
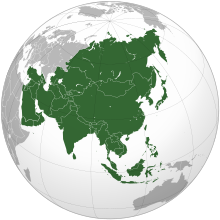
 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleThe law school of Berytus (also known as the law school of Beirut) was a center for the study of Roman law in classical antiquity located in Berytus (modern-day Beirut, Lebanon). It flourished under the patronage of the Roman emperors and functioned as the Roman Empire's preeminent center of jurisprudence until its destruction in AD 551. The law schools of the Roman Empire established organized repositories of imperial constitutions and institutionalized the study and practice of jurisprudence to relieve the busy imperial courts. The archiving of imperial constitutions facilitated the task of jurists in referring to legal precedents. The origins of the law school of Beirut are obscure, but probably it was under Augustus in the first century. The earliest written mention of the school dates to 238–239 AD, when its reputation had already been established. The school attracted young, affluent Roman citizens, and its professors made major contributions to the Codex of Justinian. The school achieved such wide recognition throughout the Empire that Beirut was known as the "Mother of Laws". Beirut was one of the few schools allowed to continue teaching jurisprudence when Byzantine emperor Justinian I shut down other provincial law schools. (Full article...)Selected Country Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the second-largest Muslim population as of 2023. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and financial centre. Pakistan is the 33rd-largest country by area and the ninth-largest in Asia. Bounded by the Arabian Sea on the south, the Gulf of Oman on the southwest, and the Sir Creek on the southeast, it shares land borders with India to the east; Afghanistan to the west; Iran to the southwest; and China to the northeast. It shares a maritime border with Oman in the Gulf of Oman, and is separated from Tajikistan in the northwest by Afghanistan's narrow Wakhan Corridor. Pakistan is the site of several ancient cultures, including the 8,500-year-old Neolithic site of Mehrgarh in Balochistan, the Indus Valley civilisation of the Bronze Age, and the ancient Gandhara civilisation. The regions that compose the modern state of Pakistan were the realm of multiple empires and dynasties, including the Achaemenid, the Maurya, the Kushan, the Gupta; the Umayyad Caliphate in its southern regions, the Samma, the Hindu Shahis, the Shah Miris, the Ghaznavids, the Delhi Sultanate, the Mughals, and most recently, the British Raj from 1858 to 1947. (Full article...)Featured biographyZhang Heng (Chinese: 張衡; AD 78–139), formerly romanized Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Han dynasty. Educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, he achieved success as an astronomer, mathematician, seismologist, hydraulic engineer, inventor, geographer, cartographer, ethnographer, artist, poet, philosopher, politician, and literary scholar. Zhang Heng began his career as a minor civil servant in Nanyang. Eventually, he became Chief Astronomer, Prefect of the Majors for Official Carriages, and then Palace Attendant at the imperial court. His uncompromising stance on historical and calendrical issues led to his becoming a controversial figure, preventing him from rising to the status of Grand Historian. His political rivalry with the palace eunuchs during the reign of Emperor Shun (r. 125–144) led to his decision to retire from the central court to serve as an administrator of Hejian Kingdom in present-day Hebei. Zhang returned home to Nanyang for a short time, before being recalled to serve in the capital once more in 138. He died there a year later, in 139. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureUtamaro's Ase o fuku onna ("Woman wiping sweat"), an example of bijinga (literally, "pictures of beautiful people"), a central theme of the ukiyo-e genre of Japanese art. Nearly all ukiyo-e artists produced bijinga, but a few, including Utamaro, Suzuki Harunobu, Toyohara Chikanobu, and Torii Kiyonaga, are widely regarded as the greatest innovators and masters of the form.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
A panoramic view of the Hiroshima Peace Memorial, the site of the first atomic bomb to be used in warfare on August 6, 1945, during the final stages of World War II. Over 70,000 people were killed immediately, and another 70,000 suffered fatal injuries from the radiation, after the U.S. Army Air Force bomber Enola Gay dropped the bomb, codenamed "Little Boy". The Genbaku ("A-bomb") Dome (center) was directly beneath the blast, but managed to survive mostly intact. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |






























































































