Syrian civil war Part of the Arab Spring , Arab Winter , the spillover of the War in Iraq , war against the Islamic State , war on terror , Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict , Iran–Israel proxy conflict and the Kurdish–Turkish conflict Top: A ruined neighborhood in Raqqa in 2017.Bottom: Military situation in September 2023: Syrian Arab Republic (SAA ) Syrian Interim Government (SNA ) & Turkish occupation Syrian Free Army & American occupation Syrian Salvation Government (HTS )[a] Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (SDF ) Opposition groups in reconciliation Islamic State (full list of combatants , detailed map Date 15 March 2011 (2011-03-15 ) [1] Location Status
Ongoing , ceasefire since 6 March 2020, with sporadic clashes Territorial
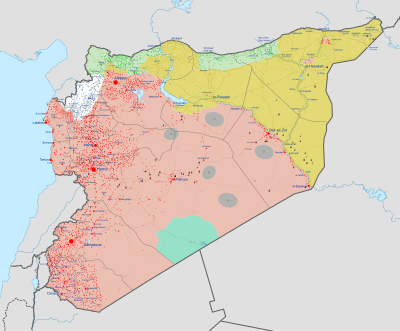
As of 1 January 2023: the SAAF controlled 63.38% of Syrian territories; SDF controlled 25.64%; and Syrian opposition forces (SFA , SNA and HTS ) controlled 10.98% of Syrian territories.[2]
Casualties and losses
Total killed [3] [4] Civilians killed [4] [5] [6]
Displaced
Syrian civil war Part of the Arab Winter , the spillover of the War in Iraq , War against the Islamic State , War on terror , Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict , Arab–Israeli conflict , Iran–Israel proxy conflict and the Kurdish–Turkish conflict Top: A ruined neighborhood in Raqqa in 2017.Bottom: Military situation as of 9 September 2021: Syrian Arab Republic (SAA ) Syrian Arab Republic & Rojava (SAA & SDF ) Rojava (SDF ) Syrian Interim Government (SNA ) & Turkish occupation Syrian Salvation Government (HTS [i] Syrian Free Army & United States' occupation Opposition groups in reconciliation
Islamic State (full list of combatants , detailed map Date 29 July 2011 (2011-07-29 ) – present Location Status
Ongoing Territorial
As of 31 March 2020: the Syrian Armed Forces held 63.57% of Syrian territories; SDF 25.57%; rebel groups (incl. HTS ) & Turkey 9.72%; Islamic State 1.14%[40]
Main belligerents
Iran Russia Hezbollah
Maghaweir al-Thowra
Commanders and leaders
[70] [71]
Units involved
See order
See order
See order
See order Strength
Syrian Armed Forces : 142,000 (2019) [97] General Security Directorate : 8,000[98] [99] (2018) [100] (2013) [101] [102] [103] [104] [105] [106] [104] Egyptian Army : 150[107] [108]
Free Syrian Army : 20,000–32,000[109] Syrian Islamic Front : 40,000–70,000[110] [111] [112] Turkish Armed Forces : 4,000–8,000[113] [114]
Ahrar al-Sham : 18,000–20,000+[115] [116]
Tahrir al-Sham : 20,000–30,000 (per U.S., late 2018)[117]
Islamic State: 10,000+ (in Syria and Iraq, 2022) [118]
SDF : 60,000–75,000 (2017 est.)
YPG & YPJ: 20,000–30,000 (2017 est.)
Syriac Military Council (MFS): 1,000 (2017 est.)
Al-Sanadid Forces: 2,000–4,000 (2017 est.)
SDF Military Councils: 10,000+[122] [123] [124] United States Armed Forces :[125] Casualties and losses
Syrian Arab Republic: [126] [127] