The white-lored spinetail (Synallaxis albilora) is a species of bird in the Furnariinae subfamily of the ovenbird family Furnariidae. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay.[2]
| White-lored spinetail | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Furnariidae |
| Genus: | Synallaxis |
| Species: | S. albilora
|
| Binomial name | |
| Synallaxis albilora Pelzeln, 1856
| |
| |
Taxonomy and systematics edit
The white-lored spinetail is monotypic.[2]
What is now the Araguaia spinetail (S. simoni) was previously treated as a subspecies of the white-lored spinetail. Before that, both were treated as subspecies of the plain-crowned spinetail (S. gujanensis).[3] The International Ornithological Committee, the Clements taxonomy, and BirdLife International's Handbook of the Birds of the World have implemented the splits.[2][4][5] However, the South American Classification Committee of the American Ornithological Society retains the Araguaia spinetail within the white-lored.[6]
Description edit
The white-lored spinetail is 15 to 16 cm (5.9 to 6.3 in) long and weighs 13 to 17 g (0.46 to 0.60 oz). The sexes have the same plumage. Adults have dull whitish lores on an otherwise brownish gray face. Their crown and upper back are grayish brown, their lower back and rump bright rufous-brown, and their uppertail coverts dark rufous. Their wings are bright rufous with fuscous-brown tips on the flight feathers. Their tail is dark rufous; it is graduated and the feathers have blunt tips. Their throat is white; their underparts are mostly bright tawny ochraceous, orange, or buffy orange with a whitish center on a paler belly. Their iris is cinnamon brown, their maxilla black to dark gray, their mandible gray, and their legs and feet gray to dull brownish.[3][7]
Distribution and habitat edit
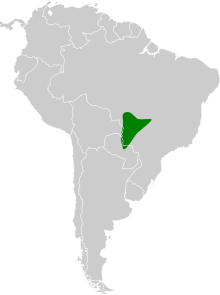
The white-lored spinetail is found in southern Mato Grosso and western Mato Grosso do Sul in Brazil and south through southeastern Bolivia into northern Paraguay. It inhabits the undergrowth of gallery forest and riparian woodland and scrublands. It occurs below 1,000 m (3,300 ft) of elevation.[3][7]
Behavior edit
Movement edit
The white-lored spinetail is a year-round resident throughout its range.[3]
Feeding edit
The white-lored spinetail feeds on arthropods. It usually forages in singly or in pairs, in vines and tangles in the understorey, mostly up to about 2 m (7 ft) above the ground. It gleans its prey from the ground, foliage, and small branches.[3][7]
Breeding edit
The white-lored spinetail's core breeding season is from August to December but it can start as early as June and extend to February. Pairs have been noted making three breeding attempts in a season. Its nest is a mass of sticks with an entrance tunnel leading to an interior chamber that is lined with leaves and other soft material. Both sexes construct the nest, typically placing it in a bush or small tree up to about 7 m (23 ft) above the ground. The clutch size is three to four eggs. The incubation period is about 15 days and fledging occurs about 13 to 14 days after hatch. Both members of the pair provision nestlings.[3]
Vocalization edit
The white-lored spinetail's song is repeated "sharp 'keeew kiw-kweet' notes".[7] It also makes a "single, nasal, and level-pitched note that is typically repeated several times". Both sexes sing. They sing mainly in the morning, and from a hidden perch in vegetation.[3]
Status edit
The IUCN has assessed the white-lored spinetail as being of Least Concern. It has a fairly large range and an unknown population size that is believed to be stable. No immediate threats have been identified.[1] It is considered common, and "very numerous in suitable habitat in the Pantanal region". It occurs in several protected areas.[3]
References edit
- ^ a b BirdLife International (2016). "White-lored Spinetail Synallaxis albilora". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T103675238A93871067. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103675238A93871067.en. Retrieved 21 November 2023.
- ^ a b c Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (July 2023). "Ovenbirds, woodcreepers". IOC World Bird List. v 13.2. Retrieved July 31, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Kirwan, G. M., J. V. Remsen, Jr., and P. F. D. Boesman (2023). White-lored Spinetail (Synallaxis albilora), version 2.0. In Birds of the World (S. M. Billerman and B. K. Keeney, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.whlspi1.02 retrieved November 21, 2023
- ^ Clements, J. F., P.C. Rasmussen, T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, A. Spencer, S. M. Billerman, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2023. The eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: v2023. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ retrieved October 28, 2023
- ^ HBW and BirdLife International (2022) Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world. Version 7. Available at: https://datazone.birdlife.org/userfiles/file/Species/Taxonomy/HBW-BirdLife_Checklist_v7_Dec22.zip retrieved December 13, 2022
- ^ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, G. Del-Rio, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 28 September 2023. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved October 20, 2023
- ^ a b c d van Perlo, Ber (2009). A Field Guide to the Birds of Brazil. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-19-530155-7.
