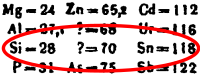Wikipedia:Today's featured article/March 2019
| << | Today's featured articles for March 2019 | >> | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Su | Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa |
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | ||||||
March 1
Germanium (Ge) is a chemical element with atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, greyish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to silicon (Si) and tin (Sn). In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted the existence of germanium (and later some of its properties) based on its position in his periodic table (extract pictured). In 1886, Clemens Winkler discovered the element in a rare mineral called argyrodite. Mendeleev's predictions closely matched the properties of germanium, and this contributed to the wider acceptance of his periodic table. Germanium is a semiconductor used in transistors and various electronic devices, fibre-optic systems, infrared optics, solar cell applications, and light-emitting diodes. It is mined primarily from sphalerite (a zinc ore), along with silver, lead, and copper ores. (Full article...)
March 2
The Battle of Auberoche was fought during the Gascon campaign of 1345 on 21 October between a 1,200-strong force composed of English and local Gascons under Henry, Earl of Derby, and a French army of 7,000 commanded by Louis of Poitiers. It was fought at the village of Auberoche near Périgueux in northern Aquitaine. At the time, Gascony was a territory of the English Crown. The battle resulted in a heavy French defeat and they suffered very high casualties, with their leaders killed or captured. The battle took place during the early stages of the Hundred Years' War. Along with the Battle of Bergerac earlier in the year, it marked a change in the military balance of power in the region after the French position collapsed. It was one of a series of victories which would lead to Henry of Derby being called "one of the best warriors in the world" by a contemporary chronicler. (Full article...)
March 3
The Liberty Head double eagle is an American twenty-dollar gold piece struck as a pattern coin in 1849, and for commerce from 1850 to 1907. The eagle, or ten-dollar piece, had been the largest denomination authorized by the Mint Act of 1792, but Congress considered new denominations of gold coinage in the 1840s after the discovery of gold in California generated a large amount of bullion. The gold dollar and double eagle were the result. After considerable infighting at the Philadelphia Mint, United States Mint Chief Engraver James B. Longacre designed the double eagle. Only one 1849 double eagle is known to survive; it rests in the National Numismatic Collection at the Smithsonian. The coin was immediately successful; merchants and banks used it in trade, and it was struck until replaced by the Saint-Gaudens double eagle in 1907. Many were melted when President Franklin D. Roosevelt recalled gold coins from the public in 1933. (Full article...)
March 4
John Adams (1735–1826) was a leader of the American Revolution and the second president of the United States (1797–1801). He was a dedicated diarist, and corresponded with his wife and advisor Abigail, recording important historical information on the era. As a lawyer, Adams was devoted to the right to counsel and presumption of innocence; he defied anti-British sentiment and successfully defended British soldiers against murder charges arising from the Boston Massacre. A political activist prior to the revolution, Adams was a Massachusetts delegate to the Continental Congress. He assisted in drafting the Declaration of Independence in 1776 and was its foremost advocate in Congress. As a diplomat in Europe, he helped negotiate the Treaty of Paris with Britain. Adams was the primary author of the Massachusetts Constitution in 1780, which influenced the United States Constitution. (Full article...)
March 5
Resident Evil 5 is a third-person shooter video game developed and published by Capcom, and produced by Jun Takeuchi (pictured). It was released for PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360 consoles on March 5, 2009. The plot involves an investigation of a terrorist threat by counter-terrorist agents Chris Redfield and Sheva Alomar in Kijuju, a fictional region of Africa. It is the seventh major installment in the Resident Evil series, and the first designed for two-player cooperative gameplay. Critics described the game as closer to the action genre than the survival horror of other games in the series. Resident Evil 5 had a mostly positive reception, although it was criticized for problems with its controls. The game was re-released for Nvidia Shield, PlayStation 4 and Xbox One in 2016. As of September 2018, it had sold over 7.4 million units, making it Capcom's second best-selling game and the best-selling game of the Resident Evil franchise. (Full article...)
