The Diocese of East Anglia (Latin: Dioecesis Angliae Orientalis) is a Latin diocese of the Catholic Church covering the counties of Cambridgeshire, Norfolk, Suffolk, and Peterborough in eastern England. The diocese makes up part of the Catholic Association Pilgrimage.
Diocese of East Anglia Dioecesis Angliae Orientalis | |
|---|---|
 Arms of the Roman Catholic Diocese of East Anglia | |
| Location | |
| Country | England |
| Territory | Counties of Norfolk, Suffolk, Cambridgeshire, and the Unitary Authority of Peterborough |
| Ecclesiastical province | Westminster |
| Deaneries | Bury St Edmunds, Cambridge, Great Yarmouth, Ipswich, King's Lynn, Norwich, Peterborough |
| Coordinates | 52°24′11″N 0°54′11″E / 52.403°N 0.903°E |
| Statistics | |
| Area | 12,570 km2 (4,850 sq mi) |
| Population - Total - Catholics | (as of 2019) 2,487,200 108,000[2] (4.3%) |
| Parishes | 50 |
| Schools | 28[1] |
| Information | |
| Denomination | Latin Church |
| Rite | Roman Rite |
| Established | 13 March 1976 |
| Cathedral | St John the Baptist Cathedral, Norwich |
| Patron saints | Our Lady of Walsingham, St. Felix, St. Etheldreda, St. Edmund |
| Secular priests | 96 |
| Current leadership | |
| Pope | Francis |
| Bishop | Peter Collins |
| Metropolitan Archbishop | Vincent Nichols |
| Vicar General | David Bagstaff |
| Bishops emeritus | Alan Hopes |
| Map | |
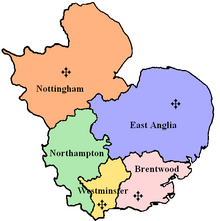 Roman Catholic Diocese of East Anglia, within the Province of Westminster | |
| Website | |
| RCDEA.org.uk | |
Statistics
editThere are 85,309 members of the church, who belong to the 50 parishes in the diocese. The patrons of the diocese are Our Lady of Walsingham (24 September), St Felix (8 March), and St Edmund (20 November).
Churches
editThe diocese is divided into seven deaneries, which are in turn divided into 50 parishes. Note that the list below is not exhaustive, and includes only notable parishes.
Deanery of Bury St Edmunds (St Edmund)
edit| parish name | church | location | web | founded | building |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St Edmund | St Edmund King & Martyr, Bury St Edmunds | Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk | [1] | 1763 | 1837 |
Masses are also said at RAF Lakenheath, at Clare Priory, at the Monastery of Our Lady of Mount Carmel in Quidenham, at the care home of the Sisters of Our Lady of Grace and Compassion in Great Barton, and in the villages of Cavendish and Woolpit.[3]
Deanery of Cambridge (St Andrew)
edit| parish name | church | location | web | founded | building |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Lady & the English Martyrs | Our Lady of the Assumption & the English Martyrs, Cambridge | Cambridge, Cambridgeshire | [2] | c. 1841 | 1890 |
| St Laurence | St Laurence, Cambridge | Cambridge, Cambridgeshire | [3] | early C20th | 1958 |
| St Etheldreda | St Etheldreda, Ely | Ely, Cambridgeshire | [4] | c. 1890 | 1903 |
| Sacred Heart | Sacred Heart, St Ives | St Ives, Cambridgeshire | [5] | late C19th | 1902 |
Masses are also said at RAF Alconbury, at Blackfriars, the Dominican Priory of St Michael, Cambridge, at Fisher House University Chaplaincy, and in the villages of Bar Hill and Papworth Everard.[3]
Deanery of Great Yarmouth (St Peter)
edit| parish name | church | location | web | founded | building |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Great Yarmouth | St Mary, Great Yarmouth | Great Yarmouth, Norfolk | [6] | 1824 | 1850 |
1No longer listed on diocesan website.
Deanery of Ipswich (St Edward)
edit- Aldeburgh with Leiston Parish[4]
- St James, Ipswich
- St Mark's Parish[5]
- St Mary's Parish[6]
- St Mary Magdalen, Ipswich[7]
- St Pancras, Ipswich[8]
- Woodbridge and Framlingham Parish[9][10]
Deanery of King's Lynn (St Wilfrid)
edit- St Dominic, Downham Market[11]
- Basilica of Our Lady of Walsingham[12]
- Our Lady & St Charles Borromeo, Wisbech[13]
Deanery of Norwich (St Felix)
editDeanery of Peterborough (St Hugh)
editHistory
editOn 13 March 1976, by the decree Quod Ecumenicum, Pope Paul VI formed the Diocese of East Anglia (from the counties of Cambridge, Norfolk and Suffolk) out of the Diocese of Northampton.
On 2 June 1976, the new diocese received its first bishop, Alan Clark. Bishop Clark had previously been auxiliary bishop of Northampton and co-chairman of ARCIC (Anglican/Roman Catholic International Commission), with the cathedral being established at the former parish church of St John the Baptist, Norwich. As the first bishop of the new diocese, Bishop Clark had to set up all the necessary instruments and commissions for the diocese to operate successfully. The establishment of the Diocesan Pastoral Council in 1987 strengthened these.
The diocese continued to grow with the development of the diocesan offices and diocesan tribunal attached to Bishop's House in Poringland near Norwich. Bishop Clark led a number of Lourdes pilgrimages.[16]
Ordinaries
edit- Alan Charles Clark (appointed on 26 April 1976 – retired on 21 March 1995)
- Peter David Smith (appointed on 21 March 1995 – translated to the Archdiocese of Cardiff on 26 October 2001)
- Michael Charles Evans (appointed on 14 February 2003 – died in office on 11 July 2011)
- Alan Hopes (appointed on 11 June 2013 - resignation accepted on 11 October 2022)
- Peter Collins (appointed on 11 October 2022 and installed on 14 December 2022)
Pilgrimage
editThe diocese makes up part of the Catholic Association Pilgrimage.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Find a School". www.RCDEA.org.uk. Roman Catholic Diocese of East Anglia. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- ^ "Catholic Hierarchy: Diocese of East Anglia". www.Catholic-Hierarchy.org. Retrieved 22 July 2020.
- ^ a b "Churches". www.RCDEA.org.uk. Roman Catholic Diocese of East Anglia.
- ^ aldeburghwithleistonrc. "Home – aldeburghwithleistonrc". aldeburghwithleistonrc.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Ipswich, St Mark's Catholic Parish. "St Mark's Catholic Parish". stmarksparish.org.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "st-mary.org.uk – Welcome to St Mary's Catholic Parish". st-mary.org.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Magdalen, St. Mary. "Home | St. Mary Magdalen | Roman Catholic Church, Ipswich, Suffolk, UK". marymagdalens.org. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Ltd., Glaccum Consulting. "St Pancras Catholic Church". stpancraschurch.org.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Parish of Woodbridge and Framlingham". wfrcp.org.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Calendar of Events". stthomas-woodbridge.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "St. Dominic's Catholic Church, Downham Market". stdomsdownham.blogspot.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Walsingham | National Shrine of Our Lady at Walsingham". www.walsingham.org.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Our Lady & St Charles Borromeo Roman Catholic Parish Church". catholic-wisbech.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Home". The Cathedral of St John the Baptist. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "www.stpeterandallsouls.org.uk – Welcome". stpeterandallsouls.org.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "History of the Diocese".
External links
edit- Roman Catholic diocese of East Anglia — official website