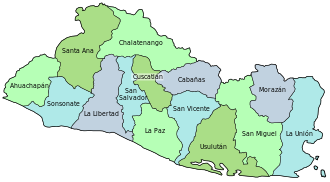
El Salvador is divided into 14 departments (Spanish: departamentos) for administrative purposes, subdivided into 44 municipalities (municipios) and 262 districts. The country is a unitary state.
| Department | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Number | 14 |
| Populations |
|
| Areas | |
| Subdivisions | |
History
editJune 12, 1824: The first Salvadoran constitution within the Federal Republic of Central America establishes a territorial division of four departments, Sonsonate, San Salvador, San Vicente, and San Miguel. Sonsonate was formerly part of Guatemala before this point.[1]
1833-1834: A short lived Department of Tejutla was established from the districts of Metapan and Tejutla in San Salvador.[2]
January 22, 1835: The Federal District of San Salvador is separated both from San Salvador department and from the State of Salvador. The remainder of San Salvador department is renamed to Cuscatlan, and Metapan district is transferred to Sonsonate department.[2][3]
May 17, 1839: Cuscatlan's Olocuitla district and San Vicente's Zacatecoluca district are combined into the new department of La Paz.[4]
July 30, 1839: The Federal District of San Salvador is dissolved, and San Salvador department is reconstituted, combining the former federal district with Opico district of Cuscatlan.[3]
March 15, 1847: La Paz department is abolished and reincorporated into San Vicente.[3]
February 21, 1852: La Paz department is restored.[3]
February 8, 1855: Santa Ana department is separated from Sonsonate.[4]
February 14, 1855: Chaltenango department is separated from Cuscatlan.[4]
January 26, 1865: La Libertad department is separated from San Salvador.[2][3]
June 22, 1865: Usulutan and La Union departments are separated from San Miguel.[2][3]
February 12, 1869: Ahuachapan department is separated from Santa Ana.[2][3]
February 10, 1873: Cabañas department is created from parts of Cuscatlan and San Vicente.[2][3]
July 14, 1875: Gotera department is separated from San Miguel. It would be renamed to Morazan department on March 14, 1887.[2][3]
Departments
edit| Map | Flag | Coat of arms | Department | ISO Code | Capital | Area (km2) | Population (2013)[5] | Municipalities | Districts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahuachapán | SV-AH | Ahuachapán | 1,239.6 | 333,406 | 3 | 12 | |||
| Cabañas | SV-CA | Sensuntepeque | 1,103.5 | 164,945 | 2 | 9 | |||
| Chalatenango | SV-CH | Chalatenango | 2,016.6 | 204,808 | 3 | 33 | |||
| Cuscatlán | SV-CU | Cojutepeque | 756.2 | 252,528 | 2 | 16 | |||
| La Libertad | SV-LI | Santa Tecla | 1,652.9 | 747,662 | 6 | 22 | |||
| La Paz | SV-PA | Zacatecoluca | 1,223.6 | 328,221 | 3 | 22 | |||
| La Unión | SV-UN | La Unión | 2,074.3 | 263,271 | 2 | 18 | |||
| Morazán | SV-MO | San Francisco Gotera | 1,447.4 | 199,519 | 2 | 26 | |||
| San Miguel | SV-SM | San Miguel | 2,077.1 | 478,792 | 3 | 20 | |||
| San Salvador | SV-SS | San Salvador | 886.2 | 1,740,847 | 5 | 19 | |||
| San Vicente | SV-SV | San Vicente | 1,184.0 | 174,561 | 2 | 13 | |||
| Santa Ana | SV-SA | Santa Ana | 2,023.2 | 572,081 | 4 | 13 | |||
| Sonsonate | SV-SO | Sonsonate | 1,225.2 | 463,732 | 4 | 16 | |||
| Usulután | SV-US | Usulután | 2,130.4 | 366,040 | 3 | 23 |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Constitución Política de la República de El Salvador de 1824 | Biblioteca Virtual Miguel de Cervantes". www.cervantesvirtual.com.
- ^ a b c d e f g Sistema de Información Territorial (2004). Viceministerio de Vivienda y Desarrollo Urbano (ed.). Poblamiento, ciudades, regiones y demarcaciones. Sistema de ciudades y demarcaciones territoriales a los efectos de planificación y desarrollo territorial. Plan Nacional de Ordenamiento y Desarrollo Territorial.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Lardé y Larín, Jorge. Ministerio de Cultura (ed.). El Salvador: historia de sus pueblos, villas y ciudades.
- ^ a b c Menéndez, Isidro (1855). Recopilación de las Leyes del Salvador. Vol. Tomo I.
- ^ "El Salvador, General Information". GeoHive. Archived from the original on 28 September 2016.