Tin(II) fluoride, commonly referred to commercially as stannous fluoride[1][2] (from Latin stannum, 'tin'), is a chemical compound with the formula SnF2. It is a colourless solid used as an ingredient in toothpastes.
 Sn2+; F−
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tin(II) fluoride
| |
| Other names
Stannous fluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.090 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3288 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| SnF2 | |
| Molar mass | 156.69 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 4.57 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K) |
| Boiling point | 850 °C (1,560 °F; 1,120 K) |
| 31 g/100 mL (0 °C); 35 g/100 mL (20 °C); 78.5 g/100 mL (106 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in KOH, KF; negligible in ethanol, ether, chloroform |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mS48 | |
| C2/c, No. 15 | |
| Pharmacology | |
| A01AA04 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0860 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Tin(II) chloride, Tin(II) bromide, Tin(II) iodide |
Other cations
|
Difluorocarbene, Carbon tetrafluoride, Difluorosilylene, Silicon tetrafluoride, Difluorogermylene, Germanium tetrafluoride, Tin tetrafluoride, Lead(II) fluoride, Lead(IV) fluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Oral health benefits
editStannous fluoride is an alternative to sodium fluoride for the prevention of cavities (tooth decay). It was first released commercially in 1956, in Crest toothpaste. It was discovered and developed by Joseph Muhler and William Nebergall. In recognition of their innovation, they were inducted into the Inventor's Hall of Fame.[1]
The fluoride in stannous fluoride helps to convert the calcium mineral hydroxyapatite in teeth into fluorapatite, which makes tooth enamel more resistant to bacteria-generated acid attacks.[3] The calcium present in plaque and saliva reacts with fluoride to form calcium fluoride on the tooth surface; over time, this calcium fluoride dissolves to allow calcium and fluoride ions to interact with the tooth and form fluoride-containing apatite within the tooth structure.[4] This chemical reaction inhibits demineralisation and can promote remineralisation of tooth decay. The resulting fluoride-containing apatite is more insoluble, and more resistant to acid and tooth decay.[4]
In addition to fluoride, the stannous ion has benefits for oral health when incorporated in a toothpaste. At similar fluoride concentrations, toothpastes containing stannous fluoride have been shown to be more effective than toothpastes containing sodium fluoride for reducing the incidence of dental caries and dental erosion,[5][6][7][8][9] as well as reducing gingivitis.[10][11][12][13][14] Some stannous fluoride-containing toothpastes also contain ingredients that allow for better stain removal.[15][16] Stabilised stannous fluoride formulations allow for greater bioavailability of the stannous and fluoride ion, increasing their oral health benefits.[17][18] A systematic review revealed stabilised stannous fluoride-containing toothpastes had a positive effect on the reduction of plaque, gingivitis and staining, with a significant reduction in calculus and halitosis (bad breath) compared to other toothpastes.[16] A specific formulation of stabilised stannous fluoride toothpastes has shown superior protection against dental erosion and dentine hypersensitivity compared to other fluoride-containing and fluoride-free toothpastes.[19]
Stannous fluoride was once used under the trade name Fluoristan in the original formulation of the toothpaste brand Crest, though it was later replaced with sodium monofluorophosphate under the trade name Fluoristat. Stabilised stannous fluoride is now the active ingredient in Crest/Oral B Pro-Health brand toothpaste. Although concerns have been previously raised that stannous fluoride may cause tooth staining, this can be avoided by proper brushing and by using a stabilised stannous fluoride toothpaste.[15][16] Any stannous fluoride staining that occurs due to improper brushing is not permanent, and Crest/Oral B Pro-Health states that its particular formulation is resistant to staining.
