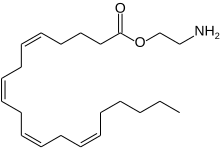
Virodhamine (O-arachidonoyl ethanolamine; O-AEA) is an endocannabinoid and a nonclassic eicosanoid, derived from arachidonic acid. O-Arachidonoyl ethanolamine is arachidonic acid and ethanolamine joined by an ester linkage, the opposite of the amide linkage found in anandamide. Based on this opposite orientation, the molecule was named virodhamine from the Sanskrit word virodha, which means opposition. It acts as an antagonist of the CB1 receptor and agonist of the CB2 receptor. Concentrations of virodhamine in the human hippocampus are similar to those of anandamide, but they are 2- to 9-fold higher in peripheral tissues that express CB2. Virodhamine lowers body temperature in mice, demonstrating cannabinoid activity in vivo.[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Aminoethyl (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoate | |
| Other names
O-Arachidonoyl ethanolamine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.921 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H37NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 347.53468 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Porter AC, Sauer JM, Knierman MD, et al. (2002). "Characterization of a novel endocannabinoid, virodhamine, with antagonist activity at the CB1 receptor". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301 (3): 1020–4. doi:10.1124/jpet.301.3.1020. PMID 12023533. S2CID 26156181. Retrieved 2007-10-31.