The wrynecks (genus Jynx) are a small but distinctive group of small Old World woodpeckers. Jynx is from the Ancient Greek iunx, the Eurasian wryneck.
| Wrynecks | |
|---|---|

| |
| Eurasian wryneck (Jynx torquilla) Punjab, India | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Piciformes |
| Family: | Picidae |
| Subfamily: | Jynginae |
| Genus: | Jynx Linnaeus, 1758 |
| Type species | |
| Jynx torquilla (Eurasian wryneck) Linnaeus, 1758
| |
| Species | |
| |
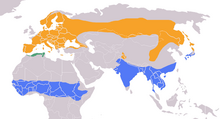
| Range map for Eurasian wryneck | |

| |
| Range map for red-necked wryneck Summer Resident Winter | |
These birds get their English name from their ability to turn their heads almost 180°. When disturbed at the nest, they use this snake-like head twisting and hissing as a threat display. It has occasionally been called "snake-bird" for that reason.[1]
Like the true woodpeckers, wrynecks have large heads, long tongues, which they use to extract their insect prey, and zygodactyl feet, with two toes pointing forward and two backwards, but they lack the stiff tail feathers that the true woodpeckers use when climbing trees, so they are more likely than their relatives to perch on a branch rather than an upright trunk. The sexes have a similar appearance.[2]
Their bills are shorter and less dagger-like than in the true woodpeckers, but their chief prey is ants and other insects, which they find in decaying wood or almost bare soil. They reuse woodpecker holes for nesting, rather than making their own holes. The eggs are white, as with many hole nesters.
The two species have cryptic plumage, with intricate patterning of greys and browns. The adult moults rapidly between July and September, although some moult continues in its winter quarters.[3]
Taxonomy and etymology
editThe woodpeckers are an ancient bird family consisting of three subfamilies, the wrynecks, the piculets and the true woodpeckers, Picinae. DNA sequencing and phylogenetic analysis show that the wrynecks are a sister clade to other woodpeckers including the Picinae and probably diverged early from the rest of the family.[4]
The wryneck subfamily Jynginae has one genus, Jynx, introduced in 1758 by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his Systema Naturae.[5] Linnaeus placed a single species in the genus, the Eurasian wryneck (Jynx torquilla), which is therefore the type species.[6] The genus name Jynx is from the Ancient Greek name for the Eurasian wryneck, ιυγξ, iunx, and ruficollis is from the Latin rufus, "rufous" and collum "neck".[7] The English "wryneck" refers to the habit of birds in this genus of twisting and writhing their necks when agitated. It was first recorded in 1585.[8] The red-throated wryneck was first identified by German ornithologist Johann Georg Wagler in 1830.[9][10] It is also known as the rufous-necked wryneck or red-breasted wryneck.[11]
The two wrynecks form a superspecies that probably separated early in their evolution from the piculets,[4] although there has subsequently been only limited divergence between the Jynx species.[12][13]
Fossil record
editThe woodpecker family appears to have diverged from other Piciformes about fifty million years ago,[4] and a 2017 study considered that the split between Jynx and other woodpeckers occurred about 22.5 million years ago.[14] A fossil dating from the early Miocene, more than twenty million years ago, consisting of the distal end of a tarsometatarsus had some ‘’Jynx’’-like features, but was classed as an early piculet.[15] By the Pliocene (five million years ago) woodpeckers were similar to those now extant. Fossil wrynecks are known from Europe in the Pleistocene, between 2.6 million and 11,700 years ago.[4]
Species
editThe two species in Jynx are restricted to the Palearctic biogeographic realm and Africa. The Eurasian wryneck breeds across temperate Europe and Asia, and one of only two Old World woodpeckers to undertake long-distance migration mainly wintering in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical Asia.[16] The rufous-necked wryneck has a disjunct distribution confined to sub-Saharan Africa.[12] It is resident, although there may be local movements and post-breeding dispersal.[17] Both wrynecks have several geographical subspecies.[10][18]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian wryneck | Jynx torquilla Linnaeus, 1758 Six subspecies
|
Palearctic from the Arctic Circle south to Spain, Algeria, Morocco, southern Siberia, Central Asia, Japan and southern China.[19][20] Winters south of the Sahara from Senegal in the west to Ethiopia in the east, and in tropical South and Southeast Asia.[18] |
Size: 17 cm (6.7 in).[21] 26 to 50 g (0.92 to 1.76 oz) {J. t. tschusii.[22] Habitat: Open countryside and gardens, especially with some old trees.[21] Diet: Mainly ants[21] |
LC
|
| Red-throated wryneck | Jynx ruficollis (Wagler, 1830) |
Resident in sub-Saharan Africa[12] from Nigeria, Cameroon, Central African Republic and Ethiopia south to South Africa and Eswatini.[19] |
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
References
edit- ^ Newton, Alfred (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 854.
- ^ "Woodpeckers, Wrynecks, and Piculets (Picidae) | Encyclopedia.com". www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ^ RSPB Handbook of British Birds (2014). UK. ISBN 978-1-4729-0647-2.
- ^ a b c d Gorman (2022) p. 3.
- ^ Linnaeus, Carl (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1 (10th ed.). Holmiae (Stockholm): Laurentii Salvii. p. 112.
- ^ Peters, James Lee, ed. (1948). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 6. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 86.
- ^ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 212, 341. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ "Wryneck". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ Wagler, Johann Georg (1830). Naturliches System der Amphibien (in German). Munich: J. G. Cotta'schen. p. 118.
- ^ a b Gorman (2022) pp. 35–36.
- ^ Gorman (2014) pp. 38–39.
- ^ a b c Gorman (2022) pp. 39–40.
- ^ Tarboton, Warwick (1976). "Aspects of the Biology of Jynx ruficollis". The Ostrich: Journal of African Ornithology. 47 (2–3): 99–112. doi:10.1080/00306525.1976.9639545.
- ^ Shakya, S B; Fuchs, J; Pons, J-M; Sheldon, F H (2017). "Tapping the woodpecker tree for evolutionary insight". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 116: 182–191. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2017.09.005. PMID 28890006.
- ^ De Pietri, Vanesa L; Manegold, Albrecht; Costeur, Loïc; Mayr, Gerald (2011). "A new species of woodpecker (Aves; Picidae) from the early Miocene of Saulcet (Allier, France)". Swiss Journal of Palaeontology. 130 (2): 307–314. doi:10.1007/s13358-011-0021-8. S2CID 129249316.
- ^ Gorman (2022) pp. 104–106.
- ^ Gorman (2022) p. 42.
- ^ a b Gorman (2022) pp. 4–6.
- ^ a b BirdLife International (2016). "Jynx ruficollis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22680689A92872725. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22680689A92872725.en.
- ^ Butchart, S.; Ekstrom, J. "Eurasian Wryneck Jynx torquilla". BirdLife International. Archived from the original on 2016-10-21. Retrieved 2013-08-06.
- ^ a b c Witherby, H. F., ed. (1943). Handbook of British Birds, Volume 2: Warblers to Owls. H. F. and G. Witherby Ltd. pp. 292–296.
- ^ CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), ISBN 978-0-8493-4258-5.
Cited texts
edit- Gorman, Gerard (2014). Woodpeckers of the World. Helm Photographic Guides. London: Christopher Helm. ISBN 978-1-4081-4715-3.
- Gorman, Gerard (2022). The Wryneck. Exeter: Pelagic. ISBN 978-1-78427-288-3.