March 6
Al-Mu'tasim (796–842) was the eighth Abbasid caliph. A younger son of Caliph Harun al-Rashid, he rose to prominence as a key lieutenant of his brother Caliph al-Ma'mun after forming a private army composed predominantly of Turkish slave-soldiers. When al-Ma'mun died on campaign in August 833, al-Mu'tasim succeeded him and continued many of his policies, including support for Mu'tazilism. The traditional Arab and Iranian elites were weakened in favour of a new elite drawn from among the Turks, while the government was centralized around the caliphal court and a new capital founded to house it at Samarra. Al-Mu'tasim also achieved lasting fame as a warrior-caliph by sacking the Byzantine city of Amorium in 838. The rise of the Turks would eventually lead to factional strife and the collapse of Abbasid power in the mid-10th century, but the slave-soldier system inaugurated by al-Mu'tasim would be widely adopted throughout the Muslim world for centuries to come. (Full article...)
March 7
Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 – 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, but both composers rejected the term. After studying at France's premier music college, the Paris Conservatoire, he developed a style that incorporated elements of baroque, neoclassicism and, in his later works, jazz. Some of his piano music, such as Gaspard de la nuit (1908), is exceptionally difficult to play. His complex orchestral work Daphnis et Chloé (1912) was commissioned by the impresario Sergei Diaghilev for the Ballets Russes. In 1922 Ravel made an orchestral arrangement of Mussorgsky's Pictures at an Exhibition. He liked to experiment with musical form, as in Boléro (1928), his best-known work. A slow and painstaking worker, Ravel wrote fewer pieces than many of his contemporaries. He was among the first composers to use recordings to reach a wider public. (Full article...)
March 8
Brie Larson (born 1989) is an American actress and filmmaker who has received many awards and nominations. At age six, she became the youngest student admitted to a training program at the American Conservatory Theater. She began her acting career in 1998 with a comedy sketch in The Tonight Show with Jay Leno. Larson played supporting roles in the comedy films Hoot (2006), Scott Pilgrim vs. the World (2010), and 21 Jump Street (2012), and appeared as a sardonic teenager in the television series United States of Tara (2009–2011). After her breakthrough with a leading role in Short Term 12 (2013), she continued to take on supporting parts in The Spectacular Now (2013) and Trainwreck (2015). For playing a kidnapping victim in the drama Room (2015), Larson won the Academy Award for Best Actress. After playing a photojournalist in the adventure film Kong: Skull Island (2017), she starred as the titular superhero in the Marvel Cinematic Universe film Captain Marvel (2019). (Full article...)
March 9
AirTrain JFK is an 8.1-mile-long (13 km) elevated people mover system and rail link serving John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York City. Its three lines and ten stations, operated by the Canadian firm Bombardier Transportation, connect the airport's six terminals with the New York City Subway in Howard Beach, Queens, and with the Long Island Rail Road and subway in Jamaica, Queens. In-depth planning for a dedicated transport system at JFK began in 1990, and construction commenced in 1998. The system opened in December 2003 after multiple delays. Since then, several improvements have been proposed for AirTrain JFK, including an extension to Manhattan. The system was originally projected to carry 4 million annual paying passengers and 8.4 million annual inter-terminal passengers, but the AirTrain has consistently exceeded these projections; in 2017, it had approximately 7.66 million paying passengers and 12.6 million inter-terminal passengers. (Full article...)
March 10
The Australasian gannet (Morus serrator) is a large seabird of the booby and gannet family, Sulidae. Adults are mostly white, with black flight feathers at the wingtips and the trailing edge of the wing. The central tail feathers are also black. The head is tinged with buff-yellow, with a pale blue-grey bill edged in black, and blue-rimmed eyes. Young birds have mottled plumage in their first year, dark above and light below, gradually acquiring more white until they reach maturity after five years. The species ranges over water above the continental shelf along the southern and eastern Australian coastline, as well as the North and South Islands of New Zealand, Lord Howe Island and Norfolk Island. Nesting takes place in colonies along the coastlines of New Zealand, Victoria and Tasmania. The birds plunge into the ocean at high speed, catching mainly squid and forage fish. The species faces few natural or man-made threats. (Full article...)
