 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /brɪˈmoʊnɪdiːn/ bri-MOH-nid-een |
| Trade names | Alphagan, Mirvaso, Lumify, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Topical: Monograph Eye: Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601232 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | topical (eye drop, gel) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Primarily liver |
| Elimination half-life | 3 hours (ocular), 12 hours (topical) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
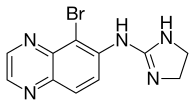
| Formula | C11H10BrN5 |
| Molar mass | 292.135 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 252 °C (486 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Brimonidine is a medication used to treat open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and rosacea.[1][2] In rosacea it improves the redness.[2] It is used as eye drops or applied to the skin.[1][2]
Common side effects when used in the eyes include itchiness, redness, and a dry mouth.[1] Common side effects when used on the skin include redness, burning, and headaches.[2] More significant side effects may include allergic reactions and low blood pressure.[2][1] Use in pregnancy appears to be safe.[2][1] When applied to the eye it works by decreasing the amount of aqueous humor made while increasing the amount that drains from the eye.[1] When applied to the skin it works by causing blood vessels to contract.[2]
Brimonidine was patented in 1972 and came into medical use in 1996.[4] It is available as a generic medication.[5] One milliliter in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 1.10 £ as of 2019.[5] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$0.60.[6] In 2017, it was the 167th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than three million prescriptions.[7][8]
References edit
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Brimonidine Tartrate eent Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Brimonidine Tartrate topical Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 13 May 2021. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ "WikiProjectMed:Translation task force/RTT(Simplified)L - WikiProjectMed". mdwiki.org. Archived from the original on 30 May 2021. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 550. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 2019-03-03.
- ^ a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 1153. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Brimonidine Tartrate - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.