This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
This page lists the municipal flags of Schleswig-Holstein. It is a part of the Lists of German municipal flags, which is split into regions, which in turn, is split into states due to its size.
Index by state
editDithmarschen
editAmt
edit| Municipality | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn |  |
 |
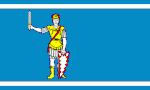
15 April 2009 | Banner of arms. The railway bridge (which crosses the Kiel Canal) comes from Burg-Süderhastedt and represents the merger of the former amts. The vine leaves come from Eddelak-Sankt Michaelisdonn and represents the windmills. The leaves represent the two former amts. Blue represents the Bordesholmer See and the Eider river. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [1][2] |
| Büsum-Wesselburen |  |
25 May 2008 | No official flag. The coat of arms depicts Saint Clement who the patron saint of seafarers. He is usually seen carrying an anchor. The four waves represent the municipality's past as an island. Designed by Hans-Frieder Kühne. | [3] | |
| Eider |  |
 |
16 November 2009 | Banner of arms. Blue represents the Eider river. Yellow and green represents the moraines and marshes respectively. The three stars represents Hennstedt and the former entities, swords represents Tellingstedt and wheel represents Lunden. Yellow represents farming. Blue represents the Baltic Sea and the Kiel Canal. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [4][5] |
| Heider Umland |  |
 |
1 January 2008 | A white flag with ten red and white stripes. The ploughs represents the eleven municipalities. The blue balance represents the former Amt Weddingstedt while the red wheel presents the former Heide-Land. Together, it represents progress, mobility and life. Five spokes of the wheel represents the municipalities of the former latter. The colors are the state colors of Schleswig-Holstein. Designed by Dirk Becker, Hermann Bolle, Heide Karstens, Uwe Nagel and Renate Stephan. | [6][7] |
| Marne-Nordsee |  |
 |
9 July 2009 | Banner of arms. The seagull is the bird that can be found anywhere in the world especially Marne-Nordsee. The wall represents Marne. The pinnacles represents the three former entities that formed the Amt. Blue represents the North Sea. The gate represents the Amt's commitment to openness and transparency. Green and blue alludes to the relationship between the marshes and the sea. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [8] |
| Mitteldithmarschen |  |
 |
27 June 2008 | Banner of arms. The design was said to be taken from the former entities that made up the Amt. The horse represents Meldorf-Land. The red stars represents Meldorf. The crosier represents Albersdorf and its patron saint, Saint Remigius. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [9] |
Municipalities
edit| Municipality | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Averlak |  |
 |
25 May 1990 | A white flag with two blue stripes, a green stripe with a hill and two houses and two blue shovels. The flag alludes to the location of the municipality. The blue represents the North Sea, the Kiel Canal and Kudensee. Shovels and houses represents the importance of soil-based construction. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [10][11] |
| Barkenholm |  |
 |
3 June 2002 | Banner of arms. Green represents the moorland, blue represents and yellow represents moraines. The seven bricks represents the seven brickyards. The wavy lines represents Broklandsau. The leaf is a common element of nature. | [12] |
| Bergewöhrden | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Brickeln |  |
 |
18 October 1995 | A white flag with two wavy blue stripes, two green leaves and a red wheel. Two green branches alludes to the name of the municipality. Two blue waves represents the creeks. The red wheel represents the former windmill. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [13][14] |
| Buchholz |  |
 |
9 February 1989 | A green-white-green flag with two leaves symboling the forests and two trees representing wood. Together, they symbolized the red beeches that used to cover the municipality. The design alludes to the origin of the name of the municipality (Buchholz = beech wood). Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [15][16] |
| Burg |  |
 |
26 August 1952 | A blue-white-blue flag with the a red castle and two blue keys. The red castle represents the Bökelnburg, which gives the municipality its name. The keys represent Saint Peter which the local church is dedicated. Two blue stripes represents the Burger Au and the Kiel Canal. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Lippert. | [17][18] |
| Büsum |  |
9 September 1991 | No official flag. The coat of arms features a red lighthouse and a blue krabbenkutter (a type of fishing boat). They both represent the North Sea and its dependence to sailors, fishers and tourists. | [19][20] | |
| Büsumer Deichhausen | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Dellstedt |  |
 |
15 April 1988 | Blue flag with the coat of arms. | [21] |
| Delve |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 8 May 1979 Flag: 11 September 1984 |
Green-yellow-green flag with the coat of arms. Green represents the rural areas, yellow represents the Eider Canal and white represents the Eider river. Designed by Hans-Jürgen Böhrnsen. | [22][23] |
| Diekhusen-Fahrstedt | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Dingen |  |
 |
5 December 1990 | A green and yellow flag with five green and yellow stripes. Yellow represents the moraines and agriculture. The green represents the marshes and meadows. The wavy lines alludes to the Friedrichshöfer Au. The chestnut and goshawk represents Dinger Donn. Designed by Gerard Peter Parkinson. | [24][25] |
| Dörpling | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Eddelak |  |
 |
25 October 1993 | Banner of arms. The coronet represents Eddelak, which in turn represents the Virgin Mary. The windmill represents the economy of Behmhusen. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [26][27] |
| Eggstedt |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 26 September 1985 Flag: 20 April 1988 |
Banner of arms. The harrow represents agriculture and the groves. Green represents pastures and farmers respectively. The corner, oak branches and the harrow alludes to the name of the municipality. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [28][29] |
| Fedderingen | No official flag or coat of arms. | ||||
| Frestedt |  |
 |
12 January 1993 | Banner of arms. The harrow represents agriculture and the groves. Green represents pastures and farmers respectively. The corner, oak branches and the harrow alludes to the name of the municipality. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [30][31] |
| Friedrichsgabekoog | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Friedrichskoog |  |
 |
2011 (de facto) | A blue and white flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms features depicts a farmhouse separated by a polder (which the municipality is named after) from the North Sea. | |
| Gaushorn | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Glüsing | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Großenrade |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 11 January 1991 Flag: 16 March 1992 |
Banner of arms. The axes and the cut down tree alludes to the name of the municipality. Green represents the woods that were cut down and nature. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [32][33] |
| Groven |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 12 November 1987 Flag: 12 November 1987 (de facto) |