March 11
The WAVES (Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service) served in the United States Naval Reserve during World War II. In July 1942, the Naval Reserve was authorized to accept women as commissioned officers and at the enlisted level, effective until six months after the war, which freed up many men for ship duty. Mildred H. McAfee (pictured), on leave as president of Wellesley College, became the first director of the WAVES. The notion of women serving in the Navy was not widely supported in Congress or by the Navy, but it was supported by the Navy's Women's Advisory Council, Margaret Chung, and Eleanor Roosevelt, the First Lady of the United States. The WAVES were primarily white, but eventually included 72 African-American women. Serving at 900 stations in the United States and the territory of Hawaii, many of the women experienced workplace hostility, but almost all of them looked upon their service as beneficial. (Full article...)
March 12
State Route 522 (SR 522) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Washington that serves the Seattle metropolitan area. Approximately 25 miles (40 km) long, it connects the city of Seattle to the northeastern suburbs of Kenmore, Bothell, Woodinville, and Monroe. Its western half is primarily an arterial street, named Lake City Way and Bothell Way, that follows the northern shore of Lake Washington; the eastern half is a grade-separated freeway that runs between Woodinville and Monroe. SR 522 connects several of the metropolitan area's major highways, including Interstate 5, Interstate 405, SR 9, and U.S. Route 2. The present day route of SR 522 was built in stages between 1907 and 1965, beginning with the Red Brick Road from Seattle to Bothell, then part of the Pacific Highway and later U.S. Route 99. Since the late 1990s, the SR 522 corridor between Woodinville and Monroe has been partially converted to a freeway to address safety concerns and a growing population. (Full article...)
March 13
The Apollo 15 postal covers incident was a scandal involving the crew of NASA's Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, who in 1971 carried about 400 unauthorized postal covers (example pictured) to the Moon's surface. American astronauts David Scott, Alfred Worden and James Irwin agreed to receive about $7,000 each for carrying the covers into space. These covers were inside the lunar lander Falcon as Scott and Irwin walked on the Moon, and were postmarked both prior to liftoff from Kennedy Space Center and after splashdown. Though the astronauts returned the money, they were reprimanded by NASA for poor judgment and were called before a closed session of a Senate committee. They were removed as the backup crew for Apollo 17 and never flew in space again; by 1977 all had left NASA. In 1983, Worden sued for the return of those covers that had been impounded in 1972, and the three men received them in an out-of-court settlement. One of the covers that had been provided to West German stamp dealer Hermann Sieger sold for over $50,000 in 2014. (Full article...)
March 14
The Packers sweep is an American football play popularized in the 1960s by Green Bay Packers coach Vince Lombardi. It is a variation on the sweep, in which a back takes a pitch or hand-off from the quarterback and runs parallel to the line of scrimmage. This allows the offensive linemen (usually the guards) and the fullback to block defenders before the runner turns upfield. According to one estimate, the Packers sweep gained an average of 8.3 yards (7.6 m) per attempt in its first three seasons. Lombardi built his offensive game plan around running it, or threatening to run it. His teams of the 1960s won five National Football League Championships and the first two Super Bowls. Five offensive players from these teams were later elected to the Pro Football Hall of Fame, and Lombardi was elected shortly after his death in 1971. (Full article...)
March 15
Planar transmission lines are flat, ribbon-shaped transmission lines with conductors, or in some cases dielectric (insulating) strips. They are used to interconnect components on printed circuits and integrated circuits working at microwave frequencies, since the planar lines are suited to the manufacturing methods for these components. Transmission line theory is used when the line is longer than a large fraction of a wavelength. At microwave frequencies, this distance is measured in millimetres, which is small enough that these lines can be used for constructing components as well as interconnecting them. The cross-section of the line is usually kept constant so that its electrical behaviour is highly predictable. The first planar transmission line, stripline, was conceived during World War II by Robert M. Barrett; other types in modern use include microstrip, suspended stripline, and coplanar waveguide. (Full article...)
March 16
Tom Thomson (1877–1917) was a Canadian artist active in the early 20th century. During his short career he produced roughly 400 oil sketches on small wood panels and around 50 larger pieces on canvas. His works consist almost entirely of landscapes depicting trees, skies, lakes, and rivers. He used broad brush strokes and a liberal application of paint to capture the beauty and colour of the Ontario landscape. His paintings The Jack Pine (pictured) and The West Wind have taken a prominent place in the culture of Canada and are some of the country's most iconic works. Although he died before the formal establishment of the Group of Seven, Thomson's art is typically exhibited with theirs. Nearly all of his work remains in Canada—mainly at the Art Gallery of Ontario in Toronto, the National Gallery of Canada in Ottawa, the McMichael Canadian Art Collection in Kleinburg and the Tom Thomson Art Gallery in Owen Sound. His accidental death at 39 by drowning is seen as a tragedy for Canadian art. (Full article...)
