Nike Zeus was an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system developed by the United States Army during the late 1950s and early 1960s that was designed to destroy incoming Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile warheads before they could hit their targets. It was designed by Bell Labs' Nike team, and was initially based on the earlier Nike Hercules anti-aircraft missile. The original, Zeus A, was designed to intercept warheads in the upper atmosphere, mounting a 25 kiloton W31 nuclear warhead. During development, the concept changed to protect a much larger area and intercept the warheads at higher altitudes. This required the missile to be greatly enlarged into the totally new design, Zeus B, given the tri-service identifier XLIM-49, mounting a 400 kiloton W50 warhead. In several successful tests, the B model proved itself able to intercept warheads, and even satellites.
| Nike Zeus B | |
|---|---|
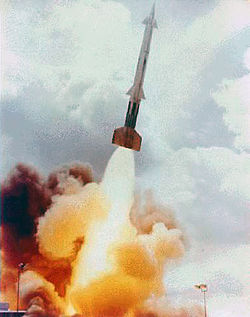 Nike Zeus B test launch at White Sands | |
| Type | Anti-ballistic missile |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| Used by | US Army |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | |
| Produced | 1961 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 24,200 lb (11,000 kg) total |
| Length | 50 feet 2 inches (15.29 m) total |
| Diameter | 36 inches (910 mm) |
Detonation mechanism | radio command |
| Engine | 450,000 lbf (2,000 kN) booster |
Operational range | 230 nmi (430 km; 260 mi) |
| Flight ceiling | over 150 nmi (280 km; 170 mi) |
| Maximum speed | greater than Mach 4 (3,000 mph; 4,900 km/h) |
Guidance system | command guidance |
Launch platform | silo |
The nature of the strategic threat changed dramatically during the period that Zeus was being developed. Originally expected to face only a few dozen ICBMs, a nationwide defense was feasible, although expensive. When the Soviets claimed to be building hundreds of missiles, the US faced the problem of building enough Zeus missiles to match them. The Air Force argued they close this missile gap by building more ICBMs of their own instead. Adding to the debate, a number of technical problems emerged that suggested Zeus would have little capability against any sort of sophisticated attack.
The system was the topic of intense inter-service rivalry throughout its lifetime. When the ABM role was given to the Army in 1958, the United States Air Force began a long series of critiques on Zeus, both within defense circles and in the press. The Army returned these attacks in kind, taking out full page advertisements in popular mass market news magazines to promote Zeus, as well as spreading development contracts across many states in order to garner the maximum political support. As deployment neared in the early 1960s, the debate became a major political issue. The question ultimately became whether a system with limited effectiveness would be better than nothing at all.
The decision whether to proceed with Zeus eventually fell to President John F. Kennedy, who became fascinated by the debate about the system. In 1963, the United States Secretary of Defense, Robert McNamara, convinced Kennedy to cancel Zeus. McNamara directed its funding toward studies of new ABM concepts being considered by ARPA, selecting the Nike-X concept, which addressed Zeus' various problems by using an extremely high-speed missile, Sprint, along with greatly improved radars and computer systems. The Zeus test site built at Kwajalein was briefly used as an anti-satellite weapon.
History
editEarly ABM studies
editThe first known serious study on attacking ballistic missiles with interceptor missiles was carried out by the Army Air Force in 1946, when two contracts were sent out as Project Wizard and Project Thumper to consider the problem of shooting down missiles of the V-2 type.[1] These projects identified the main problem being one of detection; the target could approach from anywhere within hundreds of miles, and reach their targets in only five minutes. Existing radar systems would have difficulty seeing the missile launch at those ranges, and even assuming one had detected the missile, existing command and control arrangements would have serious problems forwarding that information to the battery in time for them to attack. The task appeared impossible at that time.[2]
These results also suggested that the system might be able to work against longer-ranged missiles. These flew to a higher altitude which eased the problem of detection, and although they traveled at higher speeds, their total flight time was longer and provided more time to prepare.[2] Both projects were allowed to continue as research efforts. They were transferred to the US Air Force when that force separated from the Army in 1947. The Air Force faced significant budget constraints and canceled Thumper in 1949 in order to use its funds to continue its GAPA surface-to-air missile (SAM) efforts. The next year, Wizard's funding was also rolled into GAPA to develop a new long-range SAM design, which would emerge a decade later as the CIM-10 Bomarc. ABM research at the Air Force practically, although not officially, ended.[2][3]
Nike II
editBy the early 1950s the Army was firmly established in the surface-to-air missile field with their Nike and Nike B missile projects. These projects had been led by Bell Labs, working with Douglas.[4]
The Army contacted the Johns Hopkins University Operations Research Office (ORO) to consider the task of shooting down ballistic missiles using a Nike-like system. The ORO report took three years to complete, and the resulting The Defense of the United States Against Aircraft and Missiles was comprehensive.[5] While this study was still progressing, in February 1955 the Army began initial talks with Bell, and in March they contracted Bell's Nike team to begin a detailed 18-month study of the problem under the name Nike II.[3]
The first section of the Bell study was returned to the Army Ordnance department at the Redstone Arsenal on 2 December 1955. It considered the full range of threats including existing jet aircraft, future ramjet powered aircraft flying at up to 3,000 knots (5,600 km/h), short-range ballistic missiles of the V-2 type flying at about the same speed, and an ICBM reentry vehicle (RV) traveling at 14,000 knots (26,000 km/h).[6] They suggested that a missile with a common rocket booster could serve all of these roles by changing between two upper stages; one with fins for use in the atmosphere against aircraft, and another with vestigial fins and thrust vectoring for use above the atmosphere against missiles.[7]
Considering the ICBM problem, the study went on to suggest that the system would have to be effective between 95 and 100% of the time in order to be worthwhile. They considered attacks against the RV while the missile was in the midcourse, just as it reached the highest point in its trajectory and was traveling at its slowest speed. Practical limitations eliminated this possibility, as it required the ABM to be launched at about the same time as the ICBM in order to meet in the middle, and they could not imagine a way to arrange this. Working at much shorter ranges, during the terminal phase, seemed the only possible solution.[8]
Bell returned a further study, delivered on 4 January 1956, that demonstrated the need to intercept the incoming warheads at 100-mile (160 km) altitude, and suggested that this was within the abilities of an upgraded version of the Nike B missile.[9] Given a terminal speed up to 5 miles per second (18,000 miles per hour (29,000 km/h)), combined with the time it would take an interceptor missile to climb to the RV's altitude, the system required that the RV be initially detected at about 1,000 miles (1,600 km) range. Due to the RV's relatively small size and limited radar signature, this would demand extremely powerful radars.[9]
To ensure the destruction of the RV, or at least render the warhead within it unusable, the W31 would have to be fired when it was within a few hundred feet of the RV. Given the angular resolution of existing radars, this limited the maximum effective range significantly. Bell considered an active radar seeker, which improved accuracy as it flew toward the RV, but these proved too large to be practical.[10] A command guidance system like the early Nike systems seemed to be the only solution.[9]
The interceptor would lose maneuverability as it climbed out of the atmosphere and its aerodynamic surfaces became less effective, so it would have to be directed onto the target as rapidly as possible, leaving only minor fine-tuning later in the engagement. This required that accurate tracks be developed for both the warhead and outgoing missile very quickly in comparison to a system like Nike B where the guidance could be updated throughout the engagement. This, in turn, demanded new computers and tracking radars with much higher processing rates than the systems used on earlier Nikes. Bell suggested that the recently introduced transistor offered the solution to the data processing problem.[11]
After running 50,000 simulated intercepts on analog computers, Bell returned a final report on the concept in October 1956, indicating that the system was within the state of the art.[9] A 13 November 1956 memo gave new names to the entire Nike series; the original Nike became Nike Ajax, Nike B became Nike Hercules, and Nike II became Nike Zeus.[12][13]
Army vs. Air Force
editThe Army and Air Force had been involved in interservice fighting over missile systems since they split in 1947. The Army considered surface-to-surface missiles (SSM) an extension of conventional artillery, and surface-to-air designs as the modern replacement for their anti-aircraft artillery. The Air Force considered the nuclear SSM to be an extension of their strategic bombing role, and any sort of long-range anti-aircraft system to be their domain as it would integrate with their fighter fleet. Both forces were developing missiles for both roles, leading to considerable duplication of effort which was widely seen as wasteful.[14]