A horizontal blue-white-red flag (representing Schweig-Holstein) with the coat of arms. The coat of arms alludes to the municipality's name. The white waves represents storms. The horse and the fish represents herding and fishing respectively. Designed by Günter Brietzke. | [34] |
| Hedwigenkoog |  |
13 July 1938 | No official flag. The coat of arms is based on a local legend that during warfare, a stork (representing Hedwigenkoog) and a snake (representing Ahlen) turned into a swan and a snake respectively. Fancinated by the legend, Frederick IV named this kroog (municipality) after his wife, Hedwig Sophie upon completion of the kroog's construction. He gave this coat of arms to his wife. Designed by Gustav Adolf Cloß. | [35][36] | |
| Hellschen-Heringsand-Unterschaar | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Helse |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 18 September 1995 Flag: 23 April 1996 |
A green-yellow-green flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms features the windmill/fire wheel/water whirlpool sculpture by Paul Heinrich Gnekow (which is located in the municipality's sports centre) as a symbolism of dynamism and progress. The ring represents the Goldenen Ring polder built the 11th century and the sapphire on the ring symbolizes the North Sea. Designed by Hans Frieder Kühne. | [37][38] |
| Hemme |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 26 January 1988 Flag: 27 September 1996 |
A blue flag with nine blue and yellow stripes. The flag represents the local parish church. The crown is represents Mary being the Queen of Heaven. Roses and lilies are usually ossicated with the Virgin Mary for puritym love and justness. Designed by Günter Brietzke. | [39] |
| Hemmingstedt |  |
 |
25 October 1988 | Banner of arms with eleven red and white stripes. This flag commemorates the battle of Hemmingstedt. The halberd represents the people of Dithmarschen while the lance represents Denmark. The flame represents oil. Designed by Hans Frieder Kühne. | [40][41] |
| Hennstedt |  |
 |
14 February 2005 | Banner of arms. Green represents marshes and yellow represents moraines. The white represents the Eider river. The embowed chief represents the hill that the municipality was built on. The wheel represents mobility and crafting. The spokes represents the places of the municipality. Willows are the trees usually seen in the municipality and its leaves represents clubs in the municipality. Green and yellow were the colours of the former Amt Hennstedt. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [42] |
| Hillgroven | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Hochdonn |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 6 December 1991 Flag: 21 July 1992 |
Banner of arms. Green represents agriculture. Green represents the woods that were cut down and nature. The railway bridge represents the Kiel Canal. The oak represents the Donn spit. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [43][44] |
| Hollingstedt | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Hövede | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Karolinenkoog |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 22 June 1984 Flag: 22 June 1984 (de facto) |
Banner of arms. The crown represents Princess Wilhelmina Caroline of Denmark, who the municipality is named after. The ears of grain represents soil. Designed by Günter Brietzke. | [45] |
| Kuden |  |
 |
12 January 1995 | Banner of arms. Yellow represents moraines. Blue represents marshes. The oak represents the Donn spit. The white fort represents the Kuden Fort. A green ear of grain represents agriculture. The green stick represents the municipality's first citizen. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [46][47] |
| Norddeich |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 27 February 2003 Flag: 2 December 2014 |
Banner of arms. The yellow rafter symbolizes the Goldener Ring dikes that allows farmers to harvest grain. The two white stars stands for the municipality's location and the Vogdemannen and the Beensman families (two of the municipality's well-known residents). The halberd is said to belonged to Ralves Karsten, who is a bailiff turned knight. He fought Hamburg from 1430 to 1434 while having his blood shed which represented by red. As a result of his courage through battle, he influenced the municipality and the surrounding areas. | [48][49] |
| Oesterdeichstrich | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Oesterwurth | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Quickborn |  |
 |
18 August 1993 | A green flag with nine green and white stripes. Yellow basin was said to be built around a well. Oak leaves represents the municipality's past as a forest. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [50][51] |
| Reinsbüttel |  |
 |
30 October 2001 | Banner of arms. The blue and white wavy pattern represents the Wahrstrom strait (Büsum used to be an island until a dam was constructed in 1585–1609). The house displayed on the flag usually found on polders and represents the municipality's first inhabitants. The cart represents the hard work of farmers. Green represents marshes. Yellow represents the harvest season. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Otto Peiser. | [52][53] |
| Sankt Michaelisdonn |  |
 |
6 December 1991 | A blue flag with nine blue and yellow stripes. The farmer killing the dragon with a scythe represents the legend of Saint Michael. The vane represents the local windmill. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Lippert. | [54][55] |
| Schülp |  |
 |
17 May 2013 | No official flag. Designed by Renate Kainzberger. | [56][57] |
| Strübbel | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Süderdeich |  |
6 December 2004 | No official flag. The rafter symbolizes the 24 thatched roof houses in the municipality and their important roles, the wheel represents agriculture and the branch stands for nature. Designed by H. Schönknecht. | [58][59] | |
| Süderhastedt |  |
 |
17 February 1993 | A green flag with nine white and green stripes. The swords alludes to the name of the municipality. Two ears of grains represent agriculture. Three roses represents the local church. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [60][61] |
| Warwerort |  |
 |
8 December 2014 | No official flag. Blue and eight white waves represent the North Sea and the former Warwerort port. The farmhouse and the three corn ears represent agriculture. Designed by Reimer Sievers. | [62][63] |
| Wesselburen |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 22 February 1901 Flag: 15 July 2015 |
Banner of arms. The bar and pallets represents the drainage trenches. The farmhouse represents those built on marshes. The municipality was developed during the Middle Ages through agriculture and the grain trade. In 1901, the king of Prussia granted the coat of arms to the municipality. Designed by Reinhold Boie. | [64][65] |
| Wesselburener Deichhausen | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Wesselburenerkoog | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Kaiser-Wilhelm-Koog | 26 June 1983 – | A white-blue flag with the coat of arms. Blue represents sea and white represents land. The coat of arms contains three seagulls represents the North Sea and the Elbe river. The ears of wheat symbolizes fertile land. The letter "W" represents William I. The cornflower, which forms the letter "W", is said to be the kaiser's favourite flower. Designed by Oskar Schwindrazheim.[66][67] |
 |
