
Size of this preview: 800 × 544 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 218 pixels | 640 × 435 pixels | 1,024 × 696 pixels | 1,280 × 870 pixels | 2,835 × 1,927 pixels.
Original file (2,835 × 1,927 pixels, file size: 3.65 MB, MIME type: image/png)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:56, 13 June 2007 | 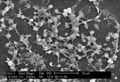 | 2,835 × 1,927 (3.65 MB) | Gkai | {{Information |Description=This electron micrograph depicted large numbers of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, which were fond on the luminal surface of an indwelling catheter. Of importance is the sticky-looking substance woven between the round cocci bac |
File usage
The following pages on the English Wikipedia use this file (pages on other projects are not listed):
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on de.wikipedia.org
- Usage on et.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fi.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ja.wikipedia.org

