Diiodobutadiyne (1,4-diiodobuta-1,3-diyne) is a small molecule related to diacetylene. It is used in the creation of the polymer poly(diiododiacetylene) (PIDA) by undergoing 1,4 polymerization.[1]
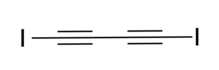
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,4-Diiodobuta-1,3-diyne
| |
| Other names
Diiododiacetylene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4I2 | |
| Molar mass | 301.853 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Solubility in hexanes | Soluble |
| Structure | |
| Linear | |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | Sensitive - may explode if struck |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Diacetylene, PIDA |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,4-Diiodobuta-1,3-diyne is light sensitive and explosive if stored out of solution as a dry solid. It will undergo random 1,2 and 1,4 polymerization, as well as decomposition in solution if kept over an extended period of time, having a half life of just about two weeks.[2]
References edit
- ^ Sun, A.; Lauher, J.W.; Goroff, N.S. (2006), "Preparation of Poly(Diiododiacetylene), an Ordered Conjugated Polymer of Carbon and Iodine", Science, 312 (5776): 1030–1034, Bibcode:2006Sci...312.1030S, doi:10.1126/science.1124621, PMID 16709780, S2CID 36045120
- ^ Luo, Liang; Wilhelm, Christopher; Sun, Aiwu; Grey, Clare P.; Lauher, Joseph W.; Goroff, Nancy S. (2008), "Poly(Diiododiacetylene): Preparation, Isolation, and Full Characterization of a Very Simple Poly(diacetylene)", Journal of the American Chemical Society, 130 (24): 7702–7709, doi:10.1021/ja8011403, PMID 18489101