, and, in 1999, a United Nations–sponsored act of self-determination led to Indonesia relinquishing control of the territory. On 20 May 2002, as Timor-Leste, it became the first new sovereign state of the 21st century. That same year, relations with Indonesia were established and normalized, with Indonesia also supporting East Timor's accession into ASEAN. (Full article...)Featured biographyRani Mukerji (pronounced [raːni mʊkʰərdʒi]; born 21 March 1978) is an Indian actress who works in Hindi films. Noted for her versatility, she is the recipient of multiple accolades, including eight Filmfare Awards. Mukerji has featured in listings of the leading and highest-paid actresses of the 2000s. Born into the Mukherjee-Samarth family, Mukerji dabbled with acting as a teenager by starring in her father Ram Mukherjee's Bengali-language film Biyer Phool and in the social drama Raja Ki Aayegi Baaraat (both 1996). Mukerji had her first commercial success with the action film Ghulam and breakthrough with the romance Kuch Kuch Hota Hai (both 1998). Following a brief setback, the year 2002 marked a turning point for her when she was cast by Yash Raj Films as the star of the drama Saathiya. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureThe Darvaza gas crater, also called the "Door to Hell" or the "Gates of Hell" by locals, a crater of natural gas that has been burning since 1971, is located in the Karakum Desert in Turkmenistan. The crater is a major tourist attraction, with hundreds of visitors arriving each year.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
Birds and flowers of the four seasons (紙本墨画花鳥図, shihon bokuga kachōzu), part of the Paintings on room partitions in the abbot's quarters (hōjō) (方丈障壁画, hōjō shōhekiga) of Jukō-in (聚光院) of Daitoku-ji (大徳寺), Kyoto, Japan. Ink on paper. This picture shows four of 16 panels on fusuma (sliding doors) in the ritual room (室中). The paintings have been designated as National Treasures of Japan in the category paintings. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |






























































































