Chloroalkyl ethers are a class of organic compounds with the general structure R-O-(CH2)n-Cl, characterized as an ether connected to a chloromethyl group via an alkane chain.
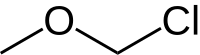
Chloromethyl methyl ether (CMME) is an ether with the formula CH3OCH2Cl. It is used as an alkylating agent and industrial solvent to manufacture dodecylbenzyl chloride, water repellents, ion-exchange resins, polymers, and as a chloromethylation reagent. In organic synthesis the compound is used for the introduction of the methoxymethyl (MOM) protecting group.
Closely related compounds of industrial importance are bis(chloromethyl) ether (BCME) (closely related to chemical weapon sulfur mustard)[1] and benzyl chloromethyl ether (BOMCl).
| Chloromethyl ether | R | Molar mass | CAS number | Boiling point °C | |
| Benzyl chloromethyl ether | Benzyl | 156.61 | 3587-60-8 | 102 °C @ 14 mmHg (1.9 kPa) | |
| Chloromethyl methyl ether | Methyl |  |
80.51 | 107-30-2 | 55-57 |
| Bis(chloromethyl) ether | 114.96 | 542-88-1 | 106 | ||
| tert-Butyl chloromethyl ether | Butyl | 124.5 | |||
| 2-Methoxyethoxymethyl chloride | 124.57 | 3970-21-6 | 50-52 °C @ 13 mmHg (1.7 kPa) | ||
| Dichloromethyl methyl ether |  |
114.96 | 4885-02-3 | 82 - 85.5 °C | |
| Representative chloroalkyl ethers[2] | |||||
Methoxymethyl ethers (MOMs) and methoxyethyl ethers (MEMs) are common protecting groups in organic synthesis.
Safety edit
Chloroalkyl ethers are strong alkylating agents with attendant dangers. These compounds are human carcinogen.[3]
References edit
- ^ Bis(Chloromethyl) ether Safety Data Sheet Archived 2009-01-13 at the Wayback Machine, Division of Occupational Health and Safety, US National Institutes of Health
- ^ "Sigma-Aldrich: Analytical, Biology, Chemistry & Materials Science products and services".
- ^ Bis(chloromethyl) Ether and Technical-Grade Chloromethyl Methyl Ether CAS Nos. 542-88-1 and 107-30-2, Report on carcinogens, Eleventh edition