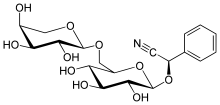
Vicianin is a cyanogenic disaccharide.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R)-[α-L-Arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy](phenyl)acetonitrile
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(R)-Phenyl{[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-({[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}acetonitrile | |
| Other names
(R)-Vicianin
6-O-Arabinopyranosylglucopyranoside β-Vicianoside | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H25NO10 | |
| Molar mass | 427.406 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
amygdalin |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
The enzyme vicianin beta-glucosidase uses (R)-vicianin and H2O to produce mandelonitrile and vicianose. It is found in seeds of Vicia angustifolia.[1]
References
edit- ^ Ahn, Y. O.; Saino, H.; Mizutani, M.; Shimizu, B.-i.; Sakata, K. (2007). "Vicianin hydrolase is a novel cyanogenic beta-glycosidase specific to beta-vicianoside (6-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside) in seeds of Vicia angustifolia". Plant and Cell Physiology. 48 (7): 938–47. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcm065. PMID 17548373.