The terminology of the British Isles comprises the words and phrases that are used to describe the (sometimes overlapping) geographical and political areas of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, and the smaller islands which surround them. The terms are often a source of confusion, partly owing to the similarity between some of the actual words used but also because they are often used loosely. Many of the words carry geographical and political connotations which are affected by the history of the islands.

Geographical feature Legal distinction
The purpose of this article is to explain the meanings of and relationships among the terms in use; many of these classifications are contentious .
Summary edit
The use of terms depends on context; words and phrases can be grouped into geographical, political, linguistic and sporting terms. In brief, the main terms and their simple explanations are as follows:
- Geographical terms:
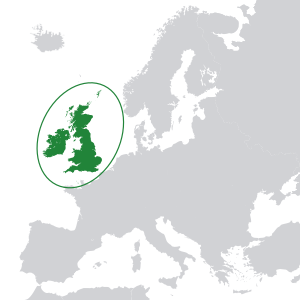
- The British Isles is an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Continental Europe. It includes Ireland, Great Britain, the Isle of Man, Shetland, Orkney and thousands of smaller islands. Traditionally the Channel Islands are included, though they are geographically closer to mainland continental Europe, off the French coast of Normandy. This, in part, has resulted in the term being disputed.[1]
- Great Britain is the largest island of the archipelago.[2]
- Ireland is the second-largest island of the archipelago and lies directly to the west of Great Britain. The island of Ireland itself has its own islands.
- The full list of islands of the British Isles includes over 6,000 islands, of which 51 have an area larger than 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi).[3]
- The British Isles is an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Continental Europe. It includes Ireland, Great Britain, the Isle of Man, Shetland, Orkney and thousands of smaller islands. Traditionally the Channel Islands are included, though they are geographically closer to mainland continental Europe, off the French coast of Normandy. This, in part, has resulted in the term being disputed.[1]
- Political terms:
- The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the parliamentary constitutional monarchy occupying the island of Great Britain, the small nearby islands (but not the Isle of Man or the Channel Islands), and the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland. Usually, it is shortened to the United Kingdom or the UK, or Britain.[4] Great Britain is sometimes used as a short form and is the name used by the UK in some international organisations.[5] The abbreviation GB is frequently used for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in international agreements, e.g. Universal Postal Union and Road Traffic Convention, as well as in the ISO 3166 country codes (GB and GBR). England was also formerly used synecdochically to refer to the whole United Kingdom but this usage became rare early in the 20th century (though it persists in other languages).
- Ireland is the sovereign republic occupying the larger portion of the island of Ireland. To distinguish the state from the island, or to distinguish either of these from Northern Ireland, it is also called "the Republic of Ireland" or simply "the Republic". In the past, its Irish-language name, Éire (or Eire without the diacritic), was often used in an English-language context to distinguish it from Northern Ireland and from the island of Ireland.
- England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are the four countries of the United Kingdom, though they are also referred to, especially in sporting contexts, as the home nations of the United Kingdom.
- England and Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland are separate legal jurisdictions within the United Kingdom.[6]
- Great Britain means the countries of England, Wales and Scotland, considered as a unit.[7]
- The British Islands consist of the United Kingdom, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. These are the polities in and near the British Isles that have the British monarch as head of state.
- Linguistic terms:
- The two sovereign states in the region, the United Kingdom and Ireland, are frequently referred to as countries. So too are England, Wales, Scotland and, to a lesser extent, Northern Ireland (as is the whole island of Ireland).
- British is an adjective of the United Kingdom; for example, a citizen of the UK is called a British citizen—but for citizenship purposes "British" includes the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man.
- "Anglo-" is often used as an adjectival prefix referring to the United Kingdom (notwithstanding that its original meaning is "English"), particularly in the field of diplomatic relations. It can also refer to the English language or to anglophone peoples, and can have a variety of other shades of meaning.
- Wales is sometimes called the Principality of Wales, although this has no modern constitutional basis.
- Northern Ireland is often referred to as a province or called Ulster, after the traditional Irish province of Ulster within which it is located.
- Sport
- Forms of national representation vary from sport to sport. England, Scotland and Wales often compete separately as nations.[8] In some sports—such as rugby and cricket—the island of Ireland competes as a nation; in others, most notably association football, Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland field separate teams. In these contexts England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland/Northern Ireland are sometimes described as the home nations.
- Forms of representation can also vary within a sport. In women's association football, for instance, England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland compete as separate nations at the FIFA Women's World Cup but join together as the Great Britain Olympic football team ("Team GB") for the Olympics.
- Rugby union players from both Ireland and Great Britain play for the British and Irish Lions representing the four "Home Unions" of England, Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
- "Great Britain" is sometimes used to mean "United Kingdom". For example, at the Olympic Games, the team called "Great Britain" marches under the letter "G" in the Parade of Nations and represents Great Britain and Northern Ireland.[9][10] However, since athletes from Northern Ireland have entitlement to dual nationality, they have the choice of participating in either the Great Britain team or the Republic of Ireland team.[10] Conversely, at the Universiade, the team marches under the full name "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" under the letter "U" in the Parade of Nations.
- In the majority of individual sports (e.g. tennis and athletics), at the international level competitors are identified as GB if they are from Great Britain or Northern Ireland. A small number of sports (e.g. golf, darts, snooker) identify participants as representing their constituent country. In the Commonwealth Games, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each compete as separate nations, as do each of the three Crown Dependencies (Ireland is not part of the Commonwealth and is not eligible to participate).
Visual guide edit
Below is a visual reference guide to some of the main concepts and territories described in this article:
-
The British Isles (broad definition including the Channel Islands)
-
The British Islands
-
The United Kingdom
-
Great Britain (island)
-
Ireland (island)
-
The Isle of Man
Terminology in detail edit
- Britain is a political and geographic term which can refer to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland,[11] or the island of Great Britain.
- Great Britain is the largest island in Europe and the political union of three nations, these being:
- England and Wales is a political and administrative term referring to the two home countries of England and Wales, which share the same legal system. Between 1746 and 1967 the term "England" did legally include Wales.
- England (see also the historical Kingdom of England).
- Wales (see also the historical Principality of Wales).
- Scotland (see also the historical Kingdom of Scotland)
- The historical Kingdom of Great Britain is Britain for the period 1707–1801.
- England and Wales is a political and administrative term referring to the two home countries of England and Wales, which share the same legal system. Between 1746 and 1967 the term "England" did legally include Wales.
- Britannia is the Latin name for Great Britain or for the Roman province of Britain, or a poetic reference to later Britain, or a female personification of Britain.
- The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, usually shortened to "the United Kingdom" (abbreviation UK),[4] is the sovereign state comprising Great Britain plus Northern Ireland since 1927. (The Partition of Ireland took place in 1922, but the consequent change in the official title of the UK was only made by Act of Parliament five years later.) The United Kingdom is often called Britain, even on official websites,[12] where such use is described as "informal".[13][11] A proposal to rename the political entity as the "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ulster" was formally recommended by civil servants to the Cabinet in 1949 but ultimately rejected.[14]
- The historical United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was Great Britain plus Ireland, for the period 1801 to 1922, although the name change after the secession of the Irish Free State only took place in 1927.