Kleve | 20 September 2004 – | Banner of arms. The division of the flag is represents the location of the municipality in the Dithmarscher Geest. The horse represents breeding and equestrianism.. The two blue waves symbolizes the Eider river and the Brocklandsau. Blue, white and red are the colours of Schleswig-Holstein. Designed by Uwe Nagel and Nanett Schnittkowski.[68] |
 |
Krempel | 24 February 1993 – | A green-yellow flag with the coat of arms. The black eagle represents the Wurtmannen family which ruled over the municipality. It also represents the power of the Holy Roman Empire until 1559. The gnarled pine stands for overcoming disasters. The pine tree represents regrowth. Green symbolizes agriculture and yellow for sand dunes and nature. Designed by Günter Brietzke.[69] |
 |
Kronprinzenkoog | 29 August 1995 – | A green and yellow flag with two black waves in the yellow stripes. The coat of arms comes from the picture window of the meeting rooms in the municipal hall in Meldorf. It depicts a sower, who is actually Frederick VI, Count of Zollern (which the polder is named after). Green stands for land, black for the marshes and yellow for the crops. Designed by Hans Frieder Kühne and Oskar Schwindrazheim.[70][71] |
 |
Lehe | 8 February 1988 – | A red-white flag with the coat of arms. The eagle and the lily is said to be symbols of the Wurtmannen family. The blue represents the Eider river which the municipality is located. The coat of arms was made to honor Peter and Markus Swyn. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Lippert.[72] |
 |
Lieth | 22 March 2002 – | Banner of arms. White represents the sky and green represents the soil. An oil well and a plough symbolizes industry.[73][74] |
 |
Linden | 14 December 1987 – | A blue-white flag with the coat of arms surrounded by twelve stars. The tree represents water as a source of agriculture. The nasselblatt represents Holstein. The star pays homage to the European Union (which Germany is a member of). Designed by Gerhard Schwabe.[75] |
 |
Lohe-Rickelshof | 15 December 2010 – | Banner of arms. The white triangle and the oak leaf represents Lohe and its beautiful scenery filled with forests and the red triangle and a gear represents Rickelshof with its powerful steel industry. Designed by Hans Heinz Domke.[76][77] |
 |
Lunden | 25 January 1991 – | Blue flag with the coat of arms. The black eagle represents the Holy Roman Empire. The red iron grid represents Saint Lawrence. Designed by Günter Brietzke.[78] |
 |
Neuenkirchen | 15 December 2010 – | Green-yellow flag with the coat of arms. The red church symbolizes the local parish while the white cottongrass represents the Weißes Moor. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[79][80] |
 |
Norderheistedt | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Norderwöhrden | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Nordhastedt | 19 January 1990 – | A white flag with seven red and white stripes. The peasant with the halberd represents the legends of female defenders of the municipality from criminals (which is an inspiration for Dorffest Frunsbeer). Designed by Georg Fink and Hans Frieder Kühne.[81][82] |
 |
Ostrohe | 9 July 1989 – | A red-white-red flag. The red stripes symbolizes the present, the oak leaf represents the beautiful forests of Behnkeforst, the cattail represents the Ostroher Moor and the ear of corn represents traditional industry through agriculture. Designed by Dirk Becker.[83][84] |
 |
Pahlen | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Rehm-Flehde-Bargen | 23 March 1990 – | A green-yellow-green flag with the coat of arms. The total number oak leaves represents Rehm, Flehde and Bargen. The oak leaves represents Rehm and the fact that the municipality used to be a forest area, the white wave represents Flehde and the hills represent Bargen. Designed by Günter Brietzke.[85] |
 |
Sankt Annen | 23 September 2010 – | A blue-white horizontal flag with the coat of arms. A blue flag with nine blue and yellow stripes. It depicts Saint Anne (representing the local church) and three fishes crucians (representing either Neufeld, Damm and Österfeld, which are the former municipalities that made up Sankt Annen, the three streams from the Eider river or Heymen Claus, Russen Marquart and Junge Claus Johann of the Russebolingmannen family). Blue symbolizes the Eider river and the location of the three former of islands of Neufeld, Damm and Österfeld. Designed by Günter Brietzke.[86] |
 |
Schalkholz | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Schlichting | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Stelle-Wittenwurth | 30 January 1998 – | The farmhouse on the hill represents a typical house that was built on the Wittenwurth hill. The oak leaves represents the oak forests that used to be located in the marshes of the municipality. White represents the North Sea and the green represents land. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[87][88] |
 |
Süderdorf | 6 May 2009 – | Banner of arms. The four quarters represents Lendern, Lüdersbüttel, Schelrade and Wellerhop (the former municipalities that made up Süderdorf). The sun acts like a cardinal point. The horseshoes represents agriculture and the farmers. The foliage leaf represents the trees. Blue stands for the two main watermills. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[89] |
 |
Süderheistedt | 25 August 1999 – | Banner of arms. The magpie and tree represents the legend of the Dithmarscher Wunderbaum tree that gained the municipality its freedom. As a result of the disappearing tree, the municipality had to plant a seedling in its place. The oak leaves represents the Süderheistedter and Mount Vogelstange. The line represents the Broklandsau. The flag expresses the location of the municipality (green for geest areas and white for moor areas). Designed by Thies Rohwedder.[90] |
 |
Tellingstedt | 23 November 2009 – | A blue flag with the eight blue and white stripes. The flag depicts Martin of Tours cutting a piece of his cape with a sword. He represents the local church. The silver jug represents the importance of pottery. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[91] |
 |
Tielenhemme | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Wallen | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Weddingstedt | 23 November 1989 – | A white flag with two red stripes. Blue, white and red are state colours. The blue scales represent the power of the authorities during Middle Ages to the 19th century. Designed by Dirk Becker.[92][93] |
 |
Welmbüttel | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Wesseln | 19 June 1989 – | Blue stands for the North Sea, yellow for corn growing on geest and green is a representation of the Rugenberg burial mound that is surrounded by marshes in meadows. The three trees represents the forests that surrounded the municipality.[94][95] |
 |
Westerborstel | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Westerdeichstrich | 12 December 2005 – | Banner of arms. The green windmill represents the Margaretha, the spade represents dykes and treforestation and the mermaid represents the tourism industry. Designed by Reinhold Boie.[96][97] |
 |
Wiemerstedt | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
 |
Wöhrden | 5 September 2005 – | Banner of arms. The green hill represents the wurt and agriculture. The red church is a depiction of the local church. The two blue waves stands for the municipality's former status as a seaport next to the North Sea. The green swords represents blood spilled from its citizens from 1319 to 1500. Designed by Manfred Rüthlein.[98][99] |
 |
Wrohm | TBA | No official flag or coat of arms. |
Former amts