For a period the capabilities of the systems being developed were different enough to provide some separation between the forces. For instance, the Army's Ajax was much shorter ranged than the Air Force's Bomarc, and the Army's Redstone much shorter in range than the Air Forces ICBM programs. But by the mid-1950s the Army's programs were rapidly improving and the fighting grew more intense. When the Army's longer-ranged Hercules began deployment, the Air Force complained that it was inferior to Bomarc and that the Army was "unfit to guard the nation".[15] When the Army started its Jupiter missile efforts, the Air Force worried it would trump their Atlas ICBM and responded by rapidly starting its own IRBM, Thor.[16] So when the Army announced Nike II, the Air Force immediately reactivated Wizard, this time as a long-range anti-ICBM system of much greater performance than Zeus.[17]
In a 26 November 1956 memorandum, US Secretary of Defense Charles Erwin Wilson attempted to end the fighting between the forces and prevent duplication of effort. His solution was to limit the Army to weapons with 200-mile (320 km) range, and those involved in surface-to-air defense to only 100 miles (160 km).[18] The memo also placed limits on Army air operations, severely limiting the weight of the aircraft it was allowed to operate. To some degree, this simply formalized what had largely already been the case in practice, but Jupiter fell outside the range limits and the Army was forced to hand them to the Air Force.[19]
The result was another round of fighting between the two forces. Jupiter had been designed to be a highly accurate weapon able to attack Soviet military bases in Europe,[20] as compared to Thor, which was intended to attack Soviet cities and had accuracy on the order of several miles.[21] Losing Jupiter, the Army was eliminated from any offensive strategic role. In return, the Air Force complained that Zeus was too long-ranged and the ABM effort should center on Wizard. But the Jupiter handover meant that Zeus was now the only strategic program being carried out by the Army, and its cancellation would mean "virtually the surrender of the defense of America to the U.S.A.F at some future date."[22]
Gaither Report, missile gap
editIn May 1957, Eisenhower tasked the President's Science Advisory Committee (PSAC) to provide a report on the potential effectiveness of fallout shelters and other means of protecting the US population in the event of a nuclear war. Chaired by Horace Rowan Gaither, the PSAC team completed their study in September, publishing it officially on 7 November as Deterrence & Survival in the Nuclear Age, but today known as the Gaither Report. After ascribing an expansionist policy to the USSR, along with suggestions that they were more heavily developing their military than the US, the Report suggested that there would be a significant gap in capability in the late 1950s due to spending levels.[23]
While the report was being prepared, in August 1957 the Soviets launched their R-7 Semyorka (SS-6) ICBM, and followed this up with the successful launch of Sputnik 1 in October. Over the next few months, a series of intelligence reviews resulted in ever increasing estimates of the Soviet missile force. National Intelligence Estimate (NIE) 11-10-57, issued in December 1957, stated that the Soviets would have perhaps 10 prototype missiles in service by mid-1958. After Nikita Khrushchev claimed to be producing them "like sausages",[24][a] the numbers began to rapidly inflate. NIE 11-5-58, released in August 1958, suggested there would be 100 ICBMs in service by 1960, and 500 by 1961 or 1962 at the latest.[26]
With the NIE reports suggesting the existence of the gap Gaither predicted, near panic broke out in military circles. In response, the US began to rush its own ICBM efforts, centered on the Atlas. These missiles would be less susceptible to attack by Soviet ICBMs than their existing bomber fleet, especially in future versions which would be launched from underground silos. But even as Atlas was rushed, it appeared there would be a missile gap; NIE estimates made during the late 1950s suggested the Soviets would have significantly more ICBMs than the US between 1959 and 1963, at which point US production would finally catch up.[26]
With even a few hundred missiles, the Soviets could afford to target every US bomber base. With no warning system in place, a sneak attack could destroy a significant amount of the US bomber fleet on the ground. The US would still have the airborne alert force and its own small ICBM fleet, but the USSR would have its entire bomber fleet and any missiles they did not launch, leaving them with a massive strategic advantage. To ensure this could not happen, the Report called for the installation of active defenses at SAC bases, Hercules in the short term and an ABM for the 1959 period, along with new early warning radars for ballistic missiles to allow alert aircraft to get away before the missiles hit.[27] Even Zeus would come too late to cover this period, and some consideration was given to an adapted Hercules or a land based version of the Navy's RIM-8 Talos as an interim ABM.[28]
Zeus B
editDouglas Aircraft had been selected to build the missiles for Zeus, known under the company designation DM-15. This was essentially a scaled-up Hercules with an improved, more powerful single piece booster replacing Hercules' cluster of four smaller boosters. Intercepts could take place at the limits of the Wilson requirements, at ranges and altitudes of about 100 miles (160 km). Prototype launches were planned for 1959. For more rapid service entry there had been some consideration given to an interim system based on the original Hercules missile, but these efforts were dropped. Likewise, early requirements for a secondary anti-aircraft role were also eventually dropped.[29][b]
Wilson signaled his intention to retire in early 1957, and Eisenhower began looking for a replacement. During his exit interview, only four days after Sputnik, Wilson told Eisenhower that "trouble is rising between the Army and the Air Force over the 'anti-missile-missile'."[30] The new Secretary of Defense, Neil McElroy, took office on 9 October 1957. McElroy was previously president of Procter & Gamble and was best known for the invention of the concept of brand management and product differentiation.[31] He had little federal experience, and the launch of Sputnik left him little time to ease into the position.[32]
Shortly after taking office, McElroy formed a panel to investigate ABM issues. The panel examined the Army and Air Force projects, and found the Zeus program considerably more advanced than Wizard. McElroy told the Air Force to stop work on ABM missiles and use Wizard funding for the development of long-range radars for early warning and raid identification. These were already under development as the BMEWS network. The Army was handed the job of actually shooting down the warheads, and McElroy gave them free hand to develop an ABM system as they saw fit, free of any range limitations.[33]
The team designed a much larger missile with a greatly enlarged upper fuselage and three stages, more than doubling the launch weight. This version extended range, with interceptions taking place as far as 200 miles (320 km) downrange and over 100 miles (160 km) in altitude. An even larger booster took the missile to hypersonic speeds while still in the lower atmosphere, so the missile fuselage had to be covered over completely with a phenolic ablative heat shield to protect the airframe from melting.[34][c] Another change was to combine the aerodynamic controls used for control in the lower atmosphere with the thrust vectoring engines, using a single set of movable jet vanes for both roles.[35]
The new DM-15B Nike Zeus B (the earlier model retroactively becoming the A) received a go-ahead for development on 16 January 1958,[36] the same date the Air Force was officially told to stop all work on a Wizard missile.[28] On 22 January 1958, the National Security Council gave Zeus S-Priority, the highest national priority.[37][38] Additional funds were requested to the Zeus program to ensure an initial service date in the fourth quarter of 1962, but these were denied, delaying service entry until some time in 1963.[39]
Exchange ratio and other problems
editWith their change of fortunes after McElroy's 1958 decision, Army General James M. Gavin publicly stated that Zeus would soon replace strategic bombers as the nation's main deterrent. In response to this turn of events, the Air Force stepped up their policy by press release efforts against the Army, as well as agitating behind the scenes within the Defense Department.[40]
As part of their Wizard research, the Air Force had developed a formula that compared the cost of an ICBM to the ABM needed to shoot it down. The formula, later known as the cost-exchange ratio, could be expressed as a dollar figure; if the cost of the ICBM was less than that figure, the economic advantage was in favor of the offense – they could build more ICBMs for less money than the ABMs needed to shoot them down. A variety of scenarios demonstrated that it was almost always the case that the offense had the advantage. The Air Force ignored this inconvenient problem while they were still working on Wizard, but as soon as the Army was handed sole control of the ABM efforts, they immediately submitted it to McElroy. McElroy identified this as an example of interservice fighting, but was concerned that the formula might be correct.[41]
For an answer, McElroy turned to the Re-entry Body Identification Group (RBIG), a sub-group of the Gaither Committee led by William E. Bradley, Jr. that had been studying the issue of penetrating a Soviet ABM system. The RBIG had delivered an extensive report on the topic on 2 April 1958 which suggested that defeating a Soviet ABM system would not be difficult. Their primary suggestion was to arm US missiles with more than one warhead, a concept known as Multiple Re-entry Vehicles (MRV). Each warhead would also be modified with radiation hardening, ensuring only a near miss could damage it. This would mean that the Soviets would have to launch at least one interceptor for each US warhead, while the US could launch multiple warheads without building a single new missile. If the Soviets added more interceptors to counter the increased number of US warheads, the US could counter this with a smaller number of new missiles of their own. The cost balance was always in favor of the offense. This basic concept would remain the primary argument against ABMs for the next two decades.[41]
Turning this argument about, the RBIG delivered a report to McElroy that agreed with the Air Force's original claims on the ineffectiveness of ABMs based on cost.[41] But then they went on to consider the Zeus system itself, and noted that its use of mechanically steered radars, with one radar per missile, meant that Zeus could only launch a small number of missiles at once. If the Soviets also deployed MRV, even a single ICBM would cause several warheads to arrive at the same time, and Zeus would simply not have time to shoot at them all. They calculated that only four warheads arriving within one minute would result in one of them hitting the Zeus base 90% of the time.[42] Thus one or two Soviet missiles would destroy all 100 Zeus missiles at the base. The RBIG noted that an ABM system "demands such a high rate of fire from an active defense system, in order to intercept the numerous reentry bodies which arrive nearly simultaneously, that the expense of the required equipment may be prohibitive". They went on to question the "ultimate impossibility" of an ABM system.[43]
Project Defender
editMcElroy responded to the RBIG report in two ways. First, he turned to the newly created ARPA group to examine the RBIG report. ARPA, directed by Chief Scientist Herbert York, returned another report broadly agreeing with everything they said.[41] Considering both the need to penetrate a Soviet ABM and a potential US ABM system, York noted that:
The problem here is the usual problem between defense and offenses, measures, countermeasures, counter-counter measures, et cetera, in which it has been my judgment and still is that the battle is so heavily weighted in favor of the offense that it is hopeless against a determined offense and that incidentally applies to our position with regard to an anti-missile that they might build. I am convinced that we can continue to have a missile system that can penetrate any Soviet defense.[44]
When this report was received, McElroy then charged ARPA to begin studying long-term solutions to the ICBM defense, looking for systems that would avoid the apparently insurmountable problem presented by the exchange ratio.[45]
ARPA responded by forming Project Defender, initially considering a wide variety of far-out concepts like particle beam weapons, lasers and huge fleets of space-borne interceptor missiles, the latter known as Project BAMBI. In May 1958, York also began working with Lincoln Labs, MIT's radar research lab, to begin researching ways to distinguish warheads from decoys by radar or other means. This project emerged as the Pacific Range Electromagnetic Signature Studies, or Project PRESS.[30]
More problems
editIn the midst of the growing debate over Zeus' abilities, the US conducted its first high yield, high altitude tests – Hardtack Teak on 1 August 1958, and Hardtack Orange on 12 August. These demonstrated a number of previously unknown or underestimated effects, notably that nuclear fireballs grew to very large size and caused all of the air in or immediately below the fireball to become opaque to radar signals, an effect that became known as nuclear blackout. This was extremely worrying for any system like Zeus, which would not be able to track warheads in or behind such a fireball, including those of the Zeus' own warheads.[46]
If this were not enough, there was a growing awareness that simple radar reflectors could be launched along with the warhead that would be indistinguishable to Zeus' radars. This problem was first alluded to in 1958 in public talks that mentioned Zeus' inability to discriminate targets.[47] If the decoys spread apart further than the lethal radius of the Zeus' warhead, several interceptors will be required to guarantee that the warhead hiding among the decoys will be destroyed.[48] Decoys are lightweight, and would slow down when they began to reenter the upper atmosphere, causing the RV to move out in front and be picked out, or decluttered. But by that time it would be so close to the Zeus base that there might not be time for the Zeus to climb to altitude.[48]
In 1959 the Defense Department ordered one more study on the basic Zeus system, this time by the PSAC. They put together a heavyweight group with some of the most famous and influential scientists forming its core, including Hans Bethe who had worked on the Manhattan Project and later on the hydrogen bomb, Wolfgang Panofsky, the director of the High-Energy Physics Lab at Stanford University, and Harold Brown, director of the Lawrence Livermore weapons lab, among similar luminaries. The PSAC report was almost a repeat of the RBIG. They recommended that Zeus should not be built, at least without significant changes to allow it to better deal with the emerging problems.[41]
Throughout, Zeus was the focus of fierce controversy in both the press and military circles. Even as testing started, it was unclear if development would continue.[34] President Eisenhower's defense secretaries, McElroy (1957–59) and Thomas S. Gates, Jr. (1959–61), were unconvinced that the system was worth the cost. Eisenhower was highly skeptical, questioning whether an effective ABM system could be developed in the 1960s.[49] Another harsh critic on cost grounds was Edward Teller, who simply stated that the exchange ratio meant the solution was to build more ICBMs.[50]
Kennedy and Zeus
editJohn F. Kennedy campaigned on the platform that Eisenhower was weak on defense and that he was not doing enough to solve the looming missile gap.[26][d] After his win in the 1960 elections he was flooded with calls and letters urging that Zeus be continued. This was a concentrated effort on the part of the Army, who was fighting back against similar Air Force tactics. They also deliberately spread the Zeus contracts over 37 states in order to gain as much political and industrial support as possible, while taking out advertisements in major mass-market magazines like Life and The Saturday Evening Post promoting the system.[52]
Kennedy appointed Army General Maxwell D. Taylor as his Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. Taylor, like most Army brass, was a major supporter of the Zeus program. Kennedy and Taylor initially agreed to build a huge Zeus deployment with seventy batteries and 7,000 missiles. Robert McNamara was also initially in favor of the system, but suggested a much smaller deployment of twelve batteries with 1,200 missiles. A contrary note was put forth by Jerome Wiesner, recently appointed as Kennedy's scientific advisor, and chair of the 1959 PSAC report. He began to educate Kennedy on the technical problems inherent to the system. He also had lengthy discussions with David Bell, the budget director, who came to realize the enormous cost of any sort of reasonable Zeus system.[53]
Kennedy was fascinated by the Zeus debate, especially the way that scientists were lined up on diametrically opposed positions for or against the system. He commented to Wiesner, "I don't understand. Scientists are supposed to be rational people. How can there be such differences on a technical issue?"[54] His fascination grew and he eventually compiled a mass of material on Zeus which took up one corner of a room where he spent hundreds of hours becoming an expert on the topic. In one meeting with Edward Teller, Kennedy demonstrated that he knew more about the Zeus and ABMs than Teller. Teller then expended considerable effort to bring himself up to the same level of knowledge.[55] Wiesner would later note that the pressure to make a decision built up until "Kennedy came to feel that the only thing anybody in the country was concerned about was Nike-Zeus."[54]
To add to the debate, it was becoming clear that the missile gap was fictional. The first Corona spy satellite mission in August 1960 put limits on the Soviet program that appeared to be well below the lower bound of any of the estimates, and a follow-up mission in late 1961 clearly demonstrated the US had a massive strategic lead.[56] A new intelligence report published in 1961 reported that the Soviets had no more than 25 ICBMs and would not be able to add more for some time.[57] It was later demonstrated the actual number of ICBMs in the Soviet fleet at that time was four.[58]
Nevertheless, Zeus continued slowly moving towards deployment. On 22 September 1961, McNamara approved funding for continued development, and approved initial deployment of a Zeus system protecting twelve selected metropolitan areas. These included Washington/Baltimore, New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Philadelphia, Detroit, Ottawa/Montreal, Boston, San Francisco, Pittsburgh, St. Louis, and Toronto/Buffalo. However, the deployment was later overturned, and in January 1962 only the development funds were released.[59]
Nike-X
editIn 1961, McNamara agreed to continue development funding through FY62, but declined to provide funds for production. He summed up both the positives and the concerns this way:
Successful development [of Zeus] may force an aggressor to expend additional resources to increase his ICBM force. It would also make accurate estimates of our defensive capabilities more difficult for a potential enemy and complicate the achievement of a successful attack. Furthermore, the protection that it would provide, even if for only a portion of our population, would be better than none at all ...