- While "United Kingdom" is normally abbreviated UK, the official ISO 3166 two-letter country code is GB and the three letter code is GBR (Ukraine has the two letter code UA and the three letter code UKR). Due to a pre-existing convention originating in the UK's JANET academic computer network,[15] the UK's Internet top-level domain is .uk, a break from the TCP/IP practice of following ISO 3166 (a .gb domain has also been used to a limited extent in the past but is now defunct).
- GB was also used on car number plates to indicate the United Kingdom until September 2021. The car sticker has been 'UK' since then.[16]
- Ireland (Irish: Éire) refers, geographically, to the island of Ireland, or to any of the following:
- Historically:
- The Kingdom of Ireland was Ireland for the period 1541–1801. (The King of Ireland remained Head of State in the Irish Free State and Ireland/Éire until the Republic of Ireland Act 1948 abolished that status).
- The Irish Republic, established by the Irish Declaration of Independence, was a 32-county republic encompassing the entire island, during the period 1919–1922—though its de facto rule did not encompass all of the island. During this period, according to British law, Ireland remained part of the UK though its independence was recognised by Russia.
- Southern Ireland was a 26-county region of Ireland that was created when Ireland was partitioned under the Government of Ireland Act 1920. It was superseded by:
- The Irish Free State is Ireland excepting Northern Ireland during the period 1922–1937.
- Present:
- Ireland (Irish: Éire) is the political entity consisting of the island of Ireland excepting Northern Ireland, 1937–present. This is the name of the state according to the Irish Constitution and the United Nations.
- "Republic of Ireland" is a commonly used description of Ireland excepting Northern Ireland, 1949–present. It is also the name used by the international association football team.
- The terms Irish Republic, Southern Ireland, the Irish Free State, the Free State, the 26 Counties and Éire (in English-language texts) have been used synonymously with the Republic of Ireland. Of these, Southern Ireland and Irish Free State, in particular, are seen as outdated. Eire (spelt without the Irish fada) was the British legal spelling from the Eire (Confirmation of Agreements) Act 1938 until the Ireland Act 1949, and informally for some years after.
- Northern Ireland (1921–present). That part of the island of Ireland northeast of the line of partition of 1921, and which is still part of the United Kingdom. Various alternative names have been used or proposed for Northern Ireland. It is sometimes referred to as "the North of Ireland", "the Six Counties" or (in extremist usage) the "occupied six counties", especially by Irish Nationalists. The "Northern" in "Northern Ireland" is not completely accurate. The most northerly point on the island, Malin Head, is in the Republic of Ireland—in County Donegal's Inishowen Peninsula.
- Ulster is the name of one of Ireland's four traditional provinces. The province contains nine northern counties, six of which make up Northern Ireland, and three of which are part of the Republic of Ireland. It is also often used by Unionists to refer to the smaller Northern Ireland. Though Ulster has not been a political entity since the ancient Gaelic provincial kingdoms, it remains associated with a geographical area and is used in sporting and cultural contexts. See Ulster (disambiguation).
- In sport
- In Gaelic games, no distinction is recognised between the GAA counties of the Republic and those of Northern Ireland. County teams play in their provincial championships (where the six counties of Ulster within Northern Ireland and three within the Republic all play in the Ulster championship) and the winners of these play in the All-Ireland championship. Even within Northern Ireland, the tricolour flag of the Republic of Ireland is flown at all games. At bigger games, where an anthem is played, it is always the national anthem of the Republic. In the case of the International Rules series against Australia, an Irish national team is chosen from all 32 counties.
- In association football, the teams correspond to political entities: Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. In accordance with UEFA and FIFA's rules, each of these countries has its own football league: the Irish Football League and the League of Ireland respectively.
- In rugby union, rugby league, field hockey, cricket, boxing, golf, athletics and others the Ireland team is drawn from the whole island (i.e. both the Republic and Northern Ireland). Many sports organisations are subdivided along provincial lines e.g. Gaelic Athletic Association, golf.
- Historically:
- "British Isles" is a term used to mean the island of Great Britain plus the island of Ireland and many smaller surrounding islands, including the Isle of Man and, in some contexts, the Channel Islands (Guernsey and Jersey). See Names of the British Isles for details of the conflict over use of this term.
- Anglo-Celtic Isles is an alternative term (in limited use) for the archipelago more commonly referred to as the British Isles. It is intended as a geographic term free of any political implication and uses the macro-cultural grouping term Anglo-Celtic, referring to the peoples from which the majority of the island group's population are descended—the Anglo-Saxons and the Celts (it can also be inclusive of the Anglo-Normans).
- "Islands of the North Atlantic" is another suggested replacement term for British Isles, without the same political connotations. However, its convolution and impracticality due to implying inclusion of fellow North Atlantic islands such as Iceland have made it unworkable and it has not come into common use. The term was used as part of the Strand 3 level of negotiations for the Belfast agreement. (Its acronym, IONA, is also the name of the small but historically important island of Iona off the coast of Scotland.)
- Great Britain and Ireland or Britain and Ireland are also used as alternatives to the term "British Isles".
- On the 2011 Jersey census, "British Isles" is used to refer to the other British islands than Jersey, but does not include the Republic of Ireland.[17]
- "British Islands" (a legal term not in common usage) is the UK, the Isle of Man, and the Channel Islands.
- Brittany, itself derived from Medieval Latin Britannia, and sometimes formerly known as Little Britain, is a historical duchy in the west of France, now a French region; for this modern administrative sense, see Brittany (administrative region).
Geographical distinctions edit
The British Isles edit
The British Isles is a group of islands in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Continental Europe. It includes Ireland, Great Britain, the Isle of Man, Shetland, Orkney, and thousands of smaller islands. Traditionally the Channel Islands, are included, but these specific islands are geographically part of mainland continental Europe, as they are positioned off the French coast of Normandy. The term is disputed (see Names of the British Isles).
Great Britain edit
Great Britain is the largest of the British Isles. On Great Britain are located the bulk of three constituent countries of the United Kingdom: Scotland in the north, England in the south and east and Wales in the west. There are also numerous smaller islands off its coast (not coloured red on the attached map) that are administered as part of England, Scotland and Wales. The inclusion of these smaller islands means political 'Great Britain' covers a slightly larger area than the island of Great Britain.
Ireland edit
The second largest island in the group is Ireland. Most of the island is in the Republic of Ireland. The northeast of the island (Northern Ireland) is part of the United Kingdom. There are also numerous smaller islands off the coast of Ireland.
Isle of Man edit
The Isle of Man lies between Great Britain and Ireland. It is governed as a British Crown dependency, having its own parliament, but with the United Kingdom responsible for its defence and external relations.