edit| Municipality | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burg-Süderhastedt |  |
15 December 1975 1 January 2008 |
No official flag. | ||
| Büsum |  |
15 April 1991 25 May 2008 |
No official flag. The coat of arms was reenacted as the coat of arms of Büsum-Wesselburen on 25 May 2008. | ||
| Eddelak-Sankt Michaelisdonn |  |
15 December 1975 1 January 2008 |
No official flag. | ||
| Heide-Land |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 22 November 2000 Flag: 8 December 2001 1 January 2008 |
Banner of arms. The wheel represents Catherine of Alexandria (who is the patron saint of Nordhastedt), agriculture, and technology. Its spokes represents the five municipalities of the amt. The fleur-de-lis represents the Virgin Mary who the patron saint of Hemmingstedt. The anchor stands for Designed by Hermann Bolle. The anchor represents Saint Nicholas who is the patron saint of Wöhrden. Red and white are country colours of Dithmarschen and green represents nature (from the moors of the Fieler Moor to the forests of Riesewohld). The green and white rays represents the farming communities of the amt. | [100] |
| Hennstedt |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 10 April 1987 Flag: 30 January 1998 1 January 2008 |
Banner of arms. Green and yellow represents the merger of Amt Delve and Hennstedt in 1970. They also represent marshes and moraines. The twelve stars represents the communities in the Amt and the European Union. Designed by Gerhard Schwabe. | [101] |
| Tellingstedt |  |
 |
13 July 1989 1 January 2008 |
A blue flag with nine blue and white stripes. The flag depicts Martin of Tours cutting a piece of his cape with a sword. He represents the local church. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Lippert. | [102] |
| Weddingstedt |  |
16 November 1999 1 January 2008 |
No official flag. | ||
| Wesselburen | No official flag or coat of arms. |
Former municipalities
edit| Municipality | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wesselburen |  |
 |
17 July 2010 15 July 2015 |
White flag with the coat of arms. |
Flensburg
edit| Municipality | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flensburg |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 1 May 1901 Flag: 30 June 1938 |
A blue flag with the coat of arms. The two blue lions represents the Duchy of Schleswig, the silver nettle leaf in the red shield represents the Duchy of Holstein. The red tower represents the defense of the city. The waves represents the city's connection to the North Sea. Designed by Johannes Holtz, Max Kirmis, Erwin Nöbbe and Heinrich Sauermann.[103][104][105] |
| Vertical variant. |
Communities
edit| Community | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mürwik |  |
A blue and yellow flag with the coat of arms. |
Herzogtum Lauenburg
editAmt
edit| Flag | Amt | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Berkenthin | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Breitenfelde | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Büchen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hohe Elbgeest | 25 June 2002 – | Red flag with the coat of arms. The eight blue pales (rays of sun) represents the municipalities. The red sun represents Herzogtum Lauenburg. The colors are the state colors of Schleswig-Holstein. Designed by Ulrich Zündel.[106] |
 |
Lauenburgische Seen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Lütau | 9 July 2008 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Walter Lehmann. |
 |
Sandesneben-Nusse | 1 January 2008 – | Banner of arms. The blue wave pattern represents the creeks while the shelves represents the rural environment. The green lozenges represents the twenty-five municipalities. The red horseheads represents the two former Amts. Designed by Wolfgang Bentin.[107] |
 |
Schwarzenbek-Land | 6 December 1991 – | Banner of arms. The horse represents Herzogtum Lauenburg. The lily comes from the Schack noble family. The balls represents nineteen municipalities. Designed by Walter Lehmann.[108] |
Municipalities
edit| Flag | Municipality | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Düchelsdorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hornbek | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Rondeshagen | TBA | No official flag. |
Kiel
edit| Municipality | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiel |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 14 May 1901 Flag: 1921 |
Banner of arms. A red flag based on the County of Schaumburg with a black boat representing the city's importance as a port. | [109] |
| Vertical variant. |
Lübeck
edit| Municipality | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lübeck |  |
 |
Coat of arms: 1450 Flag: 22 January 1941 |
White-red bicolor with a black eagle the Lübeck double eagle. | [110] |
| Vertical variant. |
Nordfriesland
editAmt
edit| Flag | Amt | Enactment Date | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Eiderstedt | 10 September 2012 – | The colours are said to have come from the coat of arms. Designed by Uwe Nagel. | [111] |
 |
Föhr-Amrum | TBA | No official flag. | |
 |
Landschaft Sylt | TBA | No official flag. | |
 |
Mittleres Nordfriesland | TBA | No official flag. | |
 |
Nordsee-Treene | TBA | No official flag. | |
 |
Pellworm | TBA | No official flag. | |
 |
Südtondern | 1 January 2008 – | Banner of arms. The lighthouse represents Südtondern while its rays of light represents the six municipalities. The flag contains the color of the flag of North Frisia. Blue represents the Wadden Sea, yellow representing the moraines, dunes and fields of rapeseeds, green represents marshes, agriculture and woods and white represents water. The cauldron is said to represent the fraternalism and attention of the Frisii. Designed by Burmeister. | [112] |
 |
Viöl | 14 April 2011 – | Banner of arms. White with thirteen red planks (representing the municipalities) forming a bridge over the blue Arlau river and two crosses (representing Viöl and Schwesing) surrounded by a white border. Designed by Kurt Hans Ernst August Peter. | [113][114] |
Ostholstein
editAmt
edit| Municipality/Amt | Flag | Coat of arms | Enactment Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Großer Plöner See | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Lensahn |  |
7 September 2001 | No official flag. | |
| Oldenburg-Land | No official flag or coat of arms. | |||
| Ostholstein-Mitte |  |
8 April 2008 | No official flag. |
Pinneberg
editAmt
edit| Flag | Amt | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Elmshorn-Land | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Geest und Marsch Südholstein | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hörnerkirchen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Pinnau | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Rantzau | 30 January 1998 – | Blue flag with the coat of arms. The first and fourth quarters comes from the County of Rantzau. The ten black lozenges represents the municipalities. The blue bend sinister wavy represents the Krückau river. The arrangement of lozenges is said to represent Lutzhorn (three), Hemdingen (four) and Bevern (three). Designed by Hannelore von Engelhardt.[115] |
Plön
editAmt
edit| Flag | Amt | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Bokhorst-Wankendorf | 27 May 2010 – | Banner of arms. The grain of ears from the coat of arms of the former Amt Wankendorf to represent the four municipalities. The wavy pattern represents the creeks and lakes. Designed by Henning Höppner.[116][117] |
 |
