Dixanthogen disulfides are a class of organosulfur compounds with the formula (ROC(S)S)2. Usually yellow solids, they are the product of the oxidation of xanthate salts.[1] A common derivative is diethyl dixanthogen disulfide. Diisopropyl dixanthogen disulfide is commercially available. They are structurally related to thiuram disulfides.
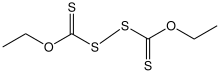
Structure of diethyl dixanthogen disulfide.
Uses and reactions edit
Diethyl dixanthogen disulfide is a component for froth flotations used, inter alia, for the separation of sulfide minerals like pyrrhotite. Diisopropyl dixanthogen disulfide is a reagent in the synthesis of sulfur heterocycles.[2]
Dialkoxy dixanthogen disulfides undergo desulfurization by cyanide to give bis(alkoxythiocarbonyl)sulfides:[3]
- (ROC(S)S)2 + CN− → (ROC(S))2S + SCN−
Dixanthogens are also ectoparasiticides.
References edit
- ^ Schroll, Alayne L.; Barany, George (1986). "Novel Symmetrical and Mixed Carbamoyl and Aminopolysulfanes by Reactions of (Alkoxydichloromethyl)polysulfanyl Substrates with N-Methylaniline". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 51 (10): 1866–1881. doi:10.1021/jo00360a039.
- ^ Gareau, Yves; Beauchemin, André (1998). "Free Radical Reaction of Diisopropyl Xanthogen Disulfide with Unsaturated Systems". Heterocycles. 48 (10): 2003. doi:10.3987/COM-98-8230 (inactive 2024-02-17).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of February 2024 (link) - ^ Tobón, Yeny A.; Castellano, Eduardo E.; Piro, Oscar E.; Della Védova, Carlos O.; Romano, Rosana M. (2009). "Spectroscopic and structural studies of bis[isopropoxy(thiocarbonyl)]sulfide, [(CH3)2CHOC(S)]2S". Journal of Molecular Structure. 930 (1–3): 43–48. Bibcode:2009JMoSt.930...43T. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2009.04.033.