Channel Islands edit
Although the Channel Islands are associated with the United Kingdom politically as Crown Dependencies, they are geographically an outcrop of the nearby French mainland (specifically, the Armorican massif), and historically they are the last remaining parts of the Duchy of Normandy, a title belonging to the British monarch.
Political terms in more detail edit
The United Kingdom edit
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the official full title of the state. This name appears on official documentation such as British passports. For convenience, the name is usually shortened to United Kingdom, UK or Britain.[4][13]
The United Kingdom is a sovereign state. Its four constituent countries are sometimes considered to be of different status. This view may be supported by the existence of devolved governments with different levels of power in Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales (see Asymmetrical federalism).
Wales is also often erroneously[18] described as a principality of the United Kingdom. The title of Prince of Wales is usually given to the heir apparent to the British throne but it has no official political or other role in respect of Wales (though since the early 20th century Princes of Wales have preferentially taken on ceremonial royal duties in Wales on an informal basis). The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has defined Wales as a "country" rather than a "principality" since 2011, following a recommendation by the British Standards Institute and the Welsh Government.[19]
Northern Ireland is sometimes described by United Kingdom citizens as a province of the United Kingdom, which derives from the Irish province of Ulster, of which Northern Ireland is a part. Northern Ireland also had, until 1972, a far greater degree of self-government than the other constituent parts of the UK.
Great Britain is both a geographical and a political entity. Geographically, it is one island, but as a political entity it also includes the smaller offshore islands that are administered as part of its constituent nations – England, Wales and Scotland – such as England's Isle of Wight, Wales' Anglesey and Scotland's Inner Hebrides, Outer Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands.
The abbreviation GB is sometimes officially used for the United Kingdom, for example in the Olympics, or as the vehicle registration plate country identification code for UK-registered cars (see also British car number plates). SCO for Scotland, CYM for Wales (Cymru), NI for Northern Ireland, or ENG for England can also be used.[20] From 28 September 2021, UK will be the official country code on car registration plates.[21]
The internet code .gb, although allocated to the UK, is virtually unused and UK web domains use .uk.
Though GB is the United Kingdom's ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code, UK is exceptionally reserved for the United Kingdom on the request of the country.
The four constituent parts of the UK are also known, particularly in sporting contexts, as Home Nations or the "Four Nations". The BBC refers to its UK-wide broadcasting operation as Nations and Regions [22] ("regions" referring to geographic regions of England. Thus the naming conventions tend towards describing distinct regions or nations which exist within a single sovereign state.
In sport, the home nations mostly have their own separate national teams – England, Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland, for example in association football. Sporting contests between the Four Nations are known as "Home internationals" (an example is the British Home Championship in football).
The governing body for football in Northern Ireland is called the Irish Football Association (the IFA), having been in existence since some forty years before Partition. Its counterpart in the Republic (plus Derry City FC) is the Football Association of Ireland (the FAI). The Northern Ireland national team retained the name "Ireland" for some fifty years after partition. Since around 1970 the two teams have been consistently referred to as "Northern Ireland" and "Republic of Ireland" respectively. The UK competes as Great Britain at the Olympic Games. According to the Olympic Charter the Olympic Council of Ireland represents the entire island of Ireland.[23] Olympic athletes from Northern Ireland may choose whether to represent the UK or the Republic of Ireland.
Since the Good Friday Agreement and the subsequent implementation legislation, sporting organisation (and several other organisations, e.g. tourism, Irish Gaelic and Ulster Scots language boards) on the island of Ireland has increasingly been cross-border.
Citizens of the UK are called British, Britons, Brits, (colloquial) or Britisher (archaic). The term Unionists may also be used when referring to supporters of the Union. Some older slang names for Britons are Tommy (for British soldiers) and Anglo. Anglo properly refers only to England, but it is sometimes used as a broader reference as an element in compound adjectives: for example, "Anglo-French relations" may be used in newspaper articles when referring to relations between the political entities France and the United Kingdom. Anglo-Saxon may be used (particularly in Continental European languages) when referring to the whole English-speaking world.
Ireland edit
Since the adoption of the Constitution of Ireland in 1937, Ireland has been the English name of the state which covers approximately five-sixths of the island of Ireland. The name Éire is used when writing in Irish.
Since the Republic of Ireland Act 1948, the term "Republic of Ireland" is the term used as the additional description of the state. This term is useful in avoiding ambiguity between the name of the island and the name of the state. However, the term "Ireland" is always used in formal diplomatic contexts such as the European Union or the United Nations. The passport of the Republic of Ireland bears the name Éire – Ireland.
Before the introduction of the 1937 constitution and the new name, the Irish Free State occupied the same territory as the modern state of Ireland. The Irish Free State became an autonomous dominion of the British Empire in 1922 when it seceded from the United Kingdom through the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The King ceased to be its Head of State in 1936 and the state ceased to be a Dominion and left the Commonwealth in 1948.
Traditionally, the island of Ireland is divided into four provinces – Leinster, Connacht, Munster and Ulster, with each of the provinces further divided into counties. The Republic of Ireland takes up 83% of the island, twenty-six of the thirty-two traditional counties of Ireland. Northern Ireland takes up the remaining area, six of the traditional nine counties of Ulster.
In Northern Ireland, Irishness is a highly contested identity, with fundamentally different perceptions of national identity between unionists (who generally perceive themselves as being British) and nationalists (who generally consider both communities to be part of the Irish nation).[24]
The Republic of Ireland is often referred to by the nationalist and Republican communities by the term "the Twenty-six Counties", with the connotation that the state constituted as such forms only a portion of the ideal political unit of the Irish Republic, which would consist of all of the thirty-two counties into which the island is divided. The term "the Six Counties" (of Northern Ireland) is also used. Other nationalist terms in use include "the North of Ireland" and "the North". These latter are terms also used by the Irish national broadcaster RTÉ.[citation needed] More extreme terms for Northern Ireland include "the occupied six counties" or "occupied Ireland", which are often used by people who reject the idea of Northern Ireland as a separate entity from the Republic of Ireland.
The Irish passport is available to Irish citizens and can also be applied for abroad through Irish Consular services and the local Irish Embassy. As per the Irish nationality law, any person born on the island of Ireland before 2005, or otherwise a first generation descendant of such a person, is allowed to apply for an Irish passport. As such, people born in Northern Ireland and their children may be Irish citizens and hold an Irish passport if they choose.
British Islands edit
Under the Interpretation Act 1978 of the United Kingdom, the legal term British Islands (as opposed to the geographical term British Isles) refers to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, together with the Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwicks of Jersey and of Guernsey (which in turn includes the smaller islands of Alderney, Herm and Sark) in the Channel Islands; and the Isle of Man.
