This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2008) |
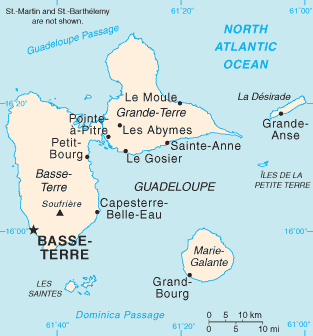
La Désirade[1] (French pronunciation: [la deziʁad]; Guadeloupean Creole: Dézirad or Déziwad) is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe,[2] an overseas region of France.[3]

History edit
Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian population lived on La Désirade from the 3rd to the 16th centuries.[4]
Spanish colonization edit
Deseada was the first island sighted by Christopher Columbus in 1493. When he landed there during his second voyage to America, he took possession of the island on behalf of the Spanish crown, followed by the island of Marie-Galante. Like other Antillean islands, it served as a hideout for pirates or corsairs who attacked Spanish overseas possessions.
Some sources indicate that the island owes its name to the relief of the members of Columbus crew who saw the first dry land since leaving the Canary Islands of Spain. They cried out: "Oh, desired island"[5] The French name La Désirade[6] is an adaptation of its historical name in Spanish (La Deseada).[7]
French colonization edit
La Désirade first belonged to the island of Dominica and then became a dependency of Guadeloupe in 1648, when some cotton plantations were installed. It also served as a hideout for pirates attacking Spanish overseas territories. Les Galets was a place of exile for the criminals of Grand-Terre and for some nobles of the metropolis. There is a legend of an international adventurer Tybalt Rosembraise born in 1798 in the penal colony to a French dissident and a Carib slave woman. The island of Desirade has had a reputation as a home base for liquor smugglers. In the 18th century, a leper hospital was founded in Baie-Mahault, at the eastern end of the island. The patients suffered difficult living conditions, and this center finally closed its doors in 1952.
On the few square meters of the "Place du Maire mendiant", named in memory of Joseph Daney de Marcillac, remembered for ''tirelessly'' touring Guadeloupe to finance the reconstruction of the island after the great cyclone of 1928, stands the church of Notre-Dame du bon secours, flanked by its bell tower and a massive pear tree high altar, the small town hall, the bust of the heroic Victor Schœlcher, the cannons and a monument to the dead in tribute to the deceased former sailors, which recalls the primordial place of fishing in the island's economy. Every year, on August 16, a fishermen's festival is celebrated with a procession.
Modern history edit
During the government of Nicolas Sarkozy, the opening of the États-Généraux de l'Outre-mer ("General States of the Overseas") was declared. Several study groups were created, one of which dealt with local governance, leading to the conception of a project of institutional modification or a new status for Guadeloupe with or without the emancipation of its remaining dependencies. At the same time, the conferences of the "southern islands" (name of the last dependencies of Guadeloupe) were opened (Marie-Galante, les Saintes and la Désirade). The problems common to these islands were presented in six study groups: equal opportunities, territorial continuity, local governance, local economic development, insertion through activity and tourism.
At that time, it was proposed that the dependence of these islands of Guadeloupe be eliminated and that the collective of the southern islands of Guadeloupe be integrated into a new entity on the basis of Article 74 of the French Constitution.
Les Saintes, like Marie-Galante, aspired to the creation of an overseas collectivity for each entity of the southern islands, or the combination of the three dependencies, on the same plan as the former northern islands of Guadeloupe (Saint-Barthélemy and Saint-Martin). Marie-Luce Penchard, a native of Guadeloupe, who joined the government's overseas portfolio on June 23, 2009, and was appointed Minister of Overseas France on November 6, 2009, opposed the initial project of her predecessor and delayed its implementation, which was stalled.[8] The island remains a dependency of Guadeloupe.
Geography edit
The island of La Désirade is located at the eastern end of the Guadeloupean archipelago, in the Lesser Antilles. It lies about 8 km off the coast of Grande-Terre, which is the eastern half of the island of Guadeloupe. Its coordinates are 16°19′N 61°3′W / 16.317°N 61.050°W.
The island is 11 km long and 2 km wide; the interior of the island forms a central plateau.[9] It has a land area of 20.64 km2 (7.97 sq mi) and a population of 1,595 in 2006, with a population density of 77 inh. per km2 (200 inh. per sq. mile) in 2006. Most residents live in the settlement of Beauséjour (formerly known as Grande-Anse).
Geologically speaking, La Désirade is the oldest island in the Lesser Antilles with its most ancient rocks, at 145 million years old,[10] being found at the easternmost point of the island. The beach at Pointe Doublé is frequently visited by geologists who come to examine the basalt and composite rocks, which give the area its striking multi-coloured appearance. The island has its own lapidary, which transforms the rocks found on the island into jewellery and souvenirs.
