Taxonomy
| Eukaryotes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2200 mya |
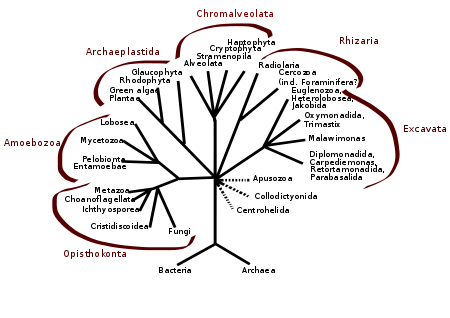
One view of the great kingdoms and their stem groups.[1][2][3][4] The Metamonada are hard to place, being sister possibly to Discoba or to Malawimonada[4] or being a paraphyletic group external to all other eukaryotes.[5]
Eukaryote classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incertae sedis |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Contents
Chordata
editExtant chordate classes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| |||
| Olfactores | |||
| |||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Extant orders of Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Major extant reptile clades | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lepidosauria | |||||
| Archelosauria |
| ||||
Opisthokonts
edit
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rozellomyceta |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aphelidiomyceta |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eumycota |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: fungi imperfecti (polyphyletic group). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also:
| Phylogeny of the Dikarya and upper-level taxa in Kingdom Fungi. |
Chromalveolata
edit
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incertae sedis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cryptobionta |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provora |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haptista |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Others
editExtant Arthropoda classes by subphylum | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| Chelicerata |
| ||||||||
| Mandibulata |
| ||||||||
italic are paraphyletic groups | |||||||||
Principal commercial fishery species groups | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Farmed | ||||||||||||||||||||
Edible crustaceans | |
|---|---|
| Shrimp/ prawns | |
| Lobsters (incl. slipper & spiny) |
|
| Crabs |
|
| Crayfish | |
| Others | |
- ^ Brown MW, Heiss AA, Kamikawa R, Inagaki Y, Yabuki A, Tice AK, Shiratori T, Ishida KI, Hashimoto T, Simpson A, Roger A (2018-01-19). "Phylogenomics Places Orphan Protistan Lineages in a Novel Eukaryotic Super-Group". Genome Biology and Evolution. 10 (2): 427–433. doi:10.1093/gbe/evy014. PMC 5793813. PMID 29360967.
- ^ Schön ME, Zlatogursky VV, Singh RP, et al. (2021). "Picozoa are archaeplastids without plastid". Nature Communications. 12 (1): 6651. bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.04.14.439778. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26918-0. PMC 8599508. PMID 34789758. S2CID 233328713.
- ^ Tikhonenkov DV, Mikhailov KV, Gawryluk RM, et al. (December 2022). "Microbial predators form a new supergroup of eukaryotes". Nature. 612 (7941): 714–719. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05511-5. PMID 36477531. S2CID 254436650.
- ^ a b Burki F, Roger AJ, Brown MW, Simpson AG (2020). "The New Tree of Eukaryotes". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 35 (1). Elsevier BV: 43–55. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2019.08.008. ISSN 0169-5347. PMID 31606140. S2CID 204545629.
- ^ Al Jewari, Caesar; Baldauf, Sandra L. (28 April 2023). "An excavate root for the eukaryote tree of life". Science Advances. 9 (17): eade4973. Bibcode:2023SciA....9E4973A. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade4973. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 10146883. PMID 37115919.