| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
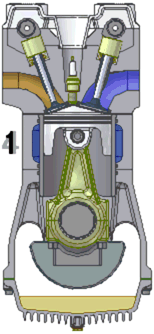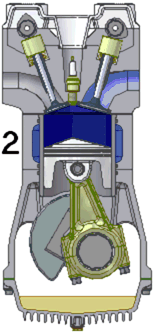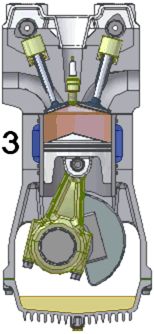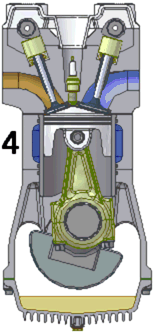
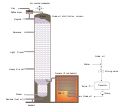
The defining feature of an internal combustion engine is that useful work is performed by the expanding hot gases acting directly to cause movement, for example by acting on pistons, rotors, or even by pressing on and moving the entire engine itself.
Internal combustion engines are most commonly used for mobile propulsion systems, where their high power-to-weight ratios, together with excellent fuel energy-density, are advantageous. They have appeared in almost all automobiles, motorbikes, many boats, and in a wide variety of aircraft and locomotives. Where very high power is required, such as jet aircraft, helicopters and large ships, they appear mostly in the form of gas turbines. They are also used for electric generators and by industry.
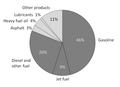
The most common fuels in use today are hydrocarbons derived from petroleum including diesel, gasoline and liquified petroleum gas. Most internal combustion engines designed for gasoline can run on natural gas or liquified petroleum gases without modifications except for the fuel delivery components. Liquid and gaseous biofuels, including ethanol and biodiesel can also be used, and trials of hydrogen fuel have been in progress for some years.
Selected image

Photo credit: Johnson Space Center/NASA
Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises and the water vapor condenses.
Did you know?
- During World War I, the German Army produced shale oil from Yarmouk oil shale deposits in Jordan to operate the Hijazi Railway (pictured)?
- Dennis Spurgeon, formerly chief operating officer at uranium supplier USEC Inc., became the United States Assistant Secretary for Nuclear Energy in 2006?
- Japan Canada Oil Sands Limited was the first offshore oil company to exploit the Athabasca oil sands in Canada?
- Teesside Power Station is the largest combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant in Europe.?
- The Klaipėda Geothermal Demonstration Plant in Lithuania was the first geothermal plant in the Baltic Sea region?
- Hitachi Zosen Corporation built the first oil tanker in Japan in 1908 per an order by Standard Oil Company?
- Coalbed methane is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds?
- When constructed in 1906, the Baku–Batumi pipeline was the world's longest kerosene pipeline?
Selected biography
Edison invented the first commercially practical electric light bulb which, by 1879 would burn for hundreds of hours. He was able to sell the concept to homes and businesses by mass-producing them and creating a complete system for the generation and distribution of electricity.
Edison patented an electric distribution system in 1880, and in January 1882 he switched on the first steam generating power station at Holborn Viaduct in London, UK. The direct current (DC) supply system provided electricity supplies to street lamps and a number of private dwellings within a short distance of the station. The first investor-owned electric utility, Pearl Street Station, New York City, started generating on September 4, 1882, providing 110 volts direct current to 59 customers in lower Manhattan.
Life magazine (USA), in a special double issue, placed Edison first in the list of the "100 Most Important People in the Last 1000 Years," noting that the light bulb he promoted "lit up the world." He was ranked thirty-fifth on Michael H. Hart's list of the most influential figures in history.
In the news
- 1 June 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Russia launches missile and drone strikes across Ukraine, injuring at least four people and damaging critical infrastructure, including energy facilities. Ukraine says that it shot down 35 of 53 missiles and 46 of 47 drones. (Reuters)
General images
Quotations
- "Without radical international measures to reduce carbon emissions within the next 10 to 15 years, there is compelling evidence to suggest we might lose the chance to control temperature rises. Failure to act will make an increase of between 2 and 5 degrees [3.6 - 9°F] in average temperatures almost inevitable." – Tony Blair, 2006
- "The question is not whether climate change is happening or not, but whether, in the face of this emergency, we ourselves can change fast enough." – Kofi Annan, 2006
- "I promise you a day will come when our children and grandchildren will look back and they will ask one of two questions. Either they will ask, 'What in God's name were they doing? Didn't they see the evidence?' Or, they may look back and say 'How did they find the uncommon moral courage to rise above politics and redeem the promise of American democracy?'" – Al Gore, 2007, on global warming.
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
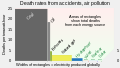
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus