This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (March 2012) |
Parallel parking is a method of parking a vehicle parallel to the road, in line with other parked vehicles. Parallel parking usually requires initially driving slightly past the parking space, parallel to the parked vehicle in front of that space, keeping a safe distance, then followed by reversing into that space. Subsequent position adjustment may require the use of forward and reverse gears.


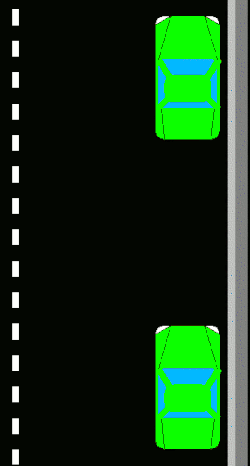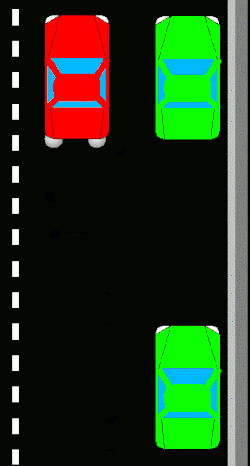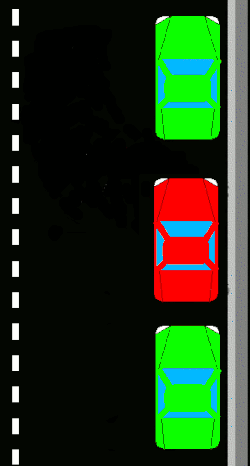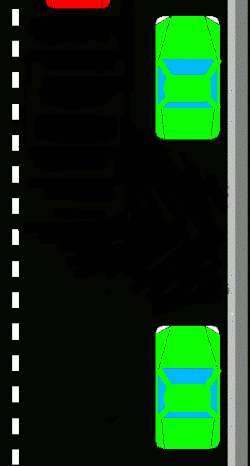

Techniques
editParallel parking is considered to be one of the most stressful and difficult skills for new drivers to learn.[1] While parallel parking is a required part of most driving tests, several states in the US have dropped it as a requirement.[2]
Parallel parking enables the driver to park a vehicle in a smaller space than would be true of forward parking. Driving forward into a parking space on the side of a road is typically not possible unless two or more successive parking spaces are empty. Reversing into the spot via the parallel parking technique allows one to take advantage of a single empty space not much longer than the car (in order to complete the parking within three wheel-turns the parking space would generally need to be about one and a half car-length long).
New drivers learn to use reference points to align themselves in relation to the car in front of the space, to determine the proper angle for backing, and to determine when to turn the steering wheel while backing. They may find it easier to briefly stop at each reference point and turn for the next step.
Steps
editTwo major types of parallel parking technique differ in whether they will use two or three positions of the steering wheel while backing. A skilled driver is theoretically able to parallel park by having their car move along two arcs, the first having its center on the parking side of the car and the second having its center on the other side. There will be a point in the transition between these curves where all the car's wheels will be parallel with each other. Less-confident drivers may choose to drive further while transitioning, making it a pronounced middle step of three. Such a step allows greater tolerances to avoid hitting anything, but forces the car to start further from the road's edge and requires more space to the rear.
Computer Assisted Parallel Parking
editBeginning in the early 2000s, automobile manufacturers began providing computer assisted automatic parking software on some models that allowed drivers to engage the software to complete the parallel parking maneuver hands-free. Depending on the system, the automatic parking feature controls the steering while the driver operates the accelerator and brakes,[3] or the software handles both steering and accelerator.[4]
Legality
editIn Japan, there is a ban on on-street parking, with a few exceptions (such as daytime and evening parking).[5][6] In addition to this, there is a proof-of-parking rule and motorists are required to present a garage certificate ("Shako shomei sho") to prove that they have a garage before being allowed to register a car.[7][8][9][10]
History
editIn the 1930s cars were developed with a fifth wheel, in between the two rear wheels and perpendicular to them, which could be lowered to the ground and used to drive sideways into a parallel parking spot. This innovation was intended to make parallel parking much easier, but it never became popular.[11]
See also
edit- Advanced Parking Guidance System
- Automatic parking
- Door zone
- Parallel parking problem: the mathematics of parallel parking
- Removal of curbside parking spaces: frees up space for bicycle lanes
- Perpendicular parking or bay parking
References
edit- ^ Nerad, Jack R. (February 8, 2021). "What Cars Park Themselves? These are the 10 Best Self-Parking Cars in 2021". JD Power. J.D. Power. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
Nothing is as taxing to most drivers as parallel parking.
- ^ Cafiero Giusti, Autumn. "Fewer states keep parallel parking on the driving test". autoinsurancecenter.com. Auto Insurance Center. Archived from the original on 2021-12-10. Retrieved 2021-12-10.
nearly one-third of the states in the union exclude parallel parking from their driving tests
- ^ Ulrich, Lawrence (January 13, 2009). "Testing Ford's Parallel Parking System". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Nerad, Jack R. (February 8, 2021). "What Cars Park Themselves? These are the 10 Best Self-Parking Cars in 2021". jdpower.com. J.D.Power. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
The systems differ in their complexity, with some providing no more than steering assistance while others can take full control and park the vehicle for you.
- ^ "Ban on overnight parking in Japan". Archived from the original on 2020-09-02. Retrieved 2020-09-03.
- ^ "Japan Road Traffic Act". Archived from the original on 2020-11-12. Retrieved 2020-09-03.
- ^ Application procedure for a vehicle parking space (garage) certificate
- ^ "Guidebook to provide foreign persons with information for living in Japan" (PDF). National Association for Japan Exchange and Teaching. March 2003. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-08-16.
- ^ "Guidebook of daily life for foreign residents" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-11-11. Retrieved 2020-09-03.
- ^ "Visitor information and life guide". Archived from the original on 2022-08-20. Retrieved 2020-09-03.
- ^ "The ingenious "fifth wheel" parallel parking tool that never hit it big". Archived from the original on 2021-12-26. Retrieved 2021-12-26.