Production
editSnF2 can be prepared by evaporating a solution of SnO in 40% HF.[20]
- SnO + 2 HF → SnF2 + H2O
Aqueous solutions
editReadily soluble in water, SnF2 is hydrolysed. At low concentration, it forms species such as SnOH+, Sn(OH)2 and Sn(OH)3−. At higher concentrations, predominantly polynuclear species are formed, including Sn2(OH)22+ and Sn3(OH)42+.[21] Aqueous solutions readily oxidise to form insoluble precipitates of SnIV, which are ineffective as a dental prophylactic.[22] Studies of the oxidation using Mössbauer spectroscopy on frozen samples suggests that O2 is the oxidizing species.[23]
Lewis acidity
editSnF2 acts as a Lewis acid. For example, it forms a 1:1 complex (CH3)3NSnF2 and 2:1 complex [(CH3)3N]2SnF2 with trimethylamine,[24] and a 1:1 complex with dimethylsulfoxide, (CH3)2SO·SnF2.[25]
In solutions containing the fluoride ion, F−, it forms the fluoride complexes SnF3−, Sn2F5−, and SnF2(OH2).[26] Crystallization from an aqueous solution containing NaF produces compounds containing polynuclear anions, e.g. NaSn2F5 or Na4Sn3F10 depending on the reaction conditions, rather than NaSnF3.[20] The compound NaSnF3, containing the pyramidal SnF3− anion, can be produced from a pyridine–water solution.[27] Other compounds containing the pyramidal SnF3− anion are known, such as Ca(SnF3)2.[28]
Reducing properties
editSnF2 is a reducing agent, with a standard reduction potential of Eo (SnIV/ SnII) = +0.15 V.[29] Solutions in HF are readily oxidised by a range of oxidizing agents (O2, SO2 or F2) to form the mixed-valence compound Sn3F8 (containing SnII and SnIV and no Sn–Sn bonds).[20]
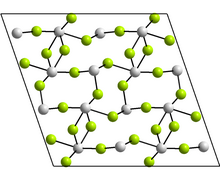
Structure
editThe monoclinic form contains tetramers, Sn4F8, where there are two distinct coordination environments for the Sn atoms. In each case, there are three nearest neighbours, with Sn at the apex of a trigonal pyramid, and the lone pair of electrons sterically active.[30] Other forms reported have the GeF2 and paratellurite structures.[30]
Molecular SnF2
editIn the vapour phase, SnF2 forms monomers, dimers, and trimers.[26] Monomeric SnF2 is a non-linear with an Sn−F bond length of 206 pm.[26] Complexes of SnF2, sometimes called difluorostannylene, with an alkyne and aromatic compounds deposited in an argon matrix at 12 K have been reported.[31][32]
Safety
editStannous fluoride can cause redness and irritation if it is inhaled or comes into contact with the eyes. If ingested, it can cause abdominal pains and shock.[33] Rare but serious allergic reactions are possible; symptoms include itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Certain formulations of stannous fluoride in dental products may cause mild tooth discoloration; this is not permanent and can be removed by brushing, or can be prevented by using a stabilised stannous fluoride toothpaste.[15][16][34]
References
edit- ^ a b "National Inventors Hall of Fame Announces 2019 Inductees at CES" (Press release). National Inventors Hall of Fame. Retrieved 6 February 2019.
- ^ "Latin Names Variable Charge Metals". Nobel.SCAS.BCIT.ca/. British Columbia Institute of Technology Chemistry Department. Archived from the original on 22 July 2020. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ^ Groeneveld, A.; Purdell-Lewis, D. J.; Arends, J. (1976). "Remineralization of artificial caries lesions by stannous fluoride". Caries Research. 10 (3): 189–200. doi:10.1159/000260201. ISSN 0008-6568. PMID 1063601.
- ^ a b Lussi, Adrian; Hellwig, Elmar; Klimek, Joachim (2012). "Fluorides - mode of action and recommendations for use". Schweizer Monatsschrift für Zahnmedizin = Revue Mensuelle Suisse d'Odonto-Stomatologie = Rivista Mensile Svizzera di Odontologia e Stomatologia. 122 (11): 1030–1042. ISSN 0256-2855. PMID 23192605.
- ^ West, N. X.; He, T.; Macdonald, E. L.; Seong, J.; Hellin, N.; Barker, M. L.; Eversole, S. L. (March 2017). "Erosion protection benefits of stabilized SnF2 dentifrice versus an arginine–sodium monofluorophosphate dentifrice: results from in vitro and in situ clinical studies". Clinical Oral Investigations. 21 (2): 533–540. doi:10.1007/s00784-016-1905-1. ISSN 1432-6981. PMC 5318474. PMID 27477786.
- ^ Ganss, C.; Lussi, A.; Grunau, O.; Klimek, J.; Schlueter, N. (2011). "Conventional and Anti-Erosion Fluoride Toothpastes: Effect on Enamel Erosion and Erosion-Abrasion". Caries Research. 45 (6): 581–589. doi:10.1159/000334318. ISSN 0008-6568. PMID 22156703. S2CID 45156274.
