The Ajmer Subah (Persian: صوبه اجمیر) was one of the original 12 subahs (provinces) that comprised the Mughal Empire after the administrative reform under the rule of Akbar. Its borders roughly corresponded to modern-day Rajasthan, and the capital was the city of Ajmer.[1]
| Ajmer Subah | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subah of Mughals | |||||||||||
| 1580–1758 | |||||||||||
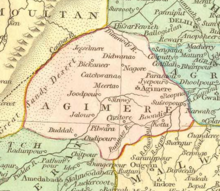 Ajmer Subah depicted in map of Mughal Empire by Robert Wilkinson (1805) | |||||||||||
| Capital | Ajmer | ||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||
| Subahdar | |||||||||||
• 1580 | Dastam Khan | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 1580 | ||||||||||
• Maratha occupation | 1758 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | India | ||||||||||
History
editMughal patronage of the city of Ajmer in the 16th century through the support of local Sufi shrines (such as one dedicated to Moinuddin Chishti) through waqfs, culminating in Akbar's pilgrimage to the city itself in 1562. Jahangir continued the legacy of pilgrimage and imperial patronage. Shah Jahan visited the shrine as well in 1628, 1636, 1643, and 1654. Aurangzeb visited once, prior to his Deccan campaigns.[2]: 28–35
For a brief period in the 1720, Ajit Singh of Marwar occupied Ajmer and declared independence from Mughal rule until the Barha Sayyids reconquered the province.
In March 1752, the Maratha peshwas demanded the governorship of Ajmer from the Mughals, and Jayappaji Rao Scindia went to war supporting Ram Singh of Marwar when the request was denied, sacking the city of Ajmer.
Geography
editAjmer Subah was bordered to the north by Multan Subah and Delhi Subah, to the west by Thatta Subah, to the South by Gujarat Subah and Malwa Subah and to the east by the Agra Subah.[3]
Government
editSubahdars
edit| Personal Name | Reign[4][2] |
|---|---|
| Dastam Khan | 1580–c. 1595 |
| Sherza Khan | 1595–? |
| Prince Salim | 1598–? |
| Iftikhar Khan | c. 1680–? |
| Shujaat Khan | c. 1710–? |
| Ajit Singh of Marwar | 1719–1723 |
| Haider Quli Khan | 1723–? |
| Qamar al-Din | |
| Jai Singh II | 1740–? |
| Maratha rule | |
| Govind Rao | 1758–? |
| Santuji | 1770s |
| Mirza Chaman Beg | 1770s |
| Pandit Govind Rai | 1780s |
| Rao Bala Inglia | c. 1807 |
| Rao Gomanji Scindia | 1810s |
Administrative divisions
editAjmer was divided into 7 sarkars under Akbar's reign.[5]
| Sarkar | Parganas |
|---|---|
| Ajmer (capital) | 24 |
| Jodhpur | 21 |
| Chittor | 28 |
| Ranthambore | 36 |
| Nagaur | 30 |
| Sirohi | |
| Bikaner |
References
edit- ^ Chaudhary, S. S. (2000). Ranthambhore Beyond Tigers. Himanshu Publications. p. 48.
- ^ a b Thelen, Elizabeth M. (2018). Intersected Communities: Urban Histories of Rajasthan, c. 1500–1800 (Thesis). University of California, Berkeley.
- ^ Saran, Parmatma (1941). The Provincial Government of the Mughals, 1526-1658. Kitabistan.
- ^ Husain, Afzal (1970). "Provincial Governors Under Akbar (1580-1605)". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 32 (1): 269-277.
- ^ Abul Fazl-i-Allami (1949, reprint 1993). Ain-i-Akbari, Vol.II (English tr. by H. S. Jarrett, rev. by J. N. Sarkar), Calcutta: The Asiatic Society, pp.101-2