Administration edit
The island of La Désirade forms part of the department of Guadeloupe, which is one of the five overseas departments and regions of France. Local administration is carried out by the local commune (municipality). The commune of La Désirade also includes the uninhabited Petite Terre Islands which lie nearby.
Energy edit
On La Désirade, which is particularly exposed to trade winds, the first anticyclonic wind farm in the department of Guadeloupe was installed in 1993, with 20 wind turbines of 25 kW each protruding from the Souffleur stretch. These wind turbines could fold up when cyclones approached, thanks to a technique that was tested for the first time on the island. They were subsequently replaced by 6 state-of-the-art wind turbines, less noisy and capable of producing a rated power of 275 kW each in light winds.
The second site was located on the heights of the Baie Mahault section: 35 wind turbines of 60 kW.
The electricity produced by the La Désirade wind farms is 3.8 mW; it is injected into the Guadeloupe electricity grid via a submarine cable because it far exceeds the consumption of local inhabitants.[11]
Water edit
It was not until 1991 that La Désirade was connected to the water network of mainland Guadeloupe. Previously, the inhabitants used rainwater collected in cisterns and drew water from springs on the island. Since the breakage of the submarine cable supplying electricity to the island by Hurricane Dean in August 2007, the municipality tried to improve its autonomy from the mainland. As a result, community cisterns were rehabilitated and individuals were encouraged to install individual cisterns.[12]
Transport edit
| Pointe Doublé lighthouse in 2009 | |
| Location | La Désirade, Guadeloupe, France |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 16°20′00″N 61°00′20″W / 16.333454°N 61.00556°W |
| Tower | |
| Constructed | Unknown |
| Construction | concrete |
| Automated | 1972 |
| Height | 20 m (66 ft) |
| Shape | triangular prism (tower), hexagonal prism (balcony) |
| Markings | white (tower), red (balcony), red (pedestal) |
| Power source | solar power |
| Light | |
| Focal height | 50 m (160 ft) |
| Range | 20 nmi (37 km; 23 mi) |
| Characteristic | Fl(2) W 10s |
The first lighthouse was constructed in 1933.[13] It was later replaced by a modern concrete lighthouse.
The municipal government of La Désirade launched a bus service called Désirbus in November 2012. Two minibuses (9 and 17 seats) and five drivers run rotations between 5:10 a.m. and 6:30 p.m., Sundays and holidays included.
Maritime boats operate from the island to Grande-Terre and, more specifically, to the municipality of Saint-François. And the island is also accessible by tourist planes that can make rotations at the airfield of La Désirade de Grande-Anse, mainly from the Guadeloupe-Polo airport in the Caribbean.
Main settlements edit
Beauséjour edit
The main settlement on the island is the village of Beauséjour, which has a post office, a library, several grocery stores and restaurants, as also the community's church, which is famous for its altar carved out of locally grown pear tree wood. The central square of the village is named ‘La Place du Maire mendiant’ (‘The begging Mayor’s square’), in memory of a beloved local figure. The ‘begging Mayor’ was the nickname given to a former Mayor, Joseph Daney de Marcillac, who, after a terrible fire had destroyed most of the village in 1922, went from door to door in Guadeloupe begging for funds and building materials in order to rebuild the two primary schools of the village.[11]
Close to the square, one can find a statue of the French abolitionist Victor Schœlcher, as also a monument in memory of the fishermen who perished at sea and the town hall, built in the style of architect Ali Tur.
Anse de Galets edit
This small bay is situated at the westernmost tip of the island, facing the Pointe des Châteaux. Providing the departure point for the colonisation of the island, this cove was also home to all those who were exiled in the 18th century.[14]
Flora and fauna edit
The island is in pristine condition, and is partly under the Réserve naturelle nationale de La Désirade. It provides a good opportunity to see varied and often rare wildlife. While the arid soil on La Montagne's plateau does not permit cultivation beyond subsistence level, the natural vegetation is amazingly rich and varied.
Some of the plant species found are the gaïac (Guaiacum officinale), the mapou (Myrsine australis) and the cashew tree (Anacardium occidentale), as well as a protected species of cacti called the "tête à l’Anglais" (in reference to its similarity to the Queen's Guards’ bearskin hats). This same region is also inhabited by rare animal species such as a type of robin called a ‘bicloitin’[citation needed], a tropical rodent with glossy brown, orange fur named an ‘agouti’ and the Lesser Antillean iguana.
The two islets of Petite Terre (Terre de Bas, the larger of the two, and Terre de Haut) were designated as a natural reserve in 1998. The two islets are separated by a lagoon 200 yards across and are located about seven miles from Désirade, to which they belong administratively.