There is still considerable uncertainty as to its technical feasibility and, even if successfully developed, there are many serious operating problems yet to be solved. The system, itself, is vulnerable to ballistic missile attack, and its effectiveness could be degraded by the use of more sophisticated ICBMs screened by multiple decoys. Saturation of the target is another possibility as ICBMs become easier and cheaper to produce in coming years. Finally, it is a very expensive system in relation to the degree of protection that it can furnish.[60]
Looking for a near term solution, McNamara once again turned to ARPA, asking it to consider the Zeus system in depth. The agency returned a new report in April 1962 that contained four basic concepts. First was the Zeus system in its current form, outlining what sort of role it might play in various war fighting scenarios. Zeus could, for instance, be used to protect SAC bases, thereby requiring the Soviets to expend more of their ICBMs to attack the bases. This would presumably mean less damage to other targets. Another considered the addition of new passive electronically scanned array radars and computers to the Zeus, which would allow it to attack dozens of targets at once over a wider area. Finally, in its last concept, ARPA replaced Zeus with a new very high speed, short range missile designed to intercept the warhead at altitudes as low as 20,000 feet (6.1 km), by which time any decoys or fireballs would be long gone.[61] This last concept became Nike-X, an ad hoc name suggested by Jack Ruina while describing the ARPA report to PSAC.[62]
Perfect or nothing
editAs work on Nike-X began, high-ranking military and civilian officials began to press for Zeus deployment as an interim system in spite of the known problems. They argued the system could be upgraded in-place as the new technologies became available. McNamara was opposed to early deployment, while Congressman Daniel J. Flood would be a prime force for immediate deployment.[63]
McNamara's argument against deployment rested on two primary issues. One was the apparent ineffectiveness of the system, and especially its benefit-cost ratio compared to other options. For instance, fallout shelters would save more Americans for far less money,[64] and in an excellent demonstration of his approach to almost any defense issue, he noted:
It is estimated that a shelter system at a cost of $2 billion would save 48.5 million lives. The cost per life saved would be about $40.00. An active ballistic missile defense system would cost about $18 billion and would save an estimated 27.8 million lives. The cost per life saved in this case would be about $700. [He later added that] I personally will never recommend an anti-ICBM program unless a fallout program does accompany it. I believe that even if we do not have an anti-ICBM program, we nonetheless should proceed with the fallout shelter program.[64]
The second issue, ironically, came about due to concerns about a Soviet ABM system. The US's existing SM-65 Atlas and SM-68 Titan both used re-entry vehicles with blunt noses that greatly slowed the warheads as they entered the lower atmosphere and made them relatively easy to attack. The new LGM-30 Minuteman missile used sharp-nosed reentry shapes that traveled at much higher terminal speeds, and included a number of decoy systems that were expected to make interception very difficult for the Soviet ABMs. This would guarantee the US's deterrent. If there was a budget choice to be made, McNamara supported Minuteman, although he tried not to say this.[65]
In one particularly telling exchange between McNamara and Flood, McNamara initially refuses to choose one option over the other:
Flood: Which comes first, the chicken or the egg? Which comes first, Minuteman because he may develop a good Zeus, or our own Zeus?
McNamara: I would say neither comes first. I would carry on each simultaneously with the maximum rate of activity that each could benefit from.[66]
But later, Flood managed to get a more accurate statement out of him:
Flood: I thought we had broken through this problem in this country, of wanting things to be perfect before we send them to the troops. I have an enemy who can kill me and I cannot defend myself against him, and I say I should hazard all risks within the rule of reason, to advance this by 2 or 3 years.
McNamara: We are spending hundreds of millions of dollars, not to stop things but to accelerate the development of an anti-ICBM system... I do not believe it would be wise for us to recommend the procurement of a system which might not be an effective anti-ICBM device. That is exactly the state in which we believe the Zeus rests today.