March 17
Saint Fin Barre's Cathedral is a Gothic revival cathedral in Cork, Ireland, whose modern building was completed in 1879, and belongs to the Church of Ireland. The cathedral is dedicated to Finbarr of Cork, patron saint of the city, who may have founded a monastery on the grounds in the seventh century. During the medieval period, the site underwent repeated construction and damage. Fin Barre's rebuilding was commissioned in the mid-19th century as the first major project for the Victorian architect William Burges, who designed most of its architecture, interior sculpture, stained glass, mosaics and interior furniture. Many of the external sculptures, including the gargoyles, were modeled by Thomas Nicholls. The exterior is capped by three spires, and is mostly built from local stone. The main entrance contains representations of over a dozen biblical figures, capped by a tympanum showing a Resurrection scene. (Full article...)
March 18
John C. Calhoun (March 18, 1782 – March 31, 1850) was a senator from South Carolina, a Cabinet member, and the seventh Vice President of the United States, from 1825 to 1832, under presidents John Quincy Adams and Andrew Jackson. Calhoun began his political career in the House of Representatives as a prominent leader of the war hawk faction supporting the War of 1812. Early in his career, he was a modernizer and a proponent of a strong national government and protective tariffs. By the late 1820s, his views reversed and he became a leading proponent of states' rights, limited government, and opposition to high tariffs. His support for South Carolina's right to nullify federal tariff legislation put him into conflict with unionists such as Jackson, and in 1832 he resigned as vice president and entered the Senate. As Secretary of State under John Tyler from 1844 to 1845, he supported the annexation of Texas as a means to promote slavery, and helped settle the Oregon boundary dispute with Britain. (Full article...)
March 19
Seattle Sounders FC is an American professional soccer club based in Seattle, Washington. The club competes in Major League Soccer (MLS), playing home matches at CenturyLink Field with a reduced capacity. It was established in November 2007 as an MLS expansion team; the first match of the club's inaugural season was played on March 19, 2009. It is the third team to bear the Sounders name, and the 15th team to join the league. In each of its first five seasons, the club set an MLS record for average attendance. It competes with its local rivals, Portland and Vancouver, for the Cascadia Cup. Brian Schmetzer has been the team's head coach since 2016, replacing Sigi Schmid. Seattle has been among the league's most successful teams, winning the U.S. Open Cup four times, the Supporters' Shield in 2014, and the MLS Cup in 2016. The team has qualified for the MLS Cup Playoffs in each of its ten seasons and competed in the CONCACAF Champions League five times, advancing as far as the semifinals. (Full article...)
March 20
The 1896 Cedar Keys hurricane was a powerful tropical cyclone that devastated much of the East Coast of the United States, starting with Florida's Cedar Keys, near the end of September. The storm's rapid movement allowed it to maintain much of its intensity after landfall, becoming one of the costliest United States hurricanes at the time. The fourth tropical cyclone of the 1896 Atlantic hurricane season, it washed out the railroad connecting the Cedar Keys to the mainland with a 10.5 ft (3.2 m) storm surge, and submerged much of the island group (Cedar Key flooding pictured). The hurricane killed at least 70 people in mainland Florida, and razed 5,000 sq mi (13,000 km2) of dense pine forests in the northern part of the state. In Savannah, Georgia, fierce winds unroofed thousands of structures. In Washington, D.C., the White House grounds were left in disarray. Monuments at the Gettysburg Battlefield were damaged. Along the storm's path, it caused at least 202 deaths. (Full article...)
March 21
Fôrça Bruta (Brute Force) is the seventh studio album by Brazilian singer-songwriter and guitarist Jorge Ben, recorded with the Trio Mocotó band (pictured) and released by Philips Records in September 1970. It introduced an acoustic samba-based music that was mellower, moodier, and less ornate than Ben's preceding work. In a largely unrehearsed nighttime recording session, the singer improvised and experimented with unconventional rhythmic arrangements, musical techniques, and elements of soul, funk, and rock. Ben's lyrics explored themes of romantic passion, melancholy, sensuality, and—in a departure from the carefree sensibility of past releases—identity politics and elements of postmodernism. A commercial and critical success, Fôrça Bruta established Ben as a leading artist in Brazil's Tropicália movement and pioneered a sound later known as samba rock. The album's first American release came in 2007, the same year that Rolling Stone Brasil named it the 61st greatest Brazilian music record. (Full article...)
