West Island (Malay: Pulau Panjang, Cocos Islands Malay: Pulu Panjang), part of the South Keeling Islands, is the capital of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands, an Australian external territory in the Indian Ocean. The population is roughly 120, making it the third smallest capital in the world, and consists mainly of Europeans. It is less populous than Home Island, the only other inhabited island.
Native name: | |
|---|---|
 | |
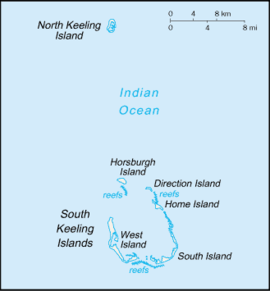 The Cocos (Keeling) Islands, showing West Island | |
West Island in the Cocos (Keeling) Islands | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Indian Ocean |
| Coordinates | 12°11′13″S 96°49′42″E / 12.18694°S 96.82833°E |
| Archipelago | Cocos (Keeling) Islands |
| Area | 6.23 km2 (2.41 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
Australia | |
| External territory of Australia | Australian Indian Ocean Territories |
| Territory | Cocos (Keeling) Islands |
| Capital city | Canberra |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 120 |
| Languages | |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
West Island was part of the Clunies-Ross plantation and an airstrip was built here during World War II. As well as all the government buildings, it contains the airport, a general store and tourist accommodation. In November 2013 it was revealed that the Australian Signals Directorate operates a listening station on West Island.[1]
Education
editCocos Islands District High School operates a primary and secondary campus on West Island. Most of the students of that campus originate from the Australian continent.[2]
Heritage listings
editWest Island contains a number of heritage-listed sites, including:
- Morea Close: Administration Building Forecourt[3]
- Air Force Road: Direction Island Houses[4]
- Qantas Close: Government House[5]
- Sydney Highway: Qantas Huts[6]
- RAAF Memorial[7]
- Air Force Road: Type 2 Residences[8]
- William Keeling Crescent: Type T Houses Precinct[9]
- Orion Close: West Island Elevated Houses[10]
- Air Force Road: West Island Housing Precinct[11]
- Alexander Street: West Island Mosque[12]
Climate
editWest Island experiences a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen: Af, Trewartha: Aral), with hot and humid conditions experiences year round. The islands experience two seasons that often overlap: the trade wind season from May/June to September/October, and the calmer doldrum season from November through to May.[13] Precipitation is moderate to high year round, thanks to its position at the southern edge of the equatorial low pressure belt. North-west monsoons deliver rain during the doldrum, while the southeastern trade winds also give rain for much of the year.[14] Cyclones have the potential to seriously effect the flora and fauna on the island. The 1989-90 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season caused damage to the islands, with Tropical Cyclone Walter hitting the island around 13 March 1990.[15] Extreme temperatures, however, are subdued by the influence of the Indian Ocean. Extremes only range from 32.8 °C (91.0 °F) on 23 February 2017 to 20.4 °C (68.7 °F) on 27 December 2018.
| Climate data for Cocos Island Airport (1991-2020 normals, extremes 1998–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.2 (90.0) |
32.8 (91.0) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.8 (91.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
30.9 (87.6) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.6 (87.1) |
30.1 (86.2) |
31.0 (87.8) |
31.1 (88.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
32.8 (91.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.1 (86.2) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.0 (86.0) |
29.5 (85.1) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.8 (83.8) |
29.2 (84.6) |
29.5 (85.1) |
29.2 (84.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.7 (81.9) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.5 (81.5) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.7 (80.1) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.1 (80.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 25.2 (77.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.0 (77.0) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.0 (77.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 21.0 (69.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
21.8 (71.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.2 (70.2) |
22.2 (72.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.9 (69.6) |
20.9 (69.6) |
21.2 (70.2) |
21.6 (70.9) |
20.4 (68.7) |
20.4 (68.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 151.7 (5.97) |
207.1 (8.15) |
239.4 (9.43) |
249.3 (9.81) |
187.7 (7.39) |
187.3 (7.37) |
180.9 (7.12) |
102.4 (4.03) |
86.2 (3.39) |
84.8 (3.34) |
89.7 (3.53) |
121.4 (4.78) |
1,886.6 (74.28) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 10.2 | 12.2 | 15.4 | 14.1 | 13.9 | 13.9 | 14.7 | 11.1 | 8.4 | 6.2 | 6.3 | 8.6 | 135.0 |
| Source: Australian Bureau of Meteorology[16] | |||||||||||||
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Dorling, Philip (1 November 2013). "Listening post revealed on Cocos Islands". Canberra Times. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013.
- ^ Home. Cocos Islands District High School. Retrieved on 8 April 2019.
- ^ "Administration Building Forecourt (Place ID 105356)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "Direction Island (DI) Houses (Place ID 105358)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "Government House (Place ID 105360)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "Qantas Huts (former) (Place ID 105354)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "RAAF Memorial (Place ID 105353)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "Type 2 Residences (Place ID 105357)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "Type T Houses Precinct (Place ID 105408)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "West Island Elevated Houses (Place ID 105359)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "West Island Housing Precinct (Place ID 105223)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "West Island Mosque (Place ID 105219)". Australian Heritage Database. Australian Government. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ "Weather & Tides | Cocos Keeling Islands". www.cocoskeelingislands.com.au. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- ^ "Climate - DAWE". www.awe.gov.au. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone WALTER". australiasevereweather.com. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- ^ "Cocos Island Airport Climate". Australian Bureau of Meteorology.