On the 2011 Jersey census, "British Isles" as a country of origin is used to refer to the other British islands than Jersey (effectively the British Islands), but does not include the Republic of Ireland.[17]
Special British passports are issued to citizens of the Crown dependencies. On the front of passports issued to residents of the Crown dependencies, the words "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" are replaced with the name of the issuing state or island. Pre-Brexit, Crown dependency also bore the title "European Union" for border control purposes. Crown dependency citizens who have no family ties to the United Kingdom were granted a special limited 'Islander Status' under EU law (article 6 of Protocol 3 in the Treaty of Accession of the UK to the European Community).[25]
Historical aspects edit
Some suggest an early known for the term might be from ancient Greek writings. Though some of the original texts have been lost, excerpts were quoted or paraphrased by later authors. Parts of the Massaliote Periplus, a merchants' handbook describing searoutes of the sixth century BC, were used in translation in the writings of Avienius around AD 400. Ireland was referred to as Ierne (Insula sacra, the sacred island, as the Greeks interpreted it) "inhabited by the race of Hiberni" (gens hiernorum), and Britain as insula Albionum, "island of the Albions".[26] Several sources from around 150 BC to AD 70 include fragments of the travel writings of the ancient Greek Pytheas around 320 BC, use the terms Albion and Ierne[27][28] and have been described as referring to the British Isles, including Ireland, as the Prettanic or Brettanic Islands (Βρεττανικαὶ νῆσοι) or as αἱ Βρεττανιαι, literally "the Britains".[26][28][29] Greek writers called the peoples of these islands the Πρεττανοί, later Bρεττανοί (alternative spellings of this and of all relative words have a single tau or a double nu), a name that possibly corresponds to the Priteni.[26] These names may have derived from a "Celtic language" term which may have reached Pytheas from the Gauls[29] who may have used it as their term for the inhabitants of the islands.
The Romans called the inhabitants of Gaul (modern France) Galli or Celtae, the latter term deriving from the Greek name Κελτοί for a central European people. Antiquarians of the seventeenth century who found language connections developed the idea of a race of Celts inhabiting the islands, but this term was not used by the Greeks or Romans for the inhabitants of Britain or Ireland,[30] nor is there any record of the inhabitants of the British Isles referring to themselves as such. Nevertheless, Roman administration later incorporated the province of Britannia into the praetorian prefecture of Gaul, in common with Hispania, which had Celtiberians. Armorica, where the Bretons would settle[when?], was part of Gallia Celtica, so there were tertiary relations between the Britons and Gallic Celts at least. In addition, the Parisii of Gallia Celtica are thought to have founded Aldborough in Britain. Belgae and Silures also came from Gallic areas, although not strictly "Celtic", but from Gallia Belgica and Aquitainia.
Priteni is the source of the Welsh language term Prydain, Britain,[29] and has the same source as the Goidelic term Cruithne. The latter referred to the early Brythonic speaking inhabitants of the Scottish highlands and the north of Scotland,[29] who are known as the Cruithne in Scottish Gaelic, and who the Romans called Picts or Caledonians.
Romans edit
Caesar's invasions of Britain brought descriptions of the peoples of what he called Britannia pars interior, "inland Britain", in 55 BC. Throughout Book 4 of his Geography, Strabo is consistent in spelling the island Britain (transliterated) as Prettanikē; he uses the terms Prettans or Brettans loosely to refer to the islands as a group – a common generalisation used by classical geographers. For example, in Geography 2.1.18, …οι νοτιώτατοι των Βρεττανών βορειότεροι τούτων εισίν ("…the most southern of the Brettans are further north than this").[31] He was writing around AD 10, although the earliest surviving copy of his work dates from the 6th century. Pliny the Elder writing around AD 70 uses a Latin version of the same terminology in section 4.102 of his Naturalis Historia. He writes of Great Britain: Albion ipsi nomen fuit, cum Britanniae vocarentur omnes de quibus mox paulo dicemus. ("Albion was its own name, when all [the islands] were called the Britannias; I will speak of them in a moment"). In the following section, 4.103, Pliny enumerates the islands he considers to make up the Britannias, listing Great Britain, Ireland, and many smaller islands. In his Geography written in the mid 2nd century and probably describing the position around AD 100,[29] Ptolemy includes both Great Britain (Albion) and Ireland (Iwernia) in the so called Bretanic island group. He entitles Book II, Chapter 1 of as Iwernia, Bretanic Island, and Chapter 2 as Alwion [sic], Bretanic Island.[32]
The name Albion for Great Britain fell from favour, and the island was described in Greek as Πρεττανία or Βρεττανία, in Latin Britannia, an inhabitant as Βρεττανός, Britannus, with the adjective Βρεττανικός, Britannicus, equating to "British".[26] With the Roman conquest of Britain the name Britannia was used for the province of Roman Britain. The Emperor Claudius was honoured with the agnomen Britannicus as if he were the conqueror, and coins were struck from AD 46 inscribed DE BRITAN, DE BRITANN, DE BRITANNI, or DE BRITANNIS. With the visit of Hadrian in AD 121 coins introduced a female figure with the label BRITANNIA as a personification or goddess of the place. These and later Roman coins introduced the seated figure of Britannia which would be reintroduced in the 17th century.[33]
In the later years of Roman rule Britons who left Latin inscriptions, both at home and elsewhere in the Empire, often described themselves as Brittanus or Britto, and where describing their citizenship gave it as cives of a British tribe or of a patria (homeland) of Britannia, not Roma.[26] From the 4th century, many Britons migrated from Roman Britain across the English Channel and founded Brittany.
Mediaeval period edit
While Latin remained the language of learning, from the early mediaeval period records begin to appear in native languages. The earliest indigenous source to use a collective term for the archipelago is the Life of Saint Columba, a hagiography recording the missionary activities of the sixth century Irish monk Saint Columba among the peoples of what is now Scotland. It was written in the late seventh century by Adomnán of Iona, an Irish monk living on the Inner Hebridean island. The collective term for the archipelago used within this work is Oceani Insulae meaning "Islands of the Ocean" (Book 2, 46 in the Sharpe edition = Book 2, 47 in Reeves edition), it is used sparingly and no Priteni-derived collective reference is made.
Another early native source to use a collective term is the Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum of Bede written in the early eighth century. The collective term for the archipelago used within this work is insularum meaning "islands" (Book 1, 8) and it too is used sparingly. He stated that Britain "studies and confesses one and the same knowledge of the highest truth in the tongues of five nations, namely the Angles, the Britons, the Scots, the Picts, and the Latins", distinguishing between the Brythonic languages of the "ancient Britons" or Old Welsh speakers and other language groups.[34]
Brythonic, Saxon and Viking kingdoms such as Strathclyde, Wessex, and Jórvík amalgamated, leading to the formation of Scotland, and England. Wales was sometimes united under princes or kings such as Gruffydd ap Llywelyn. Between 854 and 1171, a kingship of Ireland was established by kings of the regional kingdoms such as Máel Sechnaill mac Máele Ruanaid, Toirdelbach Ua Briain, Muirchertach Mac Lochlainn, and Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair, something not achieved in Britain until 1707. In subsequent Norman Ireland, local lords gained considerable autonomy from the Lordship of Ireland until it became the Kingdom of Ireland under direct English rule.
