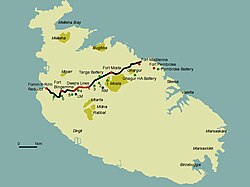
The Victoria Lines, originally known as the North West Front, are a line of fortifications that spans 12 kilometres along the width of Malta, dividing the north of the island from the more heavily populated south.[1]
| Victoria Lines | |
|---|---|
| Northern Malta (Rabat, Mġarr, Mosta, Naxxar and Għargħur) | |
 | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 35°54′12.7″N 14°22′43.5″E / 35.903528°N 14.378750°E |
| Type | Defensive line |
| Site information | |
| Condition | Partially intact |
| Website | www.victorialinesmalta.com |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1875–1899 |
| Built by | British Empire |
| In use | 1880s–1907[a] |
| Materials | Limestone |
Location
editThe Victoria Lines run along a natural geographical barrier known as the Great Fault, from Madliena in the east, through the limits of the town of Mosta in the centre of the island, to Binġemma and the limits of Rabat, on the west coast. The complex network of linear fortifications known collectively as the Victoria Lines, that cut across the width of the island north of the old capital of Mdina, was a unique monument of military architecture.
Background
editWhen built by the British military in the late 19th century, the line was designed to present a physical barrier to invading forces landing in the north of Malta, intent on attacking the harbour installations, so vital for the maintenance of the British fleet, their source of power in the Mediterranean. Although never tested in battle, this system of defences, spanning some 12 km of land and combining different types of fortifications—forts, batteries, entrenchments, stop-walls, infantry lines, searchlight emplacements and howitzer positions—constituted a unique ensemble of varied military elements all brought together to enforce the strategy adopted by the British for the defence of Malta in the latter half of the 19th century, a singular solution which exploited the defensive advantages of geography and technology as no other work of fortifications does in the Maltese islands.[2]
The Victoria Lines owe their origin to a combination of international events and the military realities of the time. The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 highlighted the importance of the Maltese islands.[2]
Beginnings
editBy 1872, the coastal works had progressed considerably, but the question of landward defences remained unsettled. Although the girdle of forts proposed by Colonel Jervois in 1866 would have considerably enhanced the defence of the harbour area, other factors had cropped up that rendered the scheme particularly difficult to implement, particularly the creation of suburbs. Another proposal, put forward by Col. Mann RE, was to take up a position well forward of the original.
The chosen position was the ridge of commanding ground north of the old City of Mdina, cutting transversely across the width of the island at a distance varying from 4 to 7 miles from Valletta. There, it was believed, a few detached forts could cut off all the westerly portion of the island containing good bays and facilities for landing. At the same time, the proposed line of forts retained the resources of the greater part of the country and the water on the side of the defenders; whereas the ground required for the building of the fortifications could be had far more cheaply than that in the vicinity of Valletta. Col. Mann estimated that the entire cost of the land and works of the new project would amount to £200,000, much less than would have been required to implement Jervois' scheme of detached forts.
This new defensive strategy was one which sought to seal off all the area around the Grand Harbour within an extended box-like perimeter, with the detached forts on the line of the Great Fault forming the north-west boundary, the cliffs to the south forming a natural, inaccessible barrier; while the north and east sides were to be defended by a line of coastal forts and batteries. In a way, the use of the Great Fault for defensive purposes was not an altogether original idea, for it had already been put forward by the Order of Saint John in the early decades of the 18th century, when they realized that they did not have the necessary manpower to defend the whole island. The Order had built a few infantry entrenchments at strategic places along the general line of the fault, namely, the Falca Lines and San Pawl tat-Tarġa, Naxxar. In fact, the use of parts of the natural escarpment for defensive purposes can be traced back even further, as illustrated by Nadur Tower at Bingemma (17th century), the Torri Falca (16th century) and the remains of a Bronze Age fortified citadel which possibly occupied the site of Fort Mosta.[3]
Building
editIn 1873, the Defence Committee approved Adye’s defensive strategy and recommended the improvement of the already strong position between the Bingemma Hills and the heights above St. George’s Bay. Work on what was originally to be called the North-West Front began in 1875 with construction of a string of isolated forts and batteries, designed to stiffen the escarpment. Three forts were to be built along the position, at Bingemma, Madliena and Mosta, (designed to cover the western and eastern extremities and the centre of the front, respectively). The first to be built was Fort Bingemma. By 1878, work had still not commenced on the other two and the entrenched position at Dwerja; all of these were to be completed within the £200,000 budget. General Simmons recommended that the old Knights’ entrenchments located along the line of the escarpment at Tarġa and Naxxar were to be restored and incorporated into the defences. He also recommended that good communication roads should be formed in the rear of the lines and that those that already existed be improved. The fortifications of Mdina, the Island’s old capital, were to be considered as falling within the defensive system.
The forts on the defensive line were designed with a dual land/coastal defence role in mind, particularly the ones at the extremities but, due to the topography in the northern part of the island, there were areas of dead ground along the coast and inland approaches which could not be properly covered by the guns in the main forts. As a result, it was decided that new works should be built between Forts Mosta and Bingemma and emplacements for guns placed in them. It was also considered advisable to have new emplacements for guns built to the left of Fort Madalena and in the area between it and Fort Pembroke. The latter fort was built on the eastern littoral, below and to the rear of Fort Madalena, in order to control the gap caused by the accessible shoreline leading towards Valletta. Gun batteries were eventually proposed at Tarġa, Għargħur and San Giovanni. Plans for these works were drawn up but only the one at San Giovanni was actually built and armed, while the two at Għargħur were never constructed and that at Tarġa, although actually built, was never armed.