Bordesholm | 13 March 2008 – | Banner of arms. The farm and leaves (which is said to be linked to a linden tree) comes from the old coat of arms. The book is also from the old coat of arms. However, the number of leaves are two instead of thirteen (representing the municipalities). Blue represents Bordesholmer See and the Eider river. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[118][119] |
 |
Großer Plöner See | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Lütjenburg | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Preetz-Land | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Probstei | 31 October 2002 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Henning Höppner. |
 |
Schrevenborn | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Selent/Schlesen | 25 February 2008 – | Blue flag with the coat of arms. Designed by Henning Höppner. |
Rendsburg-Eckernförde
editAmt
edit| Flag | Amt | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Achterwehr | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Berkenthin | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Dänischenhagen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Dänischer Wohld | 10 December 2008 – | Banner of arms. The leaves represents the eight municipalities. The white cross on red represents Denmark that Schleswig-Holstein used to be part of. The flag alludes to the name of the Amt. Designed by Henning Höppner.[120] |
 |
Eiderkanal | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Flintbek | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Fockbek | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hohner Harde | 3 September 1998 – | Banner of arms. The green hill represents Eichberg, which gave the amt's name. The rooster represents the history of the Harde area. The leaves represents the twelve municipalities. Green represents the Amt's rural environment while yellow represents Schleswig. Fesigned by Manfred Rüthlein.[121] |
 |
Hüttener Berge | 1 January 2008 – | A horizontal green-yellow bicolor flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms represents the Amt's reputation as a hunting lodge. Fesigned by Uwe Nagel.[122] |
 |
Jevenstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Mittelholstein | TBA |
Municipalities
edit| Flag | Municipality | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Achterwehr | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ascheffel | 12 April 1989 – | Banner of arms. The flag represents the "Scheffel an der Au", which the municipality gets its name from. The bushel and the ears of grain represents agriculture. The blue wavy line represents the Rohau river, located in the east. The three yellow hills represents the Hüttener mountains. Gold represents harvest and the Hüttener Berge. Blue and yellow are the traditional colours of Schleswig. Designed by Manfred Rüthlein.[123][124] |
 |
Ahlefeld-Bistensee | 14 May 1998 – | The flag was originally belonged to Bistensee. The mountain represents the Hütten Hills. Yellow represents the bloom of rapeseed. The fish in the blue represents the Binsensee. Designed by Mr. & Mrs. Kohrt and Uwe Nagel.[125][126] |
 |
Borgstedt | 30 January 1998 – | Banner of arms. The white wavy line that represents the Eider River, the Eider Canal and the Kiel Canal and their contribution to shipping. The wheel represents mobility. As the most striking manifestation of modern man's restlessness, the A7 motorway touches the municipal area in the north-east. The dingstock represents togetherness. Green represents nature. Designed by Wolfgang Wissenbach.[127][128] |
 |
Bredenbek | 7 November 1996 – | Designed by Reinhard Siedenburg. |
 |
Brekendorf | 22 August 1996 – | Banner of arms. The ant represents the ant plague (which destroyed the former location) that gave the municipality its name. The Dreiberg symbolizes the location of the town in the middle of hills on the edge of the "Hüttener Berge". The disc represents archaeology. Yellow and blue are the colours of Schleswig. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[129][130] |
 |
Bünsdorf | 17 September 1990 – | Banner of arms. The red church represents the local church. The blue wavy lines represents the Westensee. The green leaves represents the Hüttener Berge. The total number of leaves represents the settlements that made up the municipality (Bünsdorf, Schirnau, Steinrade and Wentorf). Designed by Alice Thomsen.[131][132] |
 |
Damendorf | 7 January 1985 – | Banner of arms. The wolf represents the past presence of the animal in the municipality. The oak trees and the hills represents the Hüttener Berge. The gravestone represents archaeology. Blue and yellow are colours of Schleswig. Designed by Manfred Rüthlein.[133][134] |
 |
Felde | 4 May 1993 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Uwe Nagel and Reinhard Siedenburg. |
 |
Groß Wittensee | 14 March 2017 – | Banner of arms. The alludes to the location of the municipality and the "Hüttener Berge" nature park. White hills and the trees represents wooden hilly landscape. The trees also represent the "Hüttener Harde". The flag serves as a testimony to the traditional forest wealth of the district. The blue wavy lines the Wittensee. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[135][136] |
 |
Haby | 22 August 2000 – | Banner of arms. The three horseshoes represents blacksmiths and farmers. The wild rose alludes to the name of the town. White represents the Schilksee and Westensee lakes. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[137][138] |
 |
Holtsee | 11 October 1993 – | Banner of arms. The oak tree and the waves represents the origin of the municipality's name. The name comes from a lake located in the Danish Wohlds forest area. Gold represents agriculture. Designed by Alice Thomsen.[139][140] |
 |
Holzbunge | 21 August 1995 – | Banner of arms. The beech and oak leaves and the wooden lodge represents the origin of the municipality's name. Its name means "built at the woods". The lodge represents construction and the leaves represents forests. Designed by Uwe Nagel.[141][142] |
 |
Hütten | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Klein Wittensee | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Krummwisch | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Melsdorf | 5 May 2008 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Manfred Rüthlein. |
 |
Neu Duvenstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Osterby (Rendsburg) | 21 June 1999 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Uwe Nagel. |
 |
Ottendorf | 24 May 1992 – | A blue-white-blue flag with the coat of arms. Designed by Manfred Rüthlein. |
 |
Owschlag | 9 March 2000 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Heinz Hentschel. |
 |
Quarnbek | 24 October 2002 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Gerlind Lind. |
 |
Sehestedt | 24 November 1998 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Heinz Reinhold and Alice Thomsen. |
 |
Westensee | 21 February 1990 – | Banner of arms. Designed by Manfred Rüthlein. |
Schleswig-Flensburg
editMunicipalities
edit| Flag | Municipality | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Achtrup | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ahrensbök | 22 January 1941 – | |
 |
Ahrenshöft | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ahrenshöft | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ahrenviölfeld | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Albsfelde | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Alkersum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Almdorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Arkebek | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Arlewatt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Aukrug | ||