Renaissance mapmakers edit
Abraham Ortelius makes clear his understanding that England, Scotland and Ireland were politically separate in 1570 by the full title of his map: Angliae, Scotiae et Hiberniae, sive Britannicar. insularum descriptio ('A representation of England, Scotland and Ireland, or the Britannic islands'). George Lily's 1546 map divides Britain into the two kingdoms of England and Scotland, with Ireland alongside. Some maps from this period also appear to mark Wales, and sometimes Cornwall, as separate areas within Britain, while the history of England created by Polydore Vergil[35] for Henry VIII states, "The whole country of Britain is divided into four parts, whereof the one is inhabited by Englishmen, the other of Scots, the third Welshmen and the fourth of Cornish people."[36]
Maps of the Mediaeval, Renaissance and later periods often referred to Albion. This archaic term was originally used by Ptolemy and Pliny to mean the island of Great Britain. In later centuries its meaning changed to refer only to the area we now call Scotland (Albany, or Alba in Gaelic). Albion has survived as a poetic name for Britain but it is not in everyday use.
18th and 19th centuries edit
Following the Acts of Union 1707, a fashion arose, particularly in Scotland, for referring to Scotland as North Britain, while England was sometimes dubbed South Britain. These terms gained in popularity during the 19th century. The most lasting example of this usage was in the name of the North British Railway, which became part of the London and North Eastern Railway in 1923, and in the name of the North British Hotel in Edinburgh, opened by the North British Railway in 1902, which retained the name until it reopened in 1991 as The Balmoral.
Evolution of kingdoms and states edit
The diagram on the right gives an indication of the further evolution of kingdoms and states. In 1603, James VI of Scotland inherited the English throne as "James I of England". He styled himself as King of Great Britain, France, and Ireland, although both kingdoms on Great Britain retained their sovereignty and independent parliaments, the Parliament of Scotland and the Parliament of England.[37] (The term "Great Britain" in English itself dates from Middle English as early as c. 1338, a translation of 12th-century Medieval Latin: Britannia maior and Anglo-Norman: Bretannie maiur or grant Bretaigne and derived from Ptolemy's Geography.)[37]
The Act of Union (1707) united England and Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain under the Parliament of Great Britain, then in 1800 Ireland was brought under British government control by the Act of Union (1800) creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Irish unrest culminated in the Irish War of Independence and the 1922 separation of the Irish Free State, which later became a republic with the name Ireland. The majority Protestant northeast continued to be part of what became the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
British overseas territories such as Bermuda, Gibraltar and the Falkland Islands have various relationships with the UK. The Commonwealth of Nations, initially formalised in 1931 (the British Commonwealth until 1949), is an association of independent states roughly corresponding to the former British Empire. (This has no connection with the Commonwealth of England, a short-lived republic replacing the previous kingdoms during the English Interregnum (1649–1660).)
Slang edit
Blighty is a slang word for Britain derived from the Bengali word biletī.[38] Depending on the user, it is meant either affectionately or archly. It was often used by British soldiers abroad in the First World War to refer to home.
Adjectives edit
The adjectives used to describe the contents and attributes of the various constituent parts of the British Isles also cause confusion.
In the absence of a single adjective to refer to the United Kingdom, British is generally used to refer to the United Kingdom as a whole. However, in a specifically physical geographical sense, British is used to refer to the island of Great Britain.[39] The adjectival phrase Great British is very rarely used to refer to the island, other than to contrive a pun on the word great, as in "Great British Food".
Irish, refers to people or a characteristic "of Ireland".[40] As such, its meaning is contextual on the meaning of "Ireland" being used: it can relate both to the Irish state, and to the island of Ireland. Northern Ireland, as a constituent part of the United Kingdom, can thus be both British or Irish, reflected in the ability for residents of Northern Ireland to take either British or Irish citizenship.[41] To be more specific, Northern Irish is therefore in common usage. Members of the Nationalist communities would not describe themselves as British and would only use the terms Irish, or specifically Northern Irish where needed.
The term Ulster can also be used as an adjective (e.g. "Royal Ulster Constabulary"), but this is more likely to be used by Unionists and has political connotations in the same fashion as its use as a proper noun. The term Ulsterman (or Ulsterwoman) is common and holds no such political connotation. Likewise, Nationalists might describe, say, a lake in Northern Ireland as Irish.
Note that the geographical term Irish Sea thus far appears to have escaped political connotations, even though territorial control of the waters of the Irish Sea is divided between both the Republic of Ireland and the UK, and also includes a British Crown dependency, the Isle of Man—as yet there appears to be no controversy with the term’s usage to mirror that of "British Isles".
Problems with the use of terms edit
British Isles edit
The dictionary definition of the British Isles is that it is a geographical term that refers to the whole of Ireland and Great Britain as well as the surrounding islands. It is sometimes incorrectly used as if identical to the United Kingdom, or to refer to Great Britain and the surrounding islands, excluding the island of Ireland entirely.[42] The BBC and The Times have style guides that mandate the dictionary definition but occasional misuse can be found on their websites.[43]
The term British Isles can also be considered irritating or offensive by some[44] on the grounds that the modern association of the term British with the United Kingdom makes its application to Ireland inappropriate. The term can also be considered to imply a proprietary title on the entire archipelago.[45]
The policy of the government of Ireland is that no branch of government should use the term,[46] and although it is on occasion used in a geographical sense in Irish parliamentary debates, this is often done in a way that excludes the Republic of Ireland. In October 2006, The Times quoted a spokesman for the Irish Embassy in London as saying that they would discourage its use.[47]
During a stop-over visit to the Republic of Ireland in 1989, the leader of the Soviet Union, Mikhail Gorbachev, indicated that he assumed Ireland's head of state was Queen Elizabeth II, given that she was the British Queen and his officials said that Ireland was a part of the British Isles.[48]
There have been several suggestions for replacements for the term British Isles. Although there is no single accepted replacement, the terms Great Britain and Ireland, The British Isles and Ireland and Britain and Ireland are all used. In Northern Ireland, some nationalists use these islands or these isles as an alternative.[49]
Britain edit
The word Britain is ambiguous, being used variously to mean Great Britain,[50][51] the United Kingdom,[52][51] and for some, England.[53] The usage of Britain can be contentious, with many people in Northern Ireland objecting to its application to their region.[54] While some organisations, including the BBC, prefer to use Britain as shorthand for Great Britain,[55] others prefer, where precision is not required, to use Britain to mean the United Kingdom.[56] The UK Government itself states a preference for using the UK over Britain in its style guide, but does not describe the latter as incorrect, and says elsewhere that "it is only the one specific nominal term "Great Britain", which invariably excludes Northern Ireland."[57]
England edit
The word England is sometimes used synecdochically to refer to Great Britain, or the United Kingdom as a whole, or sometimes the British Isles.[58] References to England as an island,[59] to an "English passport",[60] or to Scottish or Welsh places as being in England[60][61] are examples of this usage of the term "England".
