The yellow-billed cacique (Amblycercus holosericeus) is a species of cacique in the family Icteridae. It belongs to the monotypic genus Amblycercus.[2] There is some question as to whether or not it is a true cacique.[3][4]
| Yellow-billed cacique | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Icteridae |
| Genus: | Amblycercus Cabanis, 1851 |
| Species: | A. holosericeus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Amblycercus holosericeus (Deppe, 1830)
| |
| |
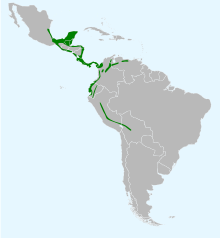
| Range of Amblycercus holosericeus | |
The plumage is entirely black. The legs and feet are dark gray. The eye is yellow or yellow-orange. The bill is yellow with a gray tinge. Measures 23 cm (9.1 in) long.[5]
It is found in Belize, Bolivia, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, and Venezuela.
Three subspecies are known:[6]
- A. h. holosericeus – (Deppe, 1830): nominate, found from southeastern Mexico to northwestern Colombia
- A. h. flavirostris – Chapman, 1915: found from western Colombia to northern Peru
- A. h. australis – Chapman, 1919: found in northern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela to eastern Peru and northern Bolivia
Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, and heavily degraded former forest.[1]
The yellow-billed cacique feeds on insects and other invertebrates, as well as some fruit. It uses a pecking technique similar to that of a woodpecker to gain access to the interior of branches and bamboo. In some areas, this species is a bamboo specialist, while in other areas, it feeds from a variety of vegetation.[3]
In the spring, the yellow-billed cacique builds a sturdy cup-shaped nest, which is unusual for its family, who tend to build hanging woven nests.[3]
References
edit- ^ a b BirdLife International (2020). "Amblycercus holosericeus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22724065A136772337. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22724065A136772337.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ "ITIS Report: Amblycercus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 19 August 2012.
- ^ a b c Ramos-Ordoñez, M.F.; Rodríguez-Flores, C.; Soberanes-González, C.; Arizmendi, M.C. (2010). Schulenberg, T.S. (ed.). "Yellow-billed Cacique (Amblycercus holosericeus)". Neotropical Birds Online. Ithaca: Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ "Yellow-billed Cacique (Amblycercus holosericeus)". The Internet Bird Collection. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ Garrigues, Richard; Dean, Robert (2007). The Birds of Costa Rica. Ithaca: Zona Tropical/Comstock/Cornell University Press. p. 320. ISBN 978-0-8014-7373-9.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David (eds.). "IOC World Bird List". International Ornithological Union. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
Further reading
edit- Skutch, Alexander F. (1954). "Chisel-billed cacique" (PDF). Life Histories of Central American Birds. Pacific Coast Avifauna, Number 31. Berkeley, California: Cooper Ornithological Society. pp. 281–286.
External links
edit- Yellow-billed cacique image at [The Animal Diversity Web (online) http://animaldiversity.org]
- BirdLife species factsheet for Amblycercus holosericeus
- "Amblycercus holosericeus". Avibase.
- Yellow-billed cacique photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Amblycercus holosericeus at IUCN Red List maps
- Audio recordings of Yellow-billed cacique on Xeno-canto.
- Amblycercus holosericeus in Field Guide: Birds of the World on Flickr