 |
Albersdorf | 24 March 1980 – | |
 |
Bargum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Barlt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Basedow | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Behrendorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Belau | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Bohmstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Bokel | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Bokholt-Hanredder | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Bondelum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Bordelum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Borgsum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Braderup | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Bramstedtlund | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Brande-Hörnerkirchen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Bröthen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Buchhorst | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Dunsum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ellerhoop | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ellhöft | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Elmenhorst (Lauenburg) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Elpersbüttel | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Embühren | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Emmelsbüll-Horsbüll | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Escheburg | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Fahren | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Fredeburg | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Fresendelf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Friedrich-Wilhelm-Lübke-Koog | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Fuhlenhagen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Garding (Kirchspiel) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Giesensdorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Grabau (Lauenburg) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Gröde | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Groß Offenseth-Aspern | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Großharrie | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Grothusenkoog | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Gudendorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Gülzow | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Haseldorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hattstedtermarsch | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Havekost | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hemdingen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Holm (Nordfriesland) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hooge | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hörsten | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Hude | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Humptrup | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Immenstedt (Dithmarschen) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Immenstedt (Nordfriesland) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Juliusburg | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Kalübbe | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Karlum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Kirchnüchel | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Klein Zecher | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Kletkamp | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Köthel (Lauenburg) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Kotzenbüll | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Klanxbüll | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Krüzen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Kühren | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Krüzen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Kulpin | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Labenz | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Langeneß | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Langenhorn | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Lanze | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Lexgaard | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Linau | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Luhnstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Lütau | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Marnerdeich | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Midlum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Mildstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Möhnsen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Mönkeberg | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Nebel | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Nettelsee | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Neu Duvenstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Neufelderkoog | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Neukirchen (Nordfriesland) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Nieblum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Norddorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Norderfriedrichskoog | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Nordermeldorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Norderwöhrden | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Nordstrand | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Norstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ockholm | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Odderade | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Oevenum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Offenbüttel | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Olderup | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Oldsum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Osterhever | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Osterhorn | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Oster-Ohrstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Pahlen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Pellworm | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Poggensee | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Poppenbüll | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Raa-Besenbek | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Ramhusen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Rantrum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Rickert | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Rodenäs | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Römnitz | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Schillsdorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Schmedeswurth | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Schönbek | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Schrum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Schwesing | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Siebeneichen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Simonsberg | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Sprakebüll | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Stedesand | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Süderende | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Süderhöft | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Südermarsch | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Tasdorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Techelsdorf | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Tensbüttel-Röst | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Tetenbüll | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Tinningstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Trennewurth | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Uphusum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Utersum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Vollerwiek | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Volsemenhusen | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wangelau | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Welt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wennbüttel | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wentorf (Sandesneben) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Westerborstel | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Westerhever | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Westre | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wester-Ohrstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wiemerstedt | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wisch (Nordfriesland) | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Witsum | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wittdün | TBA | No official flag. |
 |
Wrohm | TBA | No official flag. |
-
Bad Bramstedt
(variant) -
Fehmarn (variant)
-
Leck (variant)
-
Lütjenburg (variant 1)
-
Lütjenburg (variant 2)
-
Malente (variant)
-
Mölln (variant)
-
Neumünster (variant)
-
Ratekau (variant)
Historical
edit-
Albersdorf (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Aukrug (Amt; 1998–2012)
-
Bönningstedt (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Bredstedt-Land (Amt; 2003–2008)
-
Friedrichstadt (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Hattstedt (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Hohenwestedt-Land (Amt; 1988–2012)
-
Lunden (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Nordstrand (Amt; 2005–2008)
-
Nusse (Amt; 1999–2008)
-
Osterrönfeld (Amt; 2000–2008)
-
Sandesneben (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Stollberg (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Süderlügum (Amt; 1991–2008)
-
Treene (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Wankendorf (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Weddingstedt (Amt)[citation needed]
-
Bistensee (1998–2008)
-
Heligoland (1807–1890)
-
Klausdorf (1979–2008)
-
Lübeck (13th century; Hanseatic flag)
-
Lübeck (1903-1918)
-
Lübeck (sea flag; 1921-1935)
-
Raisdorf (1968–2007)
Segeberg
editAmt
editMunicipalities
editSteinburg
editAmt
editMunicipalities
editStormarn
editAmt
editMunincipalities
editReferences
edit- ^ "Amt Burg-St. Michaelisdonn, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung des Amtes Burg-St. Michaelisdonn" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Amt Kirchspielslandgemeinde Büsum, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Kirchspielslandgemeinden Eider, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "GESCHICHTE DES AMTES UND DEREN ANGEHÖRIGEN GEMEINDEN". Amt Eider.
- ^ "Amt Kirchspielslandgemeinde Heider Umland, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung des Amtes Kirchspielslandgemeinde Heider Umland" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Amt Marne-Nordsee, Kreis Herzogtum Lauenburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Mitteldithmarschen, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Averlak, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Averlak (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Barkenholm, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Brickeln, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Brickeln (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Buchholz, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Buchholz (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Burg (Dith), Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Burg (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Büsum, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Büsum, Kreis Dithmarschen" (PDF). Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Gemeinde Dellstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Delve, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Delve Kreis Dithmarschen". Amt Eider.
- ^ "Gemeinde Dingen, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Dingen (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Dingen, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Eddelak (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Eggstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Eggstedt (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Frestedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Frestedt (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Großenrade, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Großenrade (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Groven, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Hedwigenkoog, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Hedwigenkoog, Kreis Dithmarschen" (PDF). Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Gemeinde Helse, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Helse und 1. Änderung" (PDF). Amt Marne-Nordsee.
- ^ "Gemeinde Hemme, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Hemmingstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Hemmingstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen in der Fassung vom 19.07.2018" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Hennstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Hochdonn, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Hochdonn (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Karolinenkoog, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Kuden, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Kuden (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Norddeich, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Norddeich, Kreis Dithmarschen vom 28. Oktober 2008" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Reinsbüttel, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Quickborn (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Sankt Michaelisdonn, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Reinsbüttel, (Kreis Dithmarschen) vom 11. November 2008 *)" (PDF). Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Gemeinde Sankt Michaelisdonn, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Sankt Michaelisdonn (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Gemeinde Schülp, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Schülp, (Kreis Dithmarschen) vom 05. Januar 2009". Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Gemeinde Süderdeich, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Schülp, (Kreis Dithmarschen) vom 05. Januar 2009". Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Gemeinde Süderhastedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Süderhastedt (Kreis Dithmarschen)" (PDF). Amt Burg-Sankt Michaelisdonn.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Warwerort, Kreis Dithmarschen vom 11. Juni 2003 *)". Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Gemeinde Warwerort, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Stadt Wesselburen, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Stadt Wesselburen" (PDF). Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Gemeinde Kaiser-Wilhelm-Koog, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Kaiser-Wilhelm-Koog" (PDF). Amt Marne-Nordsee.