Flood: ... You may not be aware of it, but you have just about destroyed the Nike-Zeus. That last paragraph did that.[66]
Cancellation and the ABM gap
editBy 1963 McNamara had convinced Kennedy that the Zeus was simply not worth deploying.[67] The earlier concerns about cost and effectiveness, as well as new difficulties in terms of attack size and decoy problems, led McNamara to cancel the Zeus project on 5 January 1963.[48][68] In its place they decided to continue work on Nike-X.[69] Nike-X development was based in the existing Nike Zeus Project Office until their name was changed to Nike-X on 1 February 1964.[68]
While reporting to the Senate Armed Services Committee in February, McNamara noted that they expected the Soviets to have an initial ABM system deployed in 1966, and then later stated that the Nike-X would not be ready for use until 1970. Noting a "defensive gap", Strom Thurmond began an effort to deploy the existing Zeus as an interim system. Once again the matter spilled over into the press.[70]
On 11 April 1963, Thurmond led Congress in an effort to fund deployment of Zeus. In the first closed session of the Senate in twenty years, Zeus was debated and the decision was made to continue with the planned development of Nike-X with no Zeus deployment.[69] The Army continued the testing program until December 1964 at White Sands Missile Range, and May 1966 at Kwajalein Missile Range.[71]
Testing
editAs the debate over Zeus raged, the Nike team was making rapid progress developing the actual system. Test firings of the original A models of the missile began in 1959 at White Sands Missile Range. The first attempt on 26 August 1959 was of a live booster stage and dummy sustainer, but the booster broke up shortly before booster/sustainer separation. A similar test on 14 October was a success, followed by the first two-stage attempt on 16 December.[72] The first complete test of both stages with active guidance and thrust vectoring was successfully carried out on 3 February 1960.[73] Data collected from these tests led to changes to the design to improve speed during the ascent. The first test of the Zeus B took place in May 1961.[74] A number of Zeus missiles broke up during early test flights due to excessive heating of the control surfaces, and numerous changes were worked into the system to address this.[75]
Additional tracking tests were carried out by Target Tracking Radars (TTRs) at Bell's Whippany, NJ labs and an installation on Ascension Island. The latter was first used in an attempt to track a SM-68 Titan on 29 March 1961, but the data download from Cape Canaveral simulating Zeus Acquisition Radar (ZAR) information failed. A second test on 28 May was successful. Later in the year the Ascension site tracked a series of four test launches, two Atlas, two Titan, generating tracking information for as long as 100 seconds.[76] A ZAR at White Sands reached initial operation in June 1961, and was tested against balloons, aircraft, parachutes deployed from sounding rockets and Hercules missiles. A TTR was completed at White Sands in November, and testing with the complete system of ZAR, TTR and MTR ("all-up" tests) began that month. On 14 December a Zeus passed within 100 feet (30 m) of a Nike Hercules being used as a test target, a success that was repeated in March 1962.[77] On 5 June 1963, President Kennedy and Vice President Lyndon Johnson visited White Sands to view missile launches, including a Zeus launch.[78]
The need to test Zeus against targets flying realistic ICBM profiles presented a problem. While White Sands was fine for testing the basic missile and guidance systems, it was too small to test Zeus at its maximum range. Such testing began at Point Mugu in California. where the Zeus missiles could fly out over the Pacific. Consideration was given to using Point Mugu to launch against ICBMs flying from Cape Canaveral, but range safety requirements placed limits on the potential tests. Likewise, the Atlantic Test Range, to the northeast of Canaveral, had a high population density and little land available for building accurate downrange tracking stations, Ascension being the only suitable location.[79]
Eventually Kwajalein Island was selected, as it was 4,800 miles from California, perfect for ICBMs, and already had a US Navy base with considerable housing stocks and an airstrip. The Zeus site, known as the Kwajalein Test Site, was officially established on 1 October 1960. As it grew in size, it eventually led to the entire island complex being handed over to the Army from the Navy on 1 July 1964.[79] The site took up a considerable amount of the empty land to the north side of the airfield. The launchers were located on the far southwestern corner of the island, with the Target Tracking Radars, Missile Tracking Radars (MTRs) and various control sites and generators running along the northern side of the airfield. The ZAR transmitter and receiver were some distance away, off the northeastern edge of the airfield.[80]
A minor Army-Air Force fight then broke out about what targets would be used for the Kwajalein tests. The Army favored using its Jupiter design, fired from Johnston Atoll in the Pacific, while the Air Force recommended using Atlas fired from Vandenberg AFB in California. The Army had already begun converting the former Thor launchers to Jupiter when an Ad Hoc Panel formed by the Department of Defense considered the issue. On 26 May 1960 they decided in favor of Atlas, and this was made official on 29 June when the Secretary of Defense ended pad conversion and additional Jupiter production earmarked for Zeus testing.[81]
A key development of the testing program was a miss-distance indicator system, which independently measured the distance between the Zeus and the target at the instant the computers initiated the detonation of the warhead. There were concerns that if the Zeus' own radars were used for this ranging measure, any systematic error in ranging would also be present in the test data, and thus would be hidden.[82] The solution was the use of a separate UHF-frequency transmitter in the warhead reentry vehicle, and a receiver in the Zeus. The received signal was retransmitted to the ground, where its Doppler shift was examined to extract the range information. These instruments eventually demonstrated that the Zeus' own tracking information was accurate.[83][e] For visual tracking, a small conventional warhead was used, which provided a flash that could be seen on long exposure photographs of the interceptions.
On 24 January 1962, the Zeus Acquisition Radar at Kwajalein achieved its first returns from an ICBM target, and on 18 April was used to track Kosmos 2. On the 19 January it reacquired Kosmos 2 and successfully transferred the track to one of the TTRs.[61] On 26 June the first all-up test against an Atlas target was attempted. The ZAR began successfully tracking the target at 446 nautical miles (826 km) and properly handed off to a TTR. The TTR switched tracks from the missile fuselage to the warhead at 131 nautical miles (243 km). When the fuselage began to break up, the computer switched to clutter mode, which watched the TTR data for any derivation from the originally calculated trajectory, which would indicate that it had begun tracking debris. It also continued to predict the location of the warhead, and if the system decided it was tracking debris, it would wait for the debris and warhead to separate enough to begin tracking them again. However, the system failed to properly record when the warhead was lost, and tracking was never regained.[77]
A second test on 19 July was a partial success,[f] with the Zeus passing within 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) of the target. The control system ran out of hydraulic fluid during the last 10 seconds of the approach, causing the large miss distance, but the test was otherwise successful. The guidance program was updated to stop the rapid control cycling that led to the fluid running out. A third attempt on 12 December successfully brought the missile to very close distances, but the second missile of the planned two missile salvo failed to launch due to an instrument problem. A similar test on 22 December also suffered a failure in the second missile, but the first passed only 200 metres (660 ft) from its target.[82]
| Mission | Date | Target | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 26 June 1962 | Atlas D | Failure, tracking |
| K2 | 19 July 1962 | Atlas D | Partial success, large miss distance |
| K6 | 12 December 1962 | Atlas D | Success, second missile failed |
| K7 | 22 December 1962 | Atlas D | Success, second missile failed |
| K8 | 13 February 1963 | Atlas D | Partial success |
| K10 | 28 February 1963 | Atlas D | Partial success |
| K17 | 30 March 1963 | Titan I | Success |
| K21 | 13 April 1963 | Titan I | Success |
| K15 | 12 June 1963 | Atlas D | Success |
| K23 | 4 July 1963 | Atlas E | Success |
| K26 | 15 August 1963 | Titan I | Success |
| K28 | 24 August 1963 | Atlas E | Success |
| K24 | 14 November 1963 | Titan I | Success |
Of the tests carried out over the two year test cycle, ten of them were successful in bringing the Zeus within its lethal range.[84][g]
Anti-satellite use
editIn April 1962, McNamara asked the Nike team to consider using the Zeus site on Kwajalein as an operational anti-satellite base after the main Zeus testing had completed. The Nike team responded that a system could be readied for testing by May 1963. The concept was given the name Project Mudflap.[85]
Development was a straightforward conversion of the DM-15B into the DM-15S. The changes were mainly concerned with providing more upper stage maneuverability through the use of a new two-stage hydraulic pump, batteries providing 5 minutes of power instead of 2, and an improved fuel in the booster to provide higher peak altitudes. A test of the new booster with a DM-15B upper was carried out at White Sands on 17 December 1962, reaching an altitude of 100 nautical miles (190 km), the highest of any launch from White Sands to that point. A second test with a complete DM-15S on 15 February 1963 reached 151 nautical miles (280 km).[83]
Testing then moved to Kwajalein. The first test on 21 March 1963 failed when the MTR failed to lock onto the missile. A second on 19 April also failed when the missile's tracking beacon failed 30 seconds before intercept. The third test, this time using an actual target consisting of an Agena-D upper stage equipped with a Zeus miss-distance transmitter, was carried out on 24 May 1963, and was a complete success. From that point until 1964, one DM-15S was kept in a state of instant readiness and teams continually trained on the missile.[86]
After 1964 the Kwajalein site was no longer required to be on alert, and returned primarily to Zeus testing. The system was kept active in a non-alert role between 1964 and 1967, known as Program 505. In 1967 it was replaced by a Thor based system, Program 437.[87] A total of 12 launches, including those at White Sands, were carried out as part of the 505 program between 1962 and 1966.
