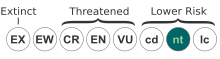
Pterogyne is a monotypic genus in the legume family, Fabaceae, subfamily Caesalpinioideae.[2] The sole species is Pterogyne nitens. Spanish common names include guiraró, palo coca, or tipa colorado.[1] In Portuguese, it is commonly known as amendoim bravo, cocal or madeira nova. It is found in Brazil, Paraguay, Bolivia and Argentina.[1] It is threatened by habitat loss and harvesting for timber.[1]
| Pterogyne | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Tribe: | Caesalpinieae |
| Genus: | Pterogyne Tul. |
| Species: | P. nitens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pterogyne nitens Tul.
| |
Five guanidine alkaloid natural products were isolated from the leaves of Pterogyne nitens: nitensidine D, nitensidine E, pterogynine, pterogynidine, and galegine.[3]
References
editWikimedia Commons has media related to Pterogyne.
- ^ a b c d Prado, D. (1998). "Pterogyne nitens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 1998: e.T32977A9739802. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.1998.RLTS.T32977A9739802.en. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ The Legume Phylogeny Working Group (LPWG). (2017). "A new subfamily classification of the Leguminosae based on a taxonomically comprehensive phylogeny". Taxon. 66 (1): 44–77. doi:10.12705/661.3. hdl:10568/90658.
- ^ Regasini, Luis Octávio; Castro-Gamboa, Ian; Silva, Dulce Helena Siqueira; Furlan, Maysa; Barreiro, Eliezer Jesus; Ferreira, Paulo Michel Pinheiro; Pessoa, Cláudia; Lotufo, Letícia Veras Costa; de Moraes, Manoel Odorico; Young, Maria Claudia Marx; Bolzani, Vanderlan da Silva (2009-03-27). "Cytotoxic Guanidine Alkaloids fromPterogyne nitens△". Journal of Natural Products. 72 (3). American Chemical Society (ACS): 473–476. doi:10.1021/np800612x. ISSN 0163-3864. PMID 19159272.