Polykrikos kofoidii is a species of phagotrophic marine pseudocolonial dinoflagellates that can capture and engulf other protist prey, including the toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium tamarense.[3][4] P. kofoidii is of scientific interest due to its status as a predator of other dinoflagellates, a behavior that is significant in the control of algal blooms.[5][6][7] It has a complex life cycle of both vegetative (asexual) and sexual reproduction complicated by its pseudocolonial structure.[8]
| Polykrikos kofoidii | |
|---|---|
| |
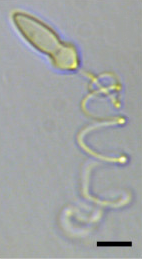
| A light micrograph of Polykrikos kofoidii showing an extruded nematocyst. Scale bar = 10µm.[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Myzozoa |
| Superclass: | Dinoflagellata |
| Class: | Dinophyceae |
| Order: | Gymnodiniales |
| Family: | Polykrikaceae |
| Genus: | Polykrikos |
| Species: | P. kofoidii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Polykrikos kofoidii | |
References edit
- ^ Hoppenrath, M; Bachvaroff, TR; Handy, SM; Delwiche, CF; Leander, BS (25 May 2009). "Molecular phylogeny of ocelloid-bearing dinoflagellates (Warnowiaceae) as inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA sequences". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 9 (1): 116. Bibcode:2009BMCEE...9..116H. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-9-116. PMC 2694157. PMID 19467154.
- ^ M. Guiry (2015). Guiry MD, Guiry GM (eds.). "Polykrikos kofoidii Chatton, 1914". AlgaeBase. National University of Ireland, Galway. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Cho, Hyun-Jin; Kazumi Matsuoka (2000). "Cell lysis of a phagotrophic dinoflagellate, Polykrikos kofoidii feeding on Alexandrium tamarense". Plankton Biology and Ecology. 47 (2): 134–136.
- ^ Hoppenrath, Mona; Brian S. Leander (2007). "Character evolution in polykrikoid dinoflagellates". Journal of Phycology. 43 (2): 366–377. Bibcode:2007JPcgy..43..366H. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2007.00319.x. S2CID 16821791.
- ^ Gavelis, Gregory S.; White, Richard A.; Suttle, Curtis A.; Keeling, Patrick J.; Leander, Brian S. (17 July 2015). "Single-cell transcriptomics using spliced leader PCR: Evidence for multiple losses of photosynthesis in polykrikoid dinoflagellates". BMC Genomics. 16 (1): 528. doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1636-8. PMC 4504456. PMID 26183220.
- ^ Matsuyama, Y; Miyamoto, M; Kotani, Y (1999). "Grazing impacts of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Polykrikos kofoidii on a bloom of Gymnodinium catenatum". Aquatic Microbial Ecology. 17: 91–98. doi:10.3354/ame017091.
- ^ JEONG, HAE JIN; KIM, SOO KYEONG; KIM, JAE SEONG; KIM, SEONG TAEK; YOO, YEONG DU; YOON, JOO YIH (May 2001). "Growth and Grazing Rates of the Heterotrophic Dinoflagellate Polykrikos kofoidii on Red-Tide and Toxic Dinoflagellates". The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 48 (3): 298–308. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.2001.tb00318.x. PMID 11411838. S2CID 27126586.
- ^ Tillmann, Urban; Hoppenrath, Mona (April 2013). "Life Cycle of the pseudocolonial dinoflagellate (Gymnodiniales, Dinoflagellata)". Journal of Phycology. 49 (2): 298–317. doi:10.1111/jpy.12037. PMID 27008517. S2CID 30674349.