Description
editNike Zeus was originally intended to be a straightforward development of the earlier Hercules system giving it the ability to hit ICBM warheads at about the same range and altitude as the maximum performance of the Hercules.[9] In theory, hitting a warhead is no more difficult than an aircraft; the interceptor does not have to travel any further or faster, the computers that guide it simply have to select an intercept point farther in front of the target to compensate for the target's much higher speed. In practice, the difficulty is detecting the target early enough that the intercept point is still within range of the missile. This demands much larger and more powerful radar systems, and faster computers.[4]
Early detection
editWhen Zeus was still in the early stages of design, Bell Labs suggested using two similar radars to provide extended range tracking and improve reaction times. Located at the Zeus bases would be the Local Acquisition Radar (LAR), a UHF monopulse radar able to track between 50 and 100 targets. The Forward Acquisition Radar (FAR) would be positioned 300 to 700 miles (480–1,130 km) ahead of the Zeus bases to provide early warning of up to 200 to 300 seconds of tracking data on up to 200 targets. The FAR would broadcast 10 MW pulses at UHF between 405 and 495 MHz, allowing it to detect a 1 square metre radar reflection at 1,020 nautical miles (1,890 km) or a more typical 0.1 m2 target at 600 nautical miles (1,100 km). Each track would be stored as a 200 bit record[h] including location, velocity, time of measure and a measure of the quality of the data. Clouds of objects would be tracked as a single object with additional data indicating the width and length of the cloud. Tracks could be updated every five seconds while the target was in view, but the antenna rotated at a relatively slow 4 RPM so targets moved significantly between rotations. Each FAR could feed data to up to three Zeus sites.[88]
By the time the Zeus plans were being finalized in 1957, plans for FAR were deemphasized, and LAR had been upgraded to become the Zeus Acquisition Radar (ZAR) which provided wide area early warning and initial tracking information.[89] This enormously powerful radar was driven by multiple 1.8 MW klystrons and broadcast through three 80-foot (24 m) wide antennas arranged as the outside edges of a rotating equilateral triangle. The ZAR spun at 10 RPM, but with three antennas it simulated a single antenna rotating three times as fast. Each target was scanned every two seconds, providing much more data than the earlier FAR/LAR concept.[88]
The signal was received on a separate set of three antennas, situated at the centre of an 80 foot (24 m) diameter Luneburg lens, which rotated synchronously with the broadcaster under a 120-foot (37 m) diameter dome.[89] Multiple feed horns were used in the receiver to allow reception from many vertical angles at once. Around the receiver dome was a large field of wire mesh, forming a flat ground plane reflector. The ZAR operated in the UHF on various frequencies between 495 and 605 MHz, giving it frequency agility. ZAR had detection range on the order of 460 nautical miles (850 km) on a 0.1 m2 target.[89]
The entire transmitter was surrounded by a 65-foot (20 m) high clutter fence located 350 feet (110 m) away from the antenna, which reflected the signal away from local objects on the ground that would otherwise create false returns. The ZAR was so powerful that the microwave energy at close range was far beyond the mandated safety limits and potentially lethal within 100 yards (91 m). In order to allow for maintenance while the radar was operating, the equipment areas were shielded in a partial Faraday cage of metal foil, and a metal tunnel was run from the outside of the clutter fence, which blocked the signal outside the fence line. The other radars completing the system featured similar protection.[89]
Battery layout
editData from the ZARs were passed to the appropriate Zeus Firing Battery to attack, with each ZAR being able to send its data to up to ten batteries. Each battery was self-contained after handoff, including all of the radars, computers and missiles needed to perform an intercept. In a typical deployment, a single Zeus Defense Center would be connected to three to six batteries, spread out by as much as 100 miles (160 km).[90]
Targets picked out by the ZAR were then illuminated by the Zeus Discrimination Radar (ZDR, also known as Decoy Discrimination Radar, DDR or DR). ZDR imaged the entire cloud using a chirped signal that allowed the receiver to accurately determine range within the cloud by passing each frequency in the chirp to a separate range gate. The range resolution was 0.25 microseconds, about 75 metres (246 ft).[91] As the signal was spread out over the entire cloud, it had to be very powerful; the ZDR produced 40 MW 2 μs pulses in the L-band between 1270 and 1400 MHz.[92] To ensure no signal was lost by scanning areas that were empty, the ZDR used a Cassegrain reflector that could be moved to focus the beam as the cloud approached to keep the area under observation constant.[93][94]
Data from the ZDR was passed to the All-Target Processor (ATP), which ran initial processing on as many as 625 objects in a cloud. As many as 50 of these could be picked out for further processing in the Discrimination and Control Computer (DCC), which ran more tests on those tracks and assigned each one a probability of being the warhead or decoy. The DCC was able to run 100 different tests. For exoatmospheric signals the tests included measure of radar return pulse-to-pulse to look for tumbling objects, as well as variations in signals strength due to changes in frequency. Within the atmosphere, the primary method was examining the velocities of the objects to determine their mass.[91]
Any target with a high probability was then passed to the Battery Control Data Processor (BCDP), which selected missiles and radars for an attack.[95] This started with the assignment of a Target Tracking Radar (TTR) to a target passed to it from the DCC. TTRs operated in the C band from 5250 to 5750 MHz at 10 MW, allowing tracking of a 0.1 m2 target at 300 nautical miles (560 km), a range they expected to be able to double with a new maser-based receiver design. Once targets were being successfully tracked and a firing order was received, the BCDP selected available Zeus missiles for launch and assigned a Missile Tracking Radar (MTR) to follow them. These were much smaller radars operating in the X-band between 8500 and 9600 MHz and assisted by a transponder on the missile, using only 300 kW to provide missile tracking to 200 nautical miles (370 km). The wide variety of available frequencies allowed up to 450 MTRs to be operating in a single Defense Center.[96] Information from the ZDR, TTR and MRTs was all fed to the Target Intercept Computer (TIC) which handled the interceptions. This used twistor memory for ROM and core memory for RAM. Guidance commands were sent to the missiles in-flight via modulation of the MTR signal.[97]
The nominal battery consisted of a single DR, three TTRs, two TICs driving six MRTs, and 24 missiles.[98] This basic battery layout could attack three warheads at once, normally using two missiles per salvo in case one failed in flight. More typically, two targets would be attacked while the third system stood by as a hot backup that could take over in-flight.[99] A maximally expanded battery included three DRs, ten TTRs, six TICs driving eighteen MTRs and 72 missiles. Sites requiring higher traffic handling would not build larger systems, but instead deploy additional batteries fed from the same ZAR and Defense Center.[98]
It was expected that the ZAR would take 20 seconds to develop a track and hand off a target to one of the TTRs, and 25 seconds for the missile to reach the target. With these sorts of salvo rates, a fully expanded Zeus installation was expected to be able to successfully attack 14 "bare" warheads per minute.[94] Its salvo rate against warheads with decoys is not recorded, but would depend on the ZDR's processing rate more than any physical limit. The actual engagement would normally take place at about 75 nautical miles (139 km) due to accuracy limitations, beyond that missiles could not be guided accurately enough to bring them within their lethal 800 foot (240 m) range against a shielded warhead.[100][101]
-
Two TTRs are closest to the camera at the bottom, and the ZDR is centered. The MTRs are located on the building in the distant background.
-
The MTRs were very small as they homed in on strong signals from a transmitter in the missile. They used a simple fabric cover to protect them from the elements.
-
Photo of "Mount Olympus", the Nike-Zeus launcher complex on Kwajalein Island. The built-up hill allowed full-sized Zeus silos to be built into land only feet above sea level.