March 22

Xixiasaurus is a genus of troodontid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous. The only known specimen (a partial skull, jaw with teeth, and forelimb) was discovered in Xixia County, Henan Province, in central China, and was given a species description in 2010. Xixiasaurus is estimated to have been 1.5 metres (5 ft) long and to have weighed 8 kilograms (18 lb). As a troodontid with some similarities to Byronosaurus, the genus would have been bird-like and lightly built, with grasping hands and an enlarged sickle-shaped claw on the second toe. Its skull was long, with a long, low snout that formed a tapering U-shape when seen from below. The frontal bone of the forehead was dome-like in side view, indicating an enlarged braincase. Troodontids had keen senses and were probably agile. The lack of serrated teeth indicates that Xixiasaurus and some other troodontids were herbivorous, as they had lost the ability to slice meat. (Full article...)
March 23
The Emesa helmet is an iron Roman cavalry helmet from the early first century AD. Its face mask, covered in a thin sheet of silver, presents the individualised portrait of a face, likely that of its owner. Decorations, some gilded, adorn the head piece. Ornately designed yet highly functional, the helmet was probably intended for both parades and battle. Its delicate covering is too fragile to have been put to use during cavalry tournaments, but the thick iron core would have defended against blows and arrows. It bears acanthus scroll ornamentation, indicating that the helmet may have come from the luxury workshops of Antioch. Confiscated by Syrian police in 1936 soon after looters discovered it amidst a complex of tombs in the modern-day city of Homs, the helmet was eventually restored at the British Museum. It has been exhibited internationally, and is now in the collection of the National Museum of Damascus. (Full article...)
March 24
Hydnum repandum, the hedgehog mushroom, is a fungus of the family Hydnaceae. First described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753, it is the type species of its genus. The cap is dry, colored yellow to light orange to brown, and often develops an irregular shape, especially when crowded. The mushrooms are characterized by spore-bearing structures—in the form of spines rather than gills—which hang down from the underside of the cap. The mushroom tissue is white with a pleasant odor and a spicy or bitter taste. All parts of the mushroom stain orange with age or when bruised. A mycorrhizal fungus, H. repandum is broadly distributed in Europe, Asia and western North America, where it fruits singly or in close groups in coniferous or deciduous woodland. This is a choice edible species, although mature specimens can develop a bitter taste. The mushrooms are sold in local markets of Europe and Canada. (Full article...)
March 25
Project E was a Cold War arrangement under which the United States provided the United Kingdom with nuclear weapons for the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was later expanded to provide warheads to the British Army, and there was a maritime version known as Project N that provided nuclear depth bombs. US personnel retained custody of the weapons, and handled their storage, maintenance and readiness. The first bombers equipped with Project E weapons were Canberras (example pictured). Due to the operational restrictions, and the loss of independence of the British nuclear deterrent, Project E bombs were phased out from their strategic role in 1962, although they still equipped tactical bombers, and were used on the Thor missiles operated by the RAF from 1959 to 1963 under Project Emily. The British Army acquired Project E warheads for its Corporal, Honest John and Lance missiles, and its artillery pieces. The last Project E weapons were withdrawn from service in 1992. (Full article...)
March 26
Diamonds Are Forever is the fourth novel by the English author Ian Fleming to feature his fictional British Secret Service agent James Bond. Fleming wrote the story at his Goldeneye estate in Jamaica, inspired by a Sunday Times article on diamond smuggling. The book was first published on 26 March 1956. The story centres on Bond's investigation of a diamond-smuggling operation that originates in the mines of Sierra Leone and runs to Las Vegas. Along the way Bond meets and falls in love with one of the members of the smuggling gang, Tiffany Case. Fleming's background research formed the basis for his non-fiction 1957 book The Diamond Smugglers. The Bond novel received broadly positive reviews at the time of publication. It was serialised in the Daily Express newspaper, first in an abridged, multi-part form and then as a comic strip. In 1971 it was adapted into the seventh film in the Bond series, and the sixth one to star Sean Connery as Bond. (Full article...)
