This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2014) |
This article needs attention from an expert in medicine. See the talk page for details. (February 2015) |
| EVLeDO/RICE | |
|---|---|
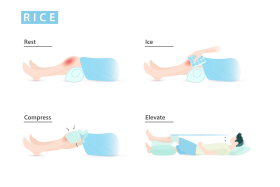 Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation |
RICE is a mnemonic acronym for the four elements of a treatment regimen that was once recommended for soft tissue injuries: rest, ice, compression, and elevation.[1][2] It is considered a first-aid treatment rather than a cure and aims to control inflammation.[3] The protocol was often used to treat sprains, strains, cuts, bruises, and other similar injuries [4]
The mnemonic was introduced by Dr. Gabe Mirkin in 1978.[5] He took back his support of this regimen in 2014 after learning of the role of inflammation in the healing process.[6]
The implementation of RICE for soft tissue injuries should be considered on a case-by-case basis, as there is not enough research on the efficacy of RICE to make general recommendations.[3] There are different variations of the protocol, which may emphasize additional protective actions. However, these variations similarly lack sufficient evidence to be broadly recommended.[7]
Primary four terms edit
Rest edit
Rest was intended to reduce inflammation and to prevent further injury.[3] Blood supply is an important component of inflammation. By resting an injury, blood flow to the area is reduced, which reduces the swelling and pain associated with inflammation.[8] The early stages of healing involve microscopic scaffolding that is built upon to repair an injury. These scaffolds are relatively weak until reinforced by later stages of healing.[9] Early and aggressive movement could potentially disrupt this process, delaying healing or worsen an existing injury.[3]
Although rest may provide some benefit immediately after an injury, early return to movement has been shown to be better at reducing pain and encouraging healing.[10]
Ice edit
Ice being applied to a leg propped on a pillow for elevation |
Ice was meant to reduce swelling and inflammation by vasoconstriction. However, adequate blood flow is essential in allowing cells and signals from our immune system to reach injured areas. By reducing the entry of these cells and signals to the injury, healing can be delayed, or possibly inhibited.[11][12][13][14]
The current research supports the role of ice in temporary pain relief, but there is little evidence supporting the use of ice to aid in healing, or even swelling reduction.[13] Further research is needed to further understand how ice should be applied. At this time, due to the lack of evidence, there is no consensus on the ideal temperature ranges, time frames, application methods, or patient populations when using ice on a soft tissue injury.[11]
Compression edit
Compression refers to wearing bandages, stockings, braces, or similar devices to apply pressure over a localized area to reduce swelling and stop bleeding.[3] The increased pressure pushes fluids into the blood vessels to drain away from the area. [13] The effects of compression on swelling reduction are temporary and gravity-dependent.[15]
Although studies have demonstrated the effects of compression on swelling, there is little evidence to support the use of compression to promote healing.[7][13] When considering the use of compression, the evidence supports the use of elastic bandages with Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) to reduce swelling and pain, while improving range of motion.[3]
Elevation edit
Elevation refers to keeping an injury above the level of the heart, such as propping up a leg with pillows. The goal is to reduce swelling by using gravity to encourage blood return from the swollen area back to the heart.[15] The reduction in swelling could improve pain by relieving pressure from the area. The effects of elevation on swelling have been shown to be temporary, as swelling often returns when the injured area is no longer elevated.[15]
However, at this time there is little evidence to support that elevation promotes healing.[3]
Current support edit
Dr. Gabe Mirkin has since recanted his support for the regimen.[6] In 2015 he wrote:
Coaches have used my 'RICE' guideline for decades, but now it appears that both ice and complete rest may delay healing, instead of helping. In a recent study, athletes were told to exercise so intensely that they developed severe muscle damage that caused extensive muscle soreness. Although cooling delayed swelling, it did not hasten recovery from this muscle damage.
Rest may play a role immediately after an injury, but the evidence supports early mobilization to promote healing.[7] Due to inhibitory effects of ice on mounting a proper inflammatory response, a protocol including extended applications of ice could delay the body's attempt at healing.[11][14] While it is unclear what the effects of elevation and compression are on the healing process, reduction of swelling is a transient effect and returns when the injury is returned to a lower, gravity-dependent position.[3][15]
Currently, the RICE protocol is no longer generally recommended and as given way to other acronyms for treating soft tissue injuries. Most recently, in 2019 the mnemonic "PEACE & LOVE" was coined by Blaise Dubois. The PEACE component stands for protection, elevation, avoid anti-inflammatories, compression, and education. It guides the treatment of acute soft tissue injuries. LOVE stands for load, optimism, vascularization, and exercise. It guides the treatment for the subchronic and chronic management of soft tissue injuries.[16]
Variations edit
Variations of the acronym are sometimes used to emphasize additional steps that should be taken. These include:
- "PRICE" – Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation[17][18]
- "POLICE" – Protection, Optimal Loading, Ice, Compression, and Elevation[7]
- "PEACE and LOVE" – Protection, Elevation, Avoid Anti-inflammatories, Compression, Education & Load, Optimism, Vascularization, Exercise[16]
See also edit
References edit
- ^ "R.I.C.E - Best for Acute Injuries". Retrieved 15 August 2007.
- ^ "Sports Medicine Advisor 2005.4: RICE: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation for Injuries". Archived from the original on 11 September 2007. Retrieved 15 August 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f g h van den Bekerom MP, Struijs PA, Blankevoort L, Welling L, van Dijk CN, Kerkhoffs GM (2012). "What is the evidence for rest, ice, compression, and elevation therapy in the treatment of ankle sprains in adults?". Journal of Athletic Training. 47 (4): 435–43. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-47.4.14. PMC 3396304. PMID 22889660.
- ^ Bayer, Monika L.; Mackey, Abigail; Magnusson, S. Peter; Krogsgaard, Michael R.; Kjær, Michael (18 February 2019). "[Treatment of acute muscle injuries]". Ugeskrift for Laeger. 181 (8): V11180753. ISSN 1603-6824. PMID 30821238.
- ^ Mirkin, G. (1981). Sports-medicine book. Boston: Little, Brown. ISBN 978-0316574365.
- ^ a b Mirkin, Dr Gabe. "Why Ice Delays Recovery | Dr. Gabe Mirkin on Health". Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ a b c d C M, Bleakley (2012). "PRICE needs updating, should we call the POLICE?". British Journal of Sports Medicine. 46 (4). BMJ: 220–221. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2011-090297. PMID 21903616. S2CID 41536790. Retrieved 5 March 2012.
- ^ Pober, JS; Sessa, WC (23 October 2014). "Inflammation and the blood microvascular system". Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology. 7 (1): a016345. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a016345. PMID 25384307.
- ^ Wallace, Heather A.; Basehore, Brandon M.; Zito, Patrick M. (2022), "Wound Healing Phases", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 29262065, retrieved 5 December 2022
- ^ Tiemstra, Jeffrey D. (15 June 2012). "Update on acute ankle sprains". American Family Physician. 85 (12): 1170–1176. ISSN 1532-0650. PMID 22962897.
- ^ a b c Wang, Zi-Ru; Ni, Guo-Xin (16 June 2021). "Is it time to put traditional cold therapy in rehabilitation of soft-tissue injuries out to pasture?". World Journal of Clinical Cases. 9 (17): 4116–4122. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4116. ISSN 2307-8960. PMC 8173427. PMID 34141774.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bleakley C, McDonough S, MacAuley D (1 January 2004). "The Use of Ice in the Treatment of Acute Soft-Tissue Injury: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 32 (1): 251–261. doi:10.1177/0363546503260757. ISSN 0363-5465. PMID 14754753. S2CID 23999521.
- ^ a b c d Scialoia, Domenic; Swartzendruber, Adam J. (30 October 2020). "The R.I.C.E Protocol is a MYTH: A Review and Recommendations". The Sport Journal. 24.
- ^ a b Takagi, Ryo; Fujita, Naoto; Arakawa, Takamitsu; Kawada, Shigeo; Ishii, Naokata; Miki, Akinori (1 February 2011). "Influence of icing on muscle regeneration after crush injury to skeletal muscles in rats". Journal of Applied Physiology (Bethesda, Md.: 1985). 110 (2): 382–388. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01187.2010. ISSN 1522-1601. PMID 21164157.
- ^ a b c d Tsang, Kavin K. W.; Hertel, Jay; Denegar, Craig R. (October–December 2003). "Volume Decreases After Elevation and Intermittent Compression of Postacute Ankle Sprains Are Negated by Gravity-Dependent Positioning". Journal of Athletic Training. 38 (4): 320–324. ISSN 1938-162X. PMC 314391. PMID 14737214.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - ^ a b Dubois, Blaise; Esculier, Jean-Francois (3 August 2019). "Soft-tissue injuries simply need PEACE and LOVE". British Journal of Sports Medicine. 54 (2): 72–73. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2019-101253. ISSN 1473-0480. PMID 31377722.
- ^ Ivins D (2006). "Acute ankle sprain: an update". American Family Physician. 74 (10): 1714–20. PMID 17137000.
- ^ Bleakley CM, O'Connor S, Tully MA, Rocke LG, Macauley DC, McDonough SM (2007). "The PRICE study (Protection Rest Ice Compression Elevation): design of a randomised controlled trial comparing standard versus cryokinetic ice applications in the management of acute ankle sprain [ISRCTN13903946]". BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 8: 125. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-8-125. PMC 2228299. PMID 18093299.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
Category:Medical treatments Category:Medical mnemonics Category:Mnemonic acronyms