Zeus missiles
editThe original Zeus A was similar to the original Hercules, but featured a revised control layout and gas puffers for maneuvering at high altitudes where the atmosphere was too thin for the aerodynamic surfaces to be effective. The Zeus B interceptor was longer at 14.7 metres (48 ft), 2.44 metres (8 ft 0 in) wide, and 0.91 metres (3 ft 0 in) in diameter. This was so much larger than the earlier Hercules that no attempt was made to have them fit into the existing Hercules/Ajax launchers. Instead, the B models were launched from silos, thus the change of numbering from MIM (mobile surface launched) to LIM (silo launched). Since the missile was designed to intercept its targets in space, it did not need the large maneuvering fins of the A model. Rather, it featured a third rocket stage with small control jets to allow it to maneuver in space. Zeus B had a maximum range of 250 miles (400 km) and altitude of 200 miles (320 km).[102]
Zeus A was designed to attack warheads through shock effects, like the Hercules, and was to be armed with a relatively small nuclear warhead. As the range and altitude requirements grew, along with a better understanding of weapons effects at high altitude, the Zeus B was intended to attack its targets through the action of neutron heating. This relied on the interceptor's warhead releasing a huge number of high energy neutrons (similar to the neutron bomb), some of which would hit the enemy warhead. These would cause fission to occur in some of the warhead's own nuclear fuel, rapidly heating the "primary", hopefully enough to cause it to melt.[103] For this to work, the Zeus mounted the W50, a 400 kt enhanced radiation warhead, and had to maneuver within 1 km of the target warhead. Against shielded targets, the warhead would be effective to as little as 800 feet (0.24 km).[100]
Specifications
editThere are at least five Zeus models mentioned in various sources, A, B, C,[104] S[105] and X2,[104] the last of which became Spartan. None of the sources explicitly list the differences of all of these in a single table. Different sources appear to confuse measures between the Zeus A, B and Spartan. The A and Spartan figures are taken from US Strategic and Defensive Missile Systems 1950–2004,[106] B from the Bell Labs history.[107]
| Name | Nike Zeus A | Nike Zeus B | Spartan (LIM-49A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model nums | DM-15A | DM-15 B, (C?), S | DM-15X2 |
| Length | 44 ft 3 in (13.5 m) | 50 ft 2 in (15.3 m) | 55 ft 1 in (16.8 m) |
| Diameter | 3 ft 0 in (0.91 m) | 3 ft 0 in (0.91 m) | 3 ft 7 in (1.09 m) |
| Fin span | 9 ft 9 in (2.98 m) | 8 ft 0 in (2.44 m) | 9 ft 9 in (2.98 m) |
| Mass | 10,980 lb (4,980 kg) | 24,200 lb (10,977 kg) | 28,900 lb (13,100 kg) |
| Maximum speed | Mach 4 > (c. 2800+ mph; 4,900 km/h arbitrary) | ||
| Range | 200 mi (320 km) | 250 mi (400 km) | 460 mi (740 km) |
| Ceiling | (not mentioned) | 170 mi (280 km) | 350 mi (560 km) |
| Booster | Thiokol TX-135 400,000 lbf (1,800 kN) |
Thiokol TX-135 450,000 lbf (2,000 kN) |
Thiokol TX-500 500,000 lbf (2,200 kN) |
| Second stage | (not mentioned) | Thiokol TX-238 | Thiokol TX-454 |
| Third stage | None | Thiokol TX-239 | Thiokol TX-239 |
| Warhead | W31 (25 kt) | W50 (400 kt) | W71 (5 Mt) |
See also
edit- Project Wizard was the US Air Force's on-again, off-again ABM system that was ultimately replaced by Nike Zeus.
- Violet Friend was a Royal Air Force project similar to Zeus in many ways.
- The A-35 anti-ballistic missile system was a Soviet system roughly equivalent to the Nike Zeus.
- The A-135 anti-ballistic missile system replaced the A-35, and is roughly equivalent of Nike-X.
- Comparison of anti-ballistic missile systems
Explanatory notes
edit- ^ When Khrushchev's son asked why he made this statement, Khrushchev explained that "the number of missiles we had wasn't so important.… The important thing was that Americans believed in our power".[25]
- ^ Although it might seem that an ABM would naturally be able to attack aircraft, this is not always the case. Bombers fly at altitudes on the order of a few miles, whereas an ICBM reaches as high as 750 miles (1,210 km). This allows the ICBM to be detected at very long range, while the bomber is subject to the local radar horizon. Attacking aircraft would require additional radars spread around the missile site to push the detection range out, as well as different command and control arrangements. As the Soviets had never built up their bomber force like the US, and it appeared they were putting all future effort into ICBMs, the extra expense of the anti-aircraft additions were considered superfluous.
- ^ The outer layer of the missile can be seen turning black in the Bell Labs film The Range Goes Green.
- ^ Kennedy publicly introduced the term "missile gap" as part of an August 1958 speech.[51]
- ^ This result proved useful during later tests of the Sprint missile, where changes in frequency and demands to encrypt all data made the adaption of this simple method much more difficult. Instead, the TTR radars from the original Zeus site were used, as the original tests had demonstrated the TTR data to be accurate.[83]
- ^ Leonard incorrectly states this took place on 19 June.[61] It is one of a number of mistakes in his Chronology section, which should always be confirmed in other references.
- ^ Canavan mentions there being 14 tests, Bell's history shows only 13 in the table.
- ^ Referred to as a "file" in the Bell documents.
References
editCitations
edit- ^ Walker, Bernstein & Lang 2003, p. 20.
- ^ a b c Jayne 1969, p. 29.
- ^ a b Leonard 2011, p. 180.
- ^ a b Zeus 1962, p. 165.
- ^ Jayne 1969, p. 30.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.2.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.3.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, pp. 1.3–1.4.
- ^ a b c d e Zeus 1962, p. 166.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.4.
- ^ Jayne 1969, p. 32.
- ^ "Nike Ajax (SAM-A-7) (MIM-3, 3A)". Federation of American Scientists. 29 June 1999.
- ^ Leonard 2011, p. 329.
- ^ Kaplan 2006, p. 4.
- ^ "Air Force Calls Army Unfit to Guard Nation". New York Times. 21 May 1956. p. 1.
- ^ MacKenzie 1993, p. 120.
- ^ Jayne 1969, p. 33.
- ^ Larsen, Douglas (1 August 1957). "New Battle Looms Over Army's Newest Missile". Sarasota Journal. p. 35. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- ^ Trest, Warren (2010). Air Force Roles and Missions: A History. Government Printing Office. p. 175. ISBN 9780160869303.
- ^ MacKenzie 1993, p. 113.
- ^ MacKenzie 1993, p. 121.
- ^ Technical Editor (6 December 1957). "Missiles 1957". Flight International. p. 896.
{{cite magazine}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Gaither 1957, p. 5.
- ^ Thielmann, Greg (May 2011). "The Missile Gap Myth and Its Progeny". Arms Control Today.
- ^ Khrushchev, Sergei (200). Nikita Khrushchev and the Creation of a Superpower. Pennsylvania State University Press. p. 314. ISBN 0271043466.
- ^ a b c Preble 2003, p. 810.
- ^ Gaither 1957, p. 6.
- ^ a b Leonard 2011, p. 332.
- ^ Leonard 2011, p. 183.
- ^ a b Slayton 2013, p. 52.
- ^ "P&G: Changing the Face of Consumer Marketing". Harvard Business School. 2000.
- ^ "Neil H. McElroy (1957–1959): Secretary of Defense". University of Virginia Miller Center. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Kaplan 2006, p. 7.
- ^ a b Zeus 1962, p. 170.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. I-20.
- ^ Berhow 2005, p. 31.
- ^ Walker, Bernstein & Lang 2003, p. 39.
- ^ Leonard 2011, p. 331.
- ^ Leonard 2011, p. 182.
- ^ Kaplan 2008, p. 80.
- ^ a b c d e Kaplan 2008, p. 81.
- ^ WSEG 1959, p. 20.
- ^ Kaplan 1983, p. 344.
- ^ Yanarella 2010, pp. 72–73.