- ^ West, Nicola X.; He, Tao; Hellin, Nikki; Claydon, Nicholas; Seong, Joon; Macdonald, Emma; Farrell, Svetlana; Eusebio, Rachelle; Wilberg, Aneta (August 2019). "Randomized in situ clinical trial evaluating erosion protection efficacy of a 0.454% stannous fluoride dentifrice". International Journal of Dental Hygiene. 17 (3): 261–267. doi:10.1111/idh.12379. ISSN 1601-5029. PMC 6850309. PMID 30556372.
- ^ Zhao, X.; He, T.; He, Y.; Chen, H. (2020-02-12). "Efficacy of a Stannous-containing Dentifrice for Protecting Against Combined Erosive and Abrasive Tooth Wear In Situ". Oral Health and Preventive Dentistry. 18 (1): 619–624. doi:10.3290/j.ohpd.a44926. PMID 32700515.
- ^ Stookey, G.K.; Mau, M.S.; Isaacs, R.L.; Gonzalez-Gierbolini, C.; Bartizek, R.D.; Biesbrock, A.R. (2004). "The Relative Anticaries Effectiveness of Three Fluoride-Containing Dentifrices in Puerto Rico". Caries Research. 38 (6): 542–550. doi:10.1159/000080584. ISSN 0008-6568. PMID 15528909. S2CID 489634.
- ^ Parkinson, C. R.; Milleman, K. R.; Milleman, J. L. (2020-03-26). "Gingivitis efficacy of a 0.454% w/w stannous fluoride dentifrice: a 24-week randomized controlled trial". BMC Oral Health. 20 (1): 89. doi:10.1186/s12903-020-01079-6. ISSN 1472-6831. PMC 7098169. PMID 32216778.
- ^ Hu, Deyu; Li, Xue; Liu, Hongchun; Mateo, Luis R.; Sabharwal, Amarpreet; Xu, Guofeng; Szewczyk, Gregory; Ryan, Maria; Zhang, Yun-Po (April 2019). "Evaluation of a stabilized stannous fluoride dentifrice on dental plaque and gingivitis in a randomized controlled trial with 6-month follow-up". The Journal of the American Dental Association. 150 (4): S32–S37. doi:10.1016/j.adaj.2019.01.005. ISSN 0002-8177. PMID 30797257. S2CID 73488958.
- ^ Mankodi, Suru; Bartizek, Robert D.; Winston, J. Leslie; Biesbrock, Aaron R.; McClanahan, Stephen F.; He, Tao (2005). "Anti-gingivitis efficacy of a stabilized 0.454% stannous fluoride/sodium hexametaphosphate dentifrice". Journal of Clinical Periodontology. 32 (1): 75–80. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2004.00639.x. ISSN 1600-051X. PMID 15642062.
- ^ Archila, Luis; Bartizek, Robert D.; Winston, J. Leslie; Biesbrock, Aaron R.; McClanahan, Stephen F.; He, Tao (2004). "The Comparative Efficacy of Stabilized Stannous Fluoride/Sodium Hexametaphosphate Dentifrice and Sodium Fluoride/Triclosan/Copolymer Dentifrice for the Control of Gingivitis: A 6-Month Randomized Clinical Study". Journal of Periodontology. 75 (12): 1592–1599. doi:10.1902/jop.2004.75.12.1592. ISSN 1943-3670. PMID 15732859.
- ^ Clark-Perry, Danielle; Levin, Liran (December 2020). "Comparison of new formulas of stannous fluoride toothpastes with other commercially available fluoridated toothpastes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". International Dental Journal. 70 (6): 418–426. doi:10.1111/idj.12588. PMC 9379195. PMID 32621315. S2CID 220336087.
- ^ a b c He, Tao; Baker, Robert; Bartizek, Robert D.; Biesbrock, Aaron R.; Chaves, Eros; Terézhalmy, Geza (2007). "Extrinsic stain removal efficacy of a stannous fluoride dentifrice with sodium hexametaphosphate". The Journal of Clinical Dentistry. 18 (1): 7–11. ISSN 0895-8831. PMID 17410949.
- ^ a b c d Johannsen, A.; Emilson, C.-G.; Johannsen, G.; Konradsson, K.; Lingström, P.; Ramberg, P. (December 2019). "Effects of stabilized stannous fluoride dentifrice on dental calculus, dental plaque, gingivitis, halitosis and stain: A systematic review". Heliyon. 5 (12): e02850. Bibcode:2019Heliy...502850J. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02850. ISSN 2405-8440. PMC 6909063. PMID 31872105.
- ^ White, D. J. (1995). "A "return" to stannous fluoride dentifrices". The Journal of Clinical Dentistry. 6: 29–36. ISSN 0895-8831. PMID 8593190.
- ^ Tinanoff, N. (1995). "Progress regarding the use of stannous fluoride in clinical dentistry". The Journal of Clinical Dentistry. 6: 37–40. ISSN 0895-8831. PMID 8593191.
- ^ West, Nicola X.; He, Tao; Zou, Yuanshu; DiGennaro, Joe; Biesbrock, Aaron; Davies, Maria (February 2021). "Bioavailable gluconate chelated stannous fluoride toothpaste meta-analyses: Effects on dentine hypersensitivity and enamel erosion". Journal of Dentistry. 105: 103566. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103566. hdl:1983/34d78138-703d-484f-864f-ece3d3610d64. ISSN 1879-176X. PMID 33383100. S2CID 229940161.
- ^ a b c Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Séby, F.; Potin-Gautier, M.; Giffaut, E.; Donard, O.F.X. (2001). "A critical review of thermodynamic data for inorganic tin species". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 65 (18): 3041–3053. Bibcode:2001GeCoA..65.3041S. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00645-7.
- ^ David B. Troy, 2005, Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, ISBN 0-7817-4673-6, ISBN 978-0-7817-4673-1
- ^ Denes, Georges; Lazanas, George (1994). "Oxidation of SnF2 stannous fluoride in aqueous solutions". Hyperfine Interactions. 90 (1): 435–439. Bibcode:1994HyInt..90..435D. doi:10.1007/BF02069152. S2CID 96184099.
- ^ Hsu, C. C. & Geanangel, R. A. (1977). "Synthesis and studies of trimethylamine adducts with tin(II) halides". Inorg. Chem. 16 (1): 2529–2534. doi:10.1021/ic50176a022.
- ^ Hsu, Chung Chun & Geanangel, R. A. (1980). "Donor and acceptor behavior of divalent tin compounds". Inorg. Chem. 19 (1): 110–119. doi:10.1021/ic50203a024.
- ^ a b c Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) Inorganic Chemistry, Elsevier ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Salami, Tolulope O.; Zavalij, Peter Y.; Oliver, Scott R.J (2004). "Synthesis and crystal structure of two tin fluoride materials: NaSnF3 (BING-12) and Sn3F3PO4". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 177 (3): 800–805. Bibcode:2004JSSCh.177..800S. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2003.09.013.
- ^ Kokunov Y. V.; Detkov D. G.; Gorbunova Yu. E.; Ershova M. M.; Mikhailov Yu. N. (2001). "Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Calcium Trifluorostannate(II)". Doklady Chemistry. 376 (4–6): 52–54. doi:10.1023/A:1018855109716. S2CID 91430538.
- ^ Housecroft, C. E.; Sharpe, A. G. (2004). Inorganic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-039913-7.
- ^ a b Wells A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry 5th edition Oxford Science Publications ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ^ Bogdanov, SE; Faustov, VI; Egorov, MP; Nefedov, OM (1994). "Matrix IR spectra and quantum chemical studies of the reaction between difluorostannylene and hept-1-yne. The first direct observation of a carbene analog π-complex with alkyne". Russian Chemical Bulletin. 43 (1): 47–49. doi:10.1007/BF00699133. S2CID 97064510.
- ^ S. E. Boganov, M. P. Egorov and O. M. Nefedov (1999). "Study of complexation between difluorostannylene and aromatics by matrix IR spectroscopy". Russian Chemical Bulletin. 48 (1): 98–103. doi:10.1007/BF02494408. S2CID 94004320.
- ^ "Stannous fluoride (International Chemical Safety Cards: 0860)". International Labour Organization. Retrieved June 21, 2021.
- ^ "Stannous Fluoride-Dental". WebMD. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
