Steganacin is an dibenzocyclooctadiene lactone, an unusual type of lignan.[1] It exhibits some antileukemic properties in vitro.[2] It has been isolated from Steganotaenia araliacea.[2] (−)-Steganacin is the natural form.[3]
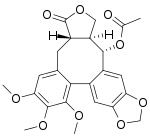 (−)-Steganacin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3aS,14S,14aS)-6,7,8-Trimethoxy-3-oxo-1,3,3a,4,14,14a-hexahydro-11H-benzo[3,4]furo[3′,4′:6,7]cycloocta[1,2-f][1,3]benzodioxol-14-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H24O9 | |
| Molar mass | 456.447 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Notes
edit- ^ Umezawa, Toshiaki (2003). "Diversity in lignan biosynthesis". Phytochemistry Reviews. 2 (3): 371–390. Bibcode:2003PChRv...2..371U. doi:10.1023/B:PHYT.0000045487.02836.32. S2CID 6276953.
- ^ a b Kupchan, SM; Britton, RW; Ziegler, MF; Gilmore, CJ; Restivo, RJ; Bryan, RF (21 February 1973). "Steganacin and steganangin, novel antileukemic lignan lactones from Steganotaenia araliacea". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 95 (4): 1335–6. doi:10.1021/ja00785a054. PMID 4687687.
- ^ Augros, David; Yalcouye, Boubacar; Choppin, Sabine; Chessé, Matthieu; Panossian, Armen; Leroux, Frédéric R. (18 January 2017). "Transition-Metal-Free Synthesis of a Known Intermediate in the Formal Synthesis of (-)-Steganacin: Transition-Metal-Free Synthesis of a Known Intermediate in the Formal Synthesis of (-)-Steganacin" (PDF). European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2017 (3): 497–503. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201601239. S2CID 100375916.