In 1974 the lighthouse keeper and his family, the last residents, left Petite Terre due to the automation of the lighthouse. In earlier times, as many as 50 inhabitants lived on the islets. Today this tiny archipelago, surrounded by clear waters and huge coral reefs is inhabited by iguanas (Iguana delicatissima), which are native to the Lesser Antilles.
Petite Terre is home to rare species of birds such as the Least Tern (Sternula antillarum), the American Oystercatcher (Haematopus palliatus), as well as various types of sandpipers. Two species of turtle, the Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas) and the Loggerhead Sea Turtle (Caretta caretta), come to the islets to lay their eggs. Tourism is regulated by the National Office of Forests,[15] in partnership with the Désiradian association of Ti Tè.
Culture edit
Festivals edit
The annual Sailors’ Commemorative Ceremony is held on 16 August. A large procession is taken out, in which Le Vétéran, a model boat normally kept in the town's church (Notre Dame de l’Assomption), is paraded all around Beauséjour. Though the ceremony itself is only for a day, the days leading up to and following it are normally festive too, with parades and parties. People from all over Guadeloupe and Metropolitan France come over to the island to partake in the event.
Every year the "Goat Festival" (Fête du Cabri) takes place during the Easter weekend. Based around a celebration of the island's favourite food, various concerts, productions and programmes are held across the isle.
Cuisine edit
The island is renowned for its fresh seafood, much of which goes straight from the fishing boats to the local restaurants. Furthermore, the lobsters and shellfish which are plentiful on Désirade are becoming increasingly rare in Guadeloupe as a whole. There are also many traditional goat recipes, including curries and stews, which make up a large part of the island's cuisine. As for desserts, the cashew fruit is a particular speciality which can be consumed on its own, with ice-cream or in rum-based drinks.
Monuments and tourist sites edit
- The national nature reserve of the Petite-Terre islands
Beach of Beauséjour in La Désirade - The Pointe Doublé lighthouse
- The former Pointe Doublé meteorological station (listed historical monument)[16]
- The marine cemetery of Beauséjour
- The beaches of Grande-Anse, Souffleur and Baie-Mahault.
- The ruins of the leper colony and the old cotton mill.
- The church of Notre-Dame-du-Bon-Secours, built in 1754 and modified after the cyclones of 1899 and 1928. A bell tower and two chapels were added in 1935. Inside, the altar is made of rough pear wood.
- The catholic chapel of Notre-Dame-du-Calvaire, built in 1905. Last stop of the Way of the Cross, the place offers a unique view of the Désirade and the surrounding islands.
- Several spaces with panoramic views around the island and the cliffs of the north coast.
See also edit
Notes edit
- ^ Henderson, James (1992). The Caribbean. Cadogan Books. ISBN 978-1-56440-003-1.
- ^ Collectif (25 November 1999). LA GUADELOUPE. La Désirade, Marie-Galante, Les Saintes (in French). D'ici Et D'ailleurs. ISBN 978-2-912273-05-5.
- ^ Countries of the World and Their Leaders: Yearbook 2001. Gale Research. 2001. ISBN 978-0-7876-3305-9.
- ^ "Les dépendances". Guadeloupe Government webpage. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ "Histoire | La-desirade". www.la-desirade.com. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- ^ Anuario de estudios americanos (in Spanish). Escuela de Estudios Hispano-Americanos, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas. 1969.
- ^ "Biblioteca Virtual del Ministerio de Defensa". bibliotecavirtualdefensa.es (in Spanish). 2012. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- ^ fxg. "Les Îles du Sud et l'Elysée". le blog fxgpariscaraibe (in French). Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- ^ Sullivan, Lynne M. Martinique, Guadeloupe, Dominica & St. Lucia, Hunter Publishing Inc., ISBN 1-55650-857-3, p. 345
- ^ "Désirade balade 20 juillet".
- ^ a b "L'Histoire du maire mendiant - "Destination Guadeloupe" N°6".
- ^ "La Désirade, paradis nature". Archived from the original on 25 September 2009. Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- ^ Rowlett, Russ. "Lighthouses of Guadeloupe". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 29 August 2016.
- ^ Gwadloup Natures, Desirade Natures, ISSN 1627-0142
- ^ "ONF - la réserve naturelle de Petite Terre, un joyau écologique". www.onf.fr. Archived from the original on 1 July 2015.
- ^ "Ministère de la Culture - Maintenance". www2.culture.gouv.fr. Retrieved 16 June 2021.
External links edit
- The official website of the island
- Tourism website for the island
- Desirade-sante.com Everything you should know about the major public health crisis that occurred in La Désirade.