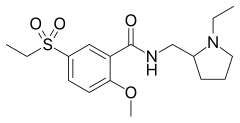
Sultopride (trade names Barnetil, Barnotil, Topral) is an atypical antipsychotic of the benzamide chemical class used in Europe, Japan, and Hong Kong for the treatment of schizophrenia.[2][3][4] It was launched by Sanofi-Aventis in 1976.[2] Sultopride acts as a selective D2 and D3 receptor antagonist.[5] It has also been shown to have clinically relevant affinity for the GHB receptor as well, a property it shares in common with amisulpride and sulpiride.[6]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Barnetil, Barnotil, Topral |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, IM |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 3–5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.053.293 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H26N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 354.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Pharmacology edit
| Site | Ki | Species | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| D2 | 1.6 | Human | [7] |
| D3 | 3.8 | Human | [7] |
References edit
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ a b Miguel Vela J, Buschmann H, Holenz J, Párraga A, Torrens A (2007). Antidepressants, Antipsychotics, Anxiolytics: From Chemistry and Pharmacology to Clinical Application. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3-527-31058-6.
- ^ Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (Book with CD-ROM). Boca Raton: Medpharm Scientific Publishers. ISBN 3-88763-075-0.
- ^ European Drug Index (4th ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. 1998. ISBN 3-7692-2114-1.
- ^ Burstein ES, Ma J, Wong S, Gao Y, Pham E, Knapp AE, et al. (December 2005). "Intrinsic efficacy of antipsychotics at human D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors: identification of the clozapine metabolite N-desmethylclozapine as a D2/D3 partial agonist". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 315 (3): 1278–1287. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.092155. PMID 16135699. S2CID 2247093.
- ^ Maitre M, Ratomponirina C, Gobaille S, Hodé Y, Hechler V (April 1994). "Displacement of [3H] gamma-hydroxybutyrate binding by benzamide neuroleptics and prochlorperazine but not by other antipsychotics". European Journal of Pharmacology. 256 (2): 211–214. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(94)90248-8. PMID 7914168.
- ^ a b Burstein ES, Ma J, Wong S, Gao Y, Pham E, Knapp AE, et al. (December 2005). "Intrinsic efficacy of antipsychotics at human D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors: identification of the clozapine metabolite N-desmethylclozapine as a D2/D3 partial agonist". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 315 (3): 1278–1287. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.092155. PMID 16135699. S2CID 2247093.