The stylopharyngeus muscle is a muscle in the head. It originates from the temporal styloid process. Some of its fibres insert onto the thyroid cartilage, while others end by intermingling with proximal structures. It is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX). It acts to elevate the larynx and pharynx, and dilate the pharynx, thus facilitating swallowing.
| Stylopharyngeus muscle | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Temporal styloid process |
| Insertion | Thyroid cartilage |
| Nerve | Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) |
| Actions | Elevates the larynx, elevates the pharynx, dilates the pharynx; facilitates swallowing |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus stylopharyngeus |
| TA98 | A05.3.01.114 |
| TA2 | 2190 |
| FMA | 46664 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Structure
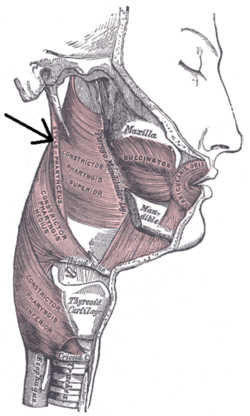
editThe stylopharyngeus is a long, slender,[1][2] tapered pharyngeal muscle.[2] It is cylindrical superiorly, and flattened inferiorly.[1]
It passes inferior-ward along the side of the pharynx[1] between the superior pharyngeal constrictor (situated deep to the stylopharyngeus) and the middle pharyngeal constrictor (situated superficial to the stylopharyngeus),[2] before spreads out beneath the mucous membrane.[1]
Origin
editIt arises from (the medial side of the base of) the temporal styloid process.[2][1]
It is the only muscle of the pharynx not to originate in the pharyngeal wall.[2]
Insertion
editSome of its fibers are lost in the superior and middle constrictor muscles, some merge with the lateral glossoepiglottic fold, while still others join with those of the palatopharyngeus muscle to insert onto the posterior border of the thyroid cartilage.[2]
Innervation
editThe stylopharyngeus is the only muscle of the pharynx innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) (all others being instead innervated by the vagus nerve (CN X)) by special visceral motor neurons with their cell bodies in[2] the rostral part of[citation needed] the nucleus ambiguus.[2]
Blood supply
editThe stylopharyngeus receives arterial supply from the paryngeal branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery.[2]
Lymphatic drainage
editThe lymphatic drainage of the region of the stylopharyngeus muscle is mediated by the middle cervical lymph nodes that drain into the supraclavicular lymph nodes.[2]
Relations
editThe stylopharyngeus is the medial-most and most vertical of the three styloid muscles.[2]
The muscle is situated in between the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery.[2]
On the lateral pharyngeal wall, it is situated posterior to the superior constrictor muscle, and anterior to the buccopharyngeal fascia.[2]
The glossopharyngeal nerve runs on the lateral side of this muscle, and crosses over it to reach the tongue.[citation needed]
Variation
editSupernumerary muscles originating from other nearby regions of the skull may be present, and may be clinically significant.[2]
Development
editEmbryological origin is the third pharyngeal arch. Its development commences between the 4th and 7th week of gestation.[2]
Function
editThe stylopharyngeus:[citation needed]
See also
editAdditional images
edit-
Stylopharyngeus muscle.
-
Left temporal bone. Inferior surface.
-
The cartilages of the larynx. Posterior view.
-
Side view of the larynx, showing muscular attachments.
-
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue. Left side.
-
Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves.
-
Stylopharyngeus muscle
-
Stylopharyngeus muscle
-
Stylopharyngeus muscle
-
Stylopharyngeus muscle
References
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1143 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d e Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. pp. 711–712. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Jain, Prachi; Rathee, Manu (2022), "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Stylopharyngeus Muscles", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 31613499, retrieved 2023-01-12