- ^ "Gemeinde Kleve, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Krempel, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Kronprinzenkoog, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Kronprinzenkoog" (PDF). Amt Marne-Nordsee.
- ^ "Gemeinde Lehe, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Lieth, Kreis Dithmarschen in der Fassung der 1. Änderungssatzung vom 28.10.2021" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Lieth, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Linden, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Lohe-Rickelshof" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Lohe-Rickelshof, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Lunden, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Neuenkirchen Kreis Dithmarschen" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Neuenkirchen, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Nordhastedt, Kreis Dithmarschen" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Nordhastedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Ostrohe in der Fassung der Änderungssatzung vom 28.10.2021" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Ostrohe, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Rehm-Flehde-Bargen, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Sankt Sankt Annen, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Stelle-Wittenwurth (Kreis Dithmarschen) in der Fassung vom 27.04.2015" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Stelle-Wittenwurth, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Süderdorf, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Süderheistedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Tellingstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Weddingstedt Kreis Dithmarschen in der Fassung der 1. Änderungssatzung vom 16.07.2018" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Weddingstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Wesseln" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Wesseln, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Stadt Westerdeichstrich, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Westerdeichstrich, Kreis Dithmarschen vom 06. Juni 2003 *)" (PDF). Amt Büsum-Wesselburen.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Wöhrden, Kreis Dithmarschen in der Fassung der 1. Änderungssatzung vom 21.09.2017" (PDF). Amt Heider Umland.
- ^ "Gemeinde Wöhrden, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Kirchspielslandgemeinde Heide-Land, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Kirchspielslandgemeinde Hennstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Kirchspielslandgemeinde Tellingstedt, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Kreisfreie Stadt Flensburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Stadtportrait". Flensburg.
- ^ Oeding, Andreas; Schwensen, Broder; Sturm, Michael (2009). Flexikon. 725 Aha Erlebnisse aus Flensburg!. Gesellschaft für Stadtgeschichte. ISBN 978-3925856617.
- ^ "Amt Hohe Elbgeest, Kreis Herzogtum Lauenburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Schwarzenbek-Land, Kreis Plön". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Schwarzenbek-Land, Kreis Plön". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ § 1 Abs. 3 der Hauptsatzung der Schleswig-Holsteinschen Landeshauptstadt Kiel
- ^ § 1 Abs. 4 der Hauptsatzung der Hansestadt Lübeck, genehmigt am 22. Januar 1941
- ^ Hauptsatzung des Amtes Eiderstedt in der Fassung, 10 September 2012
- ^ "Amt Südtondern, Kreis Nordfriesland". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Viöl, Kreis Nordfriesland". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amtswappen". Amt Viöl.
- ^ "Amt Rantzau, Kreis Pinneberg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Bokhorst-Wankendorf, Kreis Plön". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Wappen und Flagge". Amt Bokhorst-Wankendorf.
- ^ "Amt Bordesholm, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "WAPPEN". Amt Bordesholm.
- ^ "Amt Dänischer Wohld, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Hohe Elbgeest, Kreis Herzogtum Lauenburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Amt Hüttener Berge, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Gemeinde Ahrensbök, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Ascheffel". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Averlak, Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Ahlefeld-Bistensee". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Borgstedt, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Borgstedt (Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde)". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Brekendorf, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Brekendorf". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Bünsdorf, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Bünsdorf". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Damendorf, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Damendorf". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Groß Wittensee, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holste.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Groß Wittensee". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Haby, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Groß Wittensee". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Holtsee, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Holtsee". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ^ "Gemeinde Holzbunge, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Gemeinde Holzbunge". Amt Hüttener Berge.
- ReißMann, Martin (1997). Wappen der Kreise, Ämter, Städte und Gemeinden in Schleswig-Holstein. Landesarchiv Schleswig-Holstein. ISBN 978-3-88042-815-7.
- Schlothfeldt, Hans (1964). Schleswig-Holsteinische Kreis- und Ortswappen.
- Stadler, Klemens (1970). Deutsche Wappen – Bundesrepublik Deutschland, Band 5 – Die Gemeindewappen der Bundesländer Niedersachsen und Schleswig-Holstein.







































































































































































































































































































































































































![Albersdorf (Amt)[citation needed]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b0/No_flag.svg/150px-No_flag.svg.png)