Such usage often causes offence, particularly to those from the non-English parts of the United Kingdom. Because of this, most politicians and official figures have avoided this usage since the early 20th century. However, there are frequent examples of this usage from earlier times.[62] For a long time it was common for fans of the England football team to wave the British Union Jack; the use of the specifically English St George's Cross flag only gained popularity at the UEFA Euro 1996 tournament.[60]
The colloquial usage of England as a synonym for the United Kingdom is still widespread outside the country. In Germany, the term England is often used to mean Great Britain or even the entire United Kingdom (as in the anti-British slogan Gott strafe England). In many other languages, such as Chinese or Hindi the word for "English" is synonymous with "British"–see the article on Alternative words for British for more detail.
Europe edit
The term Europe may be used in one of several different meanings by British and Irish people: either to include the islands as part of Europe, or to refer only to Mainland Europe, sometimes called "continental Europe" or simply "the Continent" by some people. Europe may also be used in reference to the European Union (or, historically, to the European Economic Community).
Great Britain edit
The word "Great" means "larger", in comparison with Brittany in modern-day France. One historical term for the peninsula in France that largely corresponds to the modern French province is Lesser or Little Britain. That region was settled by many British immigrants during the period of Anglo-Saxon migration into Britain, and named "Little Britain" by them. The French term "Bretagne" now refers to the French "Little Britain", not to the British "Great Britain", which in French is called Grande-Bretagne. In classical times, the Graeco-Roman geographer Ptolemy in his Almagest also called the larger island megale Brettania (great Britain). At that time, it was in contrast to the smaller island of Ireland, which he called mikra Brettania (little Britain).[63] In his later work Geography, Ptolemy refers to Great Britain as Albion and to Ireland as Iwernia. These "new" names were likely to have been the native names for the islands at the time. The earlier names, in contrast, were likely to have been coined before direct contact with local peoples was made.[64]
Ireland edit
The word Ireland is also ambiguous, with the double meaning of the island of Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. The usage of "Ireland" as the official name of the Republic causes offence to some Unionists in Northern Ireland, who believe it implies that the state still has a territorial claim to the whole island – the terminology of "Republic of Ireland" or "Éire" is much preferred by Northern Irish unionists when referring to that political state. Similarly, some Nationalists in Northern Ireland also prefer to reserve the usage of "Ireland" to refer to the whole island.
Ulster edit
The terminology and usage of the name Ulster in Irish and British culture varies. Many within the unionist community[65] and much of the press refer to Northern Ireland as Ulster – whereas the nationalist community refer to the traditional Irish province of Ulster, which is a nine-county entity that incorporates the three counties of Donegal, Cavan and Monaghan (which are in the Republic) along with the counties of Armagh, Antrim, Down, Fermanagh, Londonderry and Tyrone in Northern Ireland.
Thus, the word Ulster has two usages:
- It is the name of one of the four Provinces of Ireland, consisting of the nine northern counties of the island, that was partitioned between the United Kingdom (six counties) and the Republic of Ireland (three counties).
- It is an alternative name for Northern Ireland, used by many in the Unionist community. It consists of the six north-eastern counties of the island that remain part of the United Kingdom.
Further information edit
Isle of Man and Channel Islands edit
The Isle of Man and the two bailiwicks of the Channel Islands are Crown Dependencies; that is, non-sovereign nations, self-governing but whose sovereignty is held by the British Crown. They control their own internal affairs, but not their defence or foreign relations. They are not part of the United Kingdom, and were not part of the European Union when the UK was a member state.
- The Isle of Man is part of the British Isles, situated in the Irish Sea between Great Britain and Ireland.
- The Channel Islands consist politically of two self-governing bailiwicks: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Bailiwick of Jersey. They are the remnants of the Duchy of Normandy, which was once in personal union with the Kingdom of England. They are sometimes, despite their location next to mainland France, considered part of the British Isles. This usage is political rather than geographic.
- The Isle of Man and the Channel Islands are British Islands in United Kingdom law.
Celtic names edit
There are five Celtic languages in current use in the region. Each has names for the islands and countries of the British Isles. They are divided into two branches:
- Brythonic – which includes Welsh and Cornish
- Goidelic – which includes Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Manx
Some of the above are:
| English | Cornwall | Wales | Ireland | Northern Ireland |
Republic of Ireland |
Scotland | Mann | England |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cornish (Kernewek) |
Kernow | Kembra | Iwerdhon | Iwerdhon Gledh | Repoblek Iwerdhon | Alban | Manow | Pow an Sawson |
| Welsh (Cymraeg) |
Cernyw | Cymru | Iwerddon | Gogledd Iwerddon | Gweriniaeth Iwerddon | Yr Alban | Manaw | Lloegr |
| Irish (Gaeilge) |
an Chorn | an Bhreatain Bheag | Éire | Tuaisceart Éireann | Poblacht na hÉireann | Albain | Manainn | Sasana |
| Scottish Gaelic (Gàidhlig) |
a' Chòrn | a' Chuimrigh | Èirinn | Èirinn a Tuath | Poblachd na h-Èireann | Alba | Manainn | Sasann |
| Manx (Gaelg) |
y Chorn | Bretyn | Nerin | Nerin Hwoaie | Pobblaght Nerin | Nalbin | Mannin | Sostyn |
The English word Welsh is from a common Germanic root meaning "Romanised foreigner" (cognate with Wallonia and Wallachia, and also cognate with the word used in Mediaeval German to refer to the French and Italians).[66]
The English names Albion and Albany are related to Alba and used poetically for either England or Scotland, or the whole island of Great Britain.
English Erin is a poetic name for Ireland derived from Éire (or rather, from its dative form Éirinn).
Terms for the British Isles in the Irish language edit
In Irish, the term Oileáin Bhriotanacha is a translation of the English term British Isles. Another translation is Oileáin Bhreataineacha, which was used in the 1937 translation from English to Irish of a 1931 geography book.[67]
Earlier dictionaries[68] give Oileáin Iarthair Eorpa as the translation, literally meaning West European Isles. Today the most common term Éire agus an Bhreatain Mhór is used, meaning, literally, Ireland and Great Britain, as provided by terminological dictionaries.[69]
See also edit
References edit
- ^ Alan, Lew; Colin, Hall; Dallen, Timothy (2008). World Geography of Travel and Tourism: A Regional Approach. Oxford: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7506-7978-7.
The British Isles comprise more than 6,000 islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe, including the countries of the United Kingdom of Great Britain (England, Scotland and Wales) and Northern Ireland, and the Republic of Ireland. The group also includes the United Kingdom crown dependencies of the Isle of Man, and by tradition, the Channel Islands (the Bailiwicks of Guernsey and Jersey), even though these islands are strictly speaking an archipelago immediately off the coast of Normandy (France) rather than part of the British Isles.