- ^ Broad, William (28 October 1986). "'Star Wars' Traced To Eisenhower Era". The New York Times.
- ^ Garvin & Bethe 1968, pp. 28–30.
- ^ Leonard 2011, pp. 186–187.
- ^ a b c Baucom 1992, p. 19.
- ^ Kaplan 2006, p. 6–8.
- ^ Papp 1987.
- ^ "US Military and Diplomatic Policies - Preparing for the Gap". JFK Library and Museum. 14 August 1958.
- ^ Kaplan 2008, p. 82.
- ^ Kaplan 1983, p. 345.
- ^ a b Kaplan 2006, p. 9.
- ^ Brown 2012, p. 91.
- ^ Day, Dwayne (3 January 2006). "Of myths and missiles: the truth about John F. Kennedy and the Missile Gap". The Space Review: 195–197.
- ^ Heppenheimer, T. A. (1998). The Space Shuttle Decision. NASA. pp. 195–197.
- ^ Day 2006.
- ^ Leonard 2011, p. 334.
- ^ Yanarella 2010, p. 68.
- ^ a b c Leonard 2011, p. 335.
- ^ Reed, Sidney (1991). DARPA Technical Accomplishments, Volume 2. Institute for Defense Analyses. pp. 1–14. Archived from the original on 1 March 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- ^ Yanarella 2010, pp. 68–69.
- ^ a b Yanarella 2010, p. 87.
- ^ Yanarella 2010, p. 69.
- ^ a b Yanarella 2010, p. 70.
- ^ "JFK Accepts McNamara View On Nike Zeus". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. 8 January 1963. p. 20.
- ^ a b Walker, Bernstein & Lang 2003, p. 49.
- ^ a b Kaplan 2006, p. 13.
- ^ Allan, Robert; Scott, Paul (26 April 1963). "McNamara Lets Reds Widen Antimissile Gap". Evening Independent. p. 3-A.
- ^ Kaplan 2006, p. 14.
- ^ Gibson 1996, p. 205.
- ^ Walker, Bernstein & Lang 2003, p. 42.
- ^ Walker, Bernstein & Lang 2003, p. 44.
- ^ A 20-Year History of the Anti-Ballistic Missile. Bell Labs. 17 May 2012. Event occurs at 15:46. Archived from the original on 21 May 2015. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.23.
- ^ a b Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.24.
- ^ John Kennedy, others (5 June 1963). Presidential Visit [JFK at White Sands]. White Sands Missile Range: John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum. Event occurs at 14 minutes.
- ^ a b Walker, Bernstein & Lang 2003, p. 41.
- ^ Kaplan 2006, p. 10.
- ^ Leonard 2011, p. 333.
- ^ a b Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.26.
- ^ a b c Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.31.
- ^ Hubbs, Mark (February 2007). "Where We Began – the Nike Zeus Program" (PDF). The Eagle. p. 14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 October 2012. Retrieved 8 May 2013.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.32.
- ^ "Program 505". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 12 June 2002. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- ^ a b WSEG 1959.
- ^ a b c d Zeus 1962, p. 167.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. II, 1.1.
- ^ a b Bell Labs 1975, p. II, 1.14.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. II, 1.12.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. II, 1.11.
- ^ a b Program For Deployment Of Nike Zeus (Technical report). 30 September 1961.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. II, 1.25.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. I, 1.18.
- ^ Zeus 1962, pp. 167, 170.
- ^ a b Bell Labs 1975, p. I, 1.4.
- ^ WSEG 1959, p. 10.
- ^ a b Bell Labs 1975, p. 1.1.
- ^ WSEG 1959, p. 160.
- ^ "Nike Zeus". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 27 August 2002. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- ^ Kaplan 2006, p. 12.
- ^ a b Bell Labs 1975, p. 10-1.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. I-31.
- ^ Berhow 2005, p. 60.
- ^ Bell Labs 1975, p. 1–33.
General bibliography
edit- Baucom, Donald (1992). The Origins of SDI, 1944–1983. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-0531-6. OCLC 25317621.
- Bell Labs (October 1975). ABM Research and Development at Bell Laboratories, Project History (PDF) (Technical report). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 December 2014. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Berhow, Mark (2005). US Strategic and Defensive Missile Systems 1950–2004. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-84176-838-0. OCLC 62889392.[permanent dead link]
- Brown, Harold (2012). Star Spangled Security: Applying Lessons Learned over Six Decades Safeguarding America. Brookings Institution Press. ISBN 9780815723837. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Canavan, Gregory (2003). Missile Defense for the 21st Century (PDF). Heritage Foundation. ISBN 0-89195-261-6. OCLC 428736422. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2015.
- Garvin, Richard; Bethe, Hans (March 1968). "Anti-Ballistic-Missile Systems" (PDF). Scientific American. Vol. 218, no. 3. pp. 21–31. Bibcode:1968SciAm.218c..21G. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0368-21. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Gibson, James (1996). Nuclear Weapons of the United States: An Illustrated History. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7643-0063-9. OCLC 35660733.
- Jayne, Edward Randolph (1969). The ABM debate: strategic defense and national security (PDF) (Technical report). Massachusetts Institute of Technology. OCLC 19300718. Retrieved 13 December 2014.[permanent dead link]
- Kaplan, Fred (1983). The Wizards of Armageddon. Stanford University Press. ISBN 9780804718844.
- Kaplan, Fred (2008). Daydream Believers: How a Few Grand Ideas Wrecked American Power. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9780470121184.
- Kaplan, Lawrence (2006). Nike Zeus: The U.S. Army's First ABM (PDF). Falls Church, Virginia: Missile Defense Agency. OCLC 232605150. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 February 2013. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- Leonard, Barry (2011). History of Strategic and Ballistic Missile Defense: Volume II: 1956–1972 (PDF). DIANE Publishing. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 December 2019. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- MacKenzie, Donald (1993). Inventing Accuracy: A Historical Sociology of Nuclear Missile Guidance. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262631471.
- Papp, Daniel (Winter 1987–88). "From Project Thumper to SDI". Airpower Journal. Archived from the original on 25 January 2017. Retrieved 6 May 2013.
- Preble, Christopher (December 2003). "'Who Ever Believed in the "Missile Gap?"': John F. Kennedy and the Politics of National Security". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 33 (4): 801–826. doi:10.1046/j.0360-4918.2003.00085.x. JSTOR 27552538.
- Security Resources Panel of the Science Advisory Committee (7 November 1957). Deterrence & Survival in the Nuclear Age (PDF) (Technical report). Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Slayton, Rebecca (2013). Arguments that Count: Physics, Computing, and Missile Defense, 1949–2012. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262019446. Retrieved 15 December 2014.
- "Nike Zeus". Flight International. 2 August 1962. pp. 165–170. ISSN 0015-3710. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- US Army Weapons Systems Evaluation Group (23 September 1959). Potential Contribution of Nike-Zeus to Defense of the U.S. Population and its Industrial Base, and the U.S. Retaliatory System (PDF) (Technical report). Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Walker, James; Bernstein, Lewis; Lang, Sharon (2010). Seize the High Ground: The U. S. Army in Space and Missile Defense (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Center of Military History. ISBN 9780813128092. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 February 2013. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- Yanarella, Ernest (2010). The Missile Defense Controversy: Technology in Search of a Mission. University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 9780813128092. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
External links
edit- "Nike Zeus". Nuclearabms.info. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- AT&T Archives: Nike Zeus Missile System, made early in the program
- The Range Goes Green, movie of a Zeus test launch at White Sands
- AT&T Archives: A 20-year History of Antiballistic Missile Systems, has several shots showing Atlas RVs and their resulting debris cloud, giving an indication of the magnitude of the discrimination problem.