March 27
SMS Schlesien was one of five Deutschland-class pre-dreadnought battleships that served in the German Imperial Navy. Named after the province of Silesia in 1906 and commissioned in 1908, Schlesien was primarily occupied with training cruises and fleet maneuvers in her early career. She served with the High Seas Fleet throughout the first two years of World War I, saw brief action at the Battle of Jutland, and became a training ship in 1917. The Treaty of Versailles permitted the German navy to keep eight obsolete battleships, including Schlesien, to defend the German coast. Modernized in the mid-1920s, the ship saw limited combat during World War II, briefly bombarding Polish forces during the invasion of Poland in September 1939. After escorting minesweepers during the invasion of Norway and Denmark in April 1940, she primarily served as a training ship and icebreaker. She was sunk by a mine in 1945 while tasked with providing fire support off the Baltic coast. (Full article...)
Part of the Battleships of Germany featured topic.
March 28
William Matthews (1770–1854) was the first person born in British America to be ordained a Catholic priest in the United States. Originally from the colonial Province of Maryland, he became influential in the establishment of Catholic parochial and educational institutions in Washington, D.C. He was the second pastor of St. Patrick's Church, the President of Georgetown College (later known as Georgetown University), and the head of the Washington Catholic Seminary, which became Gonzaga College High School, in addition to being co-founder and president of the Washington Library Company, the first public library in the District of Columbia. He founded several orphanages, schools, and parishes, and was co-director of the District of Columbia Public Schools. In 1832 he officiated at the wedding of a French diplomat and Mary Anne Lewis, a ward of President Andrew Jackson, in the first Catholic ceremony to be held in the White House. (Full article...)
March 29
The Referendum Party was a Eurosceptic political party, active in the United Kingdom from 1994 to 1997. The party's sole objective was a referendum on the nature of the UK's membership in the European Union. It was founded in November 1994 by the Anglo-French multi-millionaire businessman and politician James Goldsmith, an elected Member of the European Parliament for the Movement for France party. In the build-up to the 1997 general election, the Referendum Party spent more on press advertising than either the incumbent Conservatives or the Labour Party. It stood more candidates than any minor party had ever fielded in a UK election (in 547 of the 659 constituencies), and won 2.6% of the vote nationally, but failed to win any seats in the House of Commons. Support was strongest in southern and eastern England, and weakest in inner London, northern England, and Scotland. Goldsmith died in July 1997, and the party disbanded shortly after. (Full article...)
March 30
Albert Pierrepoint (30 March 1905 – 10 July 1992) was an English hangman who executed between 435 and 600 people in a 25-year career that ended in 1956. His first execution was in December 1932, assisting his uncle Thomas. His father Henry had also been a hangman. In October 1941 he undertook his first hanging as lead executioner. During his tenure he hanged 200 people who had been convicted of war crimes in Germany and Austria, as well as several high-profile murderers—including Gordon Cummins (the Blackout Ripper), John Haigh (the Acid Bath Murderer) and John Christie (the Rillington Place Strangler). He undertook several contentious executions, including Timothy Evans, Derek Bentley and Ruth Ellis. He executed William Joyce (also known as Lord Haw-Haw) and John Amery for high treason, and Theodore Schurch for treachery. In the 2005 film Pierrepoint he was portrayed by Timothy Spall. (Full article...)
March 31
The Car Barn is a historic building in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. Designed by the American architect Waddy Butler Wood, it was built between 1895 and 1897 by the Capital Traction Company as a union terminal for several Washington and Virginia streetcar lines. The Exorcist steps, later named after their appearance in William Friedkin's 1973 horror film The Exorcist, were built during the initial construction to connect M Street with Prospect Street. Almost immediately after its construction, it was converted to accommodate electric streetcars. The building has undergone several renovations, the most extensive in 1911, when the original Romanesque Revival façade was significantly modified and the interior was almost completely gutted. Changing ownership over time, it maintained its original function of housing streetcars until 1950, when it was redeveloped as office space. Today, it is used as an academic building by Georgetown University. (Full article...)