; "Written Answers – Official Terms" Archived 2012-10-06 at the Wayback Machine, Dáil Éireann, Volume 606, 28 September 2005. In his response, the Irish Minister for Foreign Affairs stated that "The British Isles is not an officially recognised term in any legal or inter-governmental sense. It is without any official status. The Government, including the Department of Foreign Affairs, does not use this term. Our officials in the Embassy of Ireland, London, continue to monitor the media in Britain for any abuse of the official terms as set out in the Constitution of Ireland and legislation. These include the name of the State, the President, Taoiseach and others." - ^ "Britain", Oxford English Dictionary: "More fully Great Britain. The term Great Britain includes England, Scotland and Wales; it does not include Northern Ireland. As a geographical and political term: (the main island and smaller offshore islands making up) England, Scotland, and Wales, sometimes with the Isle of Man"; New Oxford American Dictionary: "Britain: an island that consists of England, Wales, and Scotland. The name is broadly synonymous with Great Britain, but the longer form is more usual for the political unit."; "Britain", Oxford English Dictionary (Online Edition): "Britain: 1a – The proper name of the whole island containing England, Wales, and Scotland, with their dependencies; more fully called Great Britain; now also used for the British state or empire as a whole."
- ^ There are no official definitions, but Scotland has over 790 offshore islands plus numerous freshwater islands so a complete list of the British Isles would probably have between 1,000 and 2,000 entries. Haswell-Smith, Hamish (2004). The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh: Canongate. ISBN 1-84195-454-3.[better source needed]
- ^ a b c Permanent Committee on Geographical Names. "Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom". gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ "About BOA". British Olympic Authority. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ Though the statute law applicable in Wales has diverged further from that applicable in England since devolution from the UK government to the National Assembly for Wales, "England and Wales" remains a single jurisdiction.
- ^ "Great Britain", New Oxford American Dictionary: "Great Britain: England, Wales, and Scotland considered as a unit. The name is also often used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom."; "Countries within a country". Cabinet Office. 2003-01-10. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ^ World and Its Peoples, Terrytown (NY): Marshall Cavendish, 2010, p. 111,
In most sports, except soccer, Northern Ireland participates with the Republic of Ireland in a combined All-Ireland team.
- ^ "Team GB". British Olympic Association. Archived 2018-12-25 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ a b "Irish and GB in Olympic row". BBC Sport. 27 January 2004. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ^ a b "the term 'Britain' is used informally to mean the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland". Cabinet Office
- ^ "Guide to Government". Direct.gov.uk. HM Government. Archived from the original on July 14, 2007. Retrieved 2010-06-19.; "Living in Britain – 2000". Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 2009-10-05. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ^ a b "Key facts about the United Kingdom". Directgov. British Government. 3 October 2012. Archived from the original on 3 October 2012.
'Britain' is used informally, usually meaning the United Kingdom.
- ^ British Archives, Catalogue Reference:CAB/129/32 (Memorandum by PM Attlee to Cabinet appending Working Party Report); Quoted at length at Alternative names for Northern Ireland.
- ^ "Electronic Mail address changes" On the transition from big-endian to little-endian notation (Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Leeds)
- ^ "GB (now UK) car sticker?" Department for Transport
- ^ a b Jersey Census Results, p. 9. 2011. Accessed 1 March 2022.
- ^ "Wales FAQ Page". Wales.com. Archived from the original on 2011-04-14. Retrieved 2011-07-03.
- ^ "International body grants Wales country status after principality error", WalesOnline, 1 August 2011, retrieved 4 May 2016
- ^ BBC News (28 December 2001). "Flag day for patriotic drivers". Retrieved 22 October 2007.
- ^ "GB car sticker to be replaced by new 'UK' version | RAC Drive". www.rac.co.uk. Retrieved 2021-07-10.
- ^ BBC Press Office. "BBC Nations & Regions".
- ^ BBC News (2004-01-27). "Irish and GB in Olympic Row". Retrieved 2013-05-02.
- ^ CAIN: Democratic Dialogue: With all due respect – pluralism and parity of esteem (Report No. 7) by Tom Hennessey and Robin Wilson, Democratic Dialogue (1997)
- ^ "What is Islander status?". States of Guernsey. 2013. Archived from the original on 7 October 2013. Retrieved 8 December 2017.; Jersey, States of. "Islander status and your right to live and work in Europe". www.gov.je. Archived from the original on 8 December 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Snyder, Christopher A. (2003). The Britons. Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0-631-22260-X.
- ^ "Entry for Albion a 1911 Encyclopedia". Historymedren.about.com. 2010-06-14. Archived from the original on 2008-07-23. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ^ a b Greek "... ἐν τούτῳ γε μὴν νῆσοι μέγιστοι τυγχάνουσιν οὖσαι δύο, Βρεττανικαὶ λεγόμεναι, Ἀλβίων καὶ Ἰέρνη, ...", transliteration "... en toutoi ge men nesoi megistoi tynchanousin ousai dyo, Brettanikai legomenai, Albion kai Ierne, ...", Aristotle or Pseudo-Aristotle. "On the Cosmos, 393b12". On Sophistical Refutations. On Coming-to-be and Passing Away. On the Cosmos. Translated by E. S. Forster; D. J. Furley. William Heinemann, Harvard University Press.
- ^ a b c d e Donnchadh O Corrain (2001). R F Foster (ed.). Chapter 1: Prehistoric and Early Christian Ireland. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-280202-X.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ "The earliest Celts in Europe". WalesPast. Archived from the original on 2004-10-11. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ^ Translation by Roseman, op.cit.
- ^ Greek text Ptolemy's Geography, Books I-IV, pg 59
- ^ "Britannia on British Coins". 24carat.co.uk.
- ^ General survey of Lothian Archived 2006-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Map Collectors' Series, Issue 9, Map Collectors' Circle, 1972.
- ^ Thomas Kingston Derry, Michael G. Blakeway, J. Murray, The making of pre-industrial Britain: life and work between the Renaissance and the Industrial Revolution, 1969.; Philip Payton, The Making of Modern Cornwall: Historical Experience and the Persistence of "Difference", Dyllansow Truran, 1992.
- ^ a b "Britain, n.2". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). 2008. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ Wild, Kate (21 February 2014). "The English expressions coined in WW1". BBC Magazine. Retrieved 22 February 2014.
After the introduction of conscription in 1916, the distinction between soldiers and civilians became less clear, and vocabulary passed readily from one group to the other. This is the case with ... Blighty. The Urdu words vilayat ("inhabited country", specifically Europe or Britain) and vilayati ("foreign", or "British, English, European") were borrowed by the British in the 19th Century.... But it was the regional variant bilayati - rendered as Blighty in English and meaning "Britain, England, home" - which really took off in Britain. Although it was first used during the Boer war, it was not until WW1 that Blighty spread widely and developed new meanings.
- ^ "British". Collins English Dictionary. Retrieved 16 April 2014.
- ^ "Irish". Collins English Dictionary. Retrieved 16 April 2014.
- ^ "British-Irish Agreement". British-Irish. 12 December 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2014.