Limitations
editBy 1888, the line of the cliffs formed by the great geological fault and the works which had been constructed along its length from Fort Bingemma on the left to Fort Madalena on the right constituted, in the words of Nicholson and Goodenough, "a military position of great strength". The main defects inherent in the defensive position were the extremities where the high ground descended towards the shore, leaving wide gaps through which enemy forces could by-pass the whole position. Particularly weak in this respect was the western extremity. There, a considerable interval existed between Fort Bingemma and the sea. Military manoeuvres held in the area revealed that it was possible for troops to land in Fomm ir-Riħ Bay and gain the rear of the fortified line undetected from the existing works. To counter this threat, recommendations were made for the construction of two epaulements for a movable armament of quick-firing or field guns, the construction of blockhouses, the improvement of the wall which closed the head of the deep valley to the south of Fort Bingemma and the strengthening of the line of cliffs by scarping in places. It was also suggested that the existing farmhouses in the area be made defensible.
There were even suggestions for the reconstruction and re-utilization of the old Hospitaller lines at ta' Falca and Naxxar, but only the latter was put to use, mainly because these commanded the approaches to the village of Naxxar, described as a position of great importance, in the event of a landing in St. Paul's Bay.
A serious shortcoming of the North West Front defences was the lack of barrack accommodation for the troops who were required to man and defend the works. The lines extended six miles and the accommodation provided in the forts was rather scanty. Consequently, it was considered necessary to build new barracks capable of accommodating a regiment (PRO MPH 234) and later a full battalion of infantry, and a new site was chosen to the rear of the Dwerja Lines, at Mtarfa. Although initially designed as a series of detached strong-points, the fortifications along the North West Front were eventually linked together by a continuous infantry line and the whole complex, by then nearing completion, was christened the Victoria Lines in order to commemorate the Diamond Jubilee of Queen Victoria in 1897. The long stretches of infantry lines linking the various strong-points—consisting in most places of a simple masonry parapet—were completed on 6 November 1899.[4]
Other changes
editThe line of the intervening stretches followed the configuration of the crest of the ridge, along the contours of the escarpment. The nature of the wall varied greatly along its length but basically consisted of a sandwich-type construction with an outer and inner revetment, bonded at regular intervals and filled in with terreplein. The average height of the parapet was about five feet (1.5 metres). The walls were frequently topped by loopholes, of which only a very few sections have survived. In places, the debris from scarping was dumped in front of the wall to help create a glacis and ditch. In places, the rocky ground immediately behind the parapet was carved out to provide a walkway or patrol path along the length of the line. A number of valleys interrupted the line of the natural fault and, at such places, the continuation of the defensive perimeter was only permitted through the construction of shallow, defensible masonry bridges, as can still be seen today at Wied il-Faħam near Fort Madalena, Wied Anglu and Bingemma Gap. Other bridges, now demolished, existed at Mosta Ravine and Wied Filip.
During the last phase of their development, the Victoria Lines were strengthened by a number of batteries and additional fortifications. An infantry redoubt was built at the western extremity of the front at Fomm ir-Riħ and equipped with emplacements for Maxim machine guns. In 1897 a High Angle Battery was built well to the rear of the defensive lines at Għargħur and another seven howitzer batteries, each consisting of four emplacements for field guns protected by earthen traverses, were built close to the rear of the defensive line. Searchlight emplacements were built at il-Kunċizzjoni and Wied il-Faħam.
Aftermath
editMilitary training exercises staged in May 1900 revealed that the Victoria Lines were of dubious defensive value. With the exception of the coastal forts, by 1907 they were abandoned altogether. During World War Two, a joint Germans-Italian invasion seemed likely so the lines were rehabilitated and new guard posts built along them as a second line of defence to the coastal defences. Again the lines were untested.[2] Fort Mosta is still in use as an ammunitions depot, while Fort Madalena is still used by the Communications Information Systems Company of the AFM.
In 1998 the Government of Malta submitted the Victoria Lines to UNESCO for consideration as a World Heritage Site.[5]
Large parts of the fortification walls have collapsed, although some parts in the countryside remain intact and in general the Victoria Lines have fallen into obscurity. The Maltese Tourism Authority is proposing that by the end of 2019 two trails along the Lines will become Malta’s inaugural national walkway.[2]
References
edit- ^ Spiteri, Stephen C. "The Victoria Lines". MilitaryArchitecture.com. Archived from the original on 4 August 2017. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d Alexander, Adam (August 30, 2019). "The 'Great Wall' of Malta". BBC - Travel. Retrieved September 4, 2019.
- ^ Spiteri, Stephen C. (22 October 2011). "Fort Mosta". MilitaryArchitecture.com. Archived from the original on 3 June 2017. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ Vella, Leslie (24 October 2010). "The Great Wall of Malta". Malta Inside Out. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ^ "Victoria Lines Fortifications". UNESCO World Heritage Site Tentative List. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
Notes
- ^ Fort Mosta and Fort Madalena are still in use by the Armed Forces of Malta.
Further reading
edit- Spiteri, Stephen C. (2017). A Visual Guide to the Fortifications of Malta. Photography: Oliver Gatt. BDL Books. ISBN 978-99957-67-38-9.