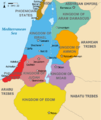
The Jordan Portal  Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and the occupied Palestinian territory of the West Bank and Israel to the west. The Jordan River, flowing into the Dead Sea, is located along the country's western border. Jordan has a small coastline along the Red Sea in its southwest, separated by the Gulf of Aqaba from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as the most populous city in the Levant. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three kingdoms emerged in Transjordan at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their kingdom centered in Petra. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and the Ottoman empires. After the Great Arab Revolt against the Ottomans in 1916 during World War I, the Greater Syria region was partitioned by Britain and France. The Emirate of Transjordan was established in 1921 by the Hashemite, then Emir, Abdullah I, and the emirate became a British protectorate. In 1946, Jordan gained independence and became officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. The country captured and annexed the West Bank during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War until it was occupied by Israel in 1967. Jordan renounced its claim to the territory to the Palestinians in 1988, and signed a peace treaty with Israel in 1994. Jordan is a semi-arid country, covering an area of 89,342 km2 (34,495 sq mi), with a population of 11.5 million, making it the eleventh-most populous Arab country. The dominant majority, or around 95% of the country's population, is Sunni Muslim, with the rest being mostly Arab Christian. Jordan was mostly unscathed by the violence that swept the region following the Arab Spring in 2010. From as early as 1948, Jordan has accepted refugees from multiple neighbouring countries in conflict. An estimated 2.1 million Palestinian (most of whom hold Jordanian citizenship) and 1.4 million Syrian refugees were present in Jordan in 2015. The kingdom is also a refuge for thousands of Christian Iraqis fleeing persecution. While Jordan continues to accept refugees, the large Syrian influx during the 2010s has placed substantial strain on national resources and infrastructure. The sovereign state is a constitutional monarchy, but the king holds wide executive and legislative powers. Jordan is a founding member of the Arab League and the Organisation of Islamic Co-operation. The country has a high Human Development Index, ranking 99th, and is considered a lower middle income economy. The Jordanian economy, one of the smallest economies in the region, is attractive to foreign investors based upon a skilled workforce. The country is a major tourist destination, also attracting medical tourism due to its well developed health sector. Nonetheless, a lack of natural resources, large flow of refugees, and regional turmoil have hampered economic growth. (Full article...) Selected article -The Zarqa River (Arabic: نهر الزرقاء, Nahr az-Zarqāʾ, lit. "the River of the Blue [City]") is the second largest tributary of the lower Jordan River, after the Yarmouk River. It is the third largest river in the region by annual discharge and its watershed encompasses the most densely populated areas east of the Jordan River. The Zarqa rises in springs near Amman, and flows through a deep and broad valley into the Jordan, at an elevation 1,090 metres (3,580 ft) lower. At its spring lays 'Ain Ghazal (Arabic: عين غزال), a major archaeological site that dates back to the Neolithic. Archaeological finds along the course of the river indicate the area was rich in flora and fauna in the past. (Full article...)Selected biography -Hussein bin Abdullah (Arabic: الحسين بن عبد الله, Al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh; born 28 June 1994) is Crown Prince of Jordan as the eldest son of King Abdullah II and Queen Rania. He is a member of the Hashemite dynasty, the royal family of Jordan since 1921, and is considered to be 42nd-generation direct descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Hussein is a Captain in the Jordanian Armed Forces, started his education in Jordan and in 2016 he graduated from Georgetown University with a degree in International History. Since reaching the age of majority in 2012, Hussein served as a regent on several occasions and has accompanied his father on a number of local and international visits. (Full article...)WikiProjectFor editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Jordan-related articles, see WikiProject Jordan. General images -The following are images from various Jordan-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected city -Aqaba (English: /ˈækəbə/ AK-ə-bə, US also /ˈɑːk-/ AHK-; Arabic: الْعَقَبَة, romanized: al-ʿAqaba, pronounced [ælˈʕæqɑba, ælˈʕæɡæba]) is the only coastal city in Jordan and the largest and most populous city on the Gulf of Aqaba. Situated in southernmost Jordan, Aqaba is the administrative center of the Aqaba Governorate. The city had a population of 148,398 in 2015 and a land area of 375 square kilometres (144.8 sq mi). Today, Aqaba plays a major role in the development of the Jordanian economy, through the vibrant trade and tourism sectors. The Port of Aqaba also serves other countries in the region. Aqaba's strategic location at the northeastern tip of the Red Sea between the continents of Asia and Africa has made its port important throughout thousands of years. The ancient city was called Elath, adopted in Latin as Aela and in Arabic as Ayla. Its strategic location and proximity to copper mines made it a regional hub for copper production and trade in the Chalcolithic period. Aela became a bishopric under Byzantine rule and later became a Latin Catholic titular see after Islamic conquest around AD 650, when it became known as Ayla; the name Aqaba is late medieval. The Great Arab Revolt's Battle of Aqaba resulted in victory for Arab forces over the Ottoman defenders. (Full article...)
See also: List of cities in Jordan
Related portalsReligions in Jordan Arab states Other countries Recognized content
Featured articlesGood articles
TopicsSelected topic overview -
CategoriesSelected picture - The Karak Castle (c. 12th century AD) built by the Crusaders, and later expanded under the Muslim Ayyubids and Mamluks.
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesDiscover Wikipedia using portals |