- ^ "The website uses the term "British Isles" in various ways, including ways that use Ireland as all of Ireland, while simultaneously using the term "The British Isles and Ireland", e.g. "Anyone using GENUKI should remember that its name is somewhat misleading — the website actually covers the British Isles and Ireland, rather than just the United Kingdom, and therefore includes information about the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man, as well as England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland." Archived 2007-11-05 at the Wayback Machine; "[1][permanent dead link] Guide to Narrow Gauge rail in the British Isles and Ireland which includes Belfast lines under the section on Ireland."
- ^ British Weather (Part One) This BBC article referred to "a small country such as the British Isles" between at least April 2004 and January 2007 (checked using the Wayback Machine at https://web.archive.org. Last accessed and checked 01/01/07. It was changed in February 2007 and now reads 'a small area such as the British Isles'; For example, see Google searches of the BBC website.
- ^ Marsh, David (2010-05-11). "Snooker and the geography of the British Isles". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2011-08-23.
- ^ Trevor Montague (2009). A to Z of Britain and Ireland (A to Z series). Little, Brown Book Group. p. introduction. ISBN 978-1-84744-087-7.
- ^ "Written Answers – Official Terms" Archived 2012-10-06 at the Wayback Machine, Dáil Éireann – Volume 606 – 28 September 2005. In his response, the Irish Minister for Foreign Affairs added that "Our officials in the Embassy of Ireland, London, continue to monitor the media in Britain for any abuse of the official terms as set out in the Constitution of Ireland and in legislation. These include the name of the State, the President, Taoiseach and others."
- ^ "New atlas lets Ireland slip shackles of Britain" A spokesman for the Irish Embassy in London said: “The British Isles has a dated ring to it, as if we are still part of the Empire. We are independent, we are not part of Britain, not even in geographical terms. We would discourage its usage. [sic]”
- ^ Eamon Delaney, 2001, An Accidental Diplomat: My Years in the Irish Foreign Service, New Island Books, Dublin, ISBN 1-902602-39-0
- ^ Guelke, Adrian (2001). "Northern Ireland and Island Status". In John McGarry (ed.). Northern Ireland and the Divided World: The Northern Ireland Conflict and the Good Friday Agreement in Comparative Perspective. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 231.
- ^ "Britain Meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary". dictionary.cambridge.org.; "Definition of Britain in English by Oxford Dictionaries". Oxford Dictionaries - English. Archived from the original on September 26, 2016.
- ^ a b "Britain definition and meaning". www.collinsdictionary.com. Collins English Dictionary.
- ^ "Britain - Definition for English-Language Learners". learnersdictionary.com. Merriam-Webster's Learner's Dictionary.
- ^ Birch, Anthony H. (2013). British System of Government. Routledge. p. 2. ISBN 9781134670567.
- ^ "Alphabetical checklist". BBC. 19 August 2002.
many people in Northern Ireland object strongly ... to the idea that they live in Britain.
- ^ "Alphabetical checklist". BBC News. BBC. Archived from the original on 2018-07-17. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
- ^ "Places and people". The Telegraph. 23 January 2018.
The United Kingdom or the abbreviation UK is to be avoided ... unless the story has a specific relevance to Northern Ireland that would make the use of "Britain" or "British" wrong.
; "Style Guide" (PDF). The Economist. 2005. p. 38.favour simplicity over precision and use Britain rather than Great Britain or the United Kingdom
- ^ "Toponymic guidelines for map and other editors, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland". www.gov.uk. UK Government.; "A to Z - Style guide". www.gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ "When people say England, they sometimes mean Great Britain, sometimes the United Kingdom, sometimes the British Isles — but never England." — George Mikes (1946), How To Be An Alien, Penguin ISBN 0-582-41686-8; "In practice, many people outside of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland incorrectly use 'England' to mean Britain..." p. 208 – Jean Rose Freedman (1998), Whistling in the Dark: Memory and Culture in Wartime London, University Press of Kentucky ISBN 0-8131-2076-4
- ^ Charlotte Augusta Sneyd (1500). A Relation or rather a True Account of the Island of England. Camden Society. Retrieved 2007-10-21.
island of england.
- ^ a b c BBC News (1999-01-14). "The English: Europe's lost tribe". Retrieved 2007-10-21.
- ^ "Learn English in Edinburgh, England". ESL Language Studies. Archived from the original on 2007-01-19. Retrieved 2007-10-21.
- ^ England expects that every man will do his duty — Horatio Nelson, message to the British Fleet 1805; "The English Prime Minister. Mr. Disraeli's Elevation To The Peerage" (PDF). New York Times. 1876-08-12. Retrieved 2007-10-21.; "The more formal use of 'Great-Britain and Ireland' and colloquial use of 'Old England' and 'old English spirit' in this description is evidence of the process of forging a national identity..." page 99 — Margarette Lincoln (1946), Representing the Royal Navy: British Sea Power, 1750–1815, Ashgate Publishing ISBN 0-7546-0830-1
- ^ Claudius Ptolemy (1898). "Ἕκθεσις τῶν κατὰ παράλληλον ἰδιωμάτων: κβ', κε'" (PDF). In Heiberg, J.L. (ed.). Claudii Ptolemaei Opera quae exstant omnia. Vol. 1 Syntaxis Mathematica. Leipzig: in aedibus B.G.Teubneri. pp. 112–113.
- ^ Philip Freeman, Ireland and the Classical World, University of Texas Press, 2001
- ^ "A Glossary of Terms Related to the Conflict". CAIN Web service. Ulster University. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
- ^ Davies, John (1994). A History of Wales. London: Penguin. p. 69. ISBN 0-14-014581-8.
- ^ Tír-Eóluíocht na h-Éireann (translation by Toirdhealbhach Ó Raithbheartaigh of Macmillan's General and Regional Geography of Ireland by T. J. Dunne), Government Publications Office, Dublin
Tá Éire ar cheann de na h-oileáin a dtugar na h-Oileáin Bhreataineacha ortha agus atá ar an taobh Thiar-Thuaidh de'n Eóraip. Tá siad tuairim a's ar chúig mhíle oileán ar fad ann. (Oileánradh an t-ainm a bheirtear ar áit ar bith i n-a bhfuil a lán oileán agus iad i n-aice a chéile mar seo.) Éire agus an Bhreatain Mhór (Sasain, an Bhreatain Bheag, agus Alba) an dá oileán is mó de na h-Oileáin Bhreataineacha.
Ireland is one of the islands which are called the British Isles and which are on the North-Western side of Europe. It is thought that there are five thousand islands in total there. (Archipelago is the name which is borne by a place in which there are many islands next to each other like these.) Ireland and Great Britain (England, Wales, and Scotland) are the two largest islands of the British Isles.
- ^ Patrick S. Dinneen, Foclóir Gaeilge Béarla, Irish-English Dictionary, Dublin, 1927
- ^ "the British Isles". téarma.ie – Dictionary of Irish Terms. Foras na Gaeilge and Dublin City University. Retrieved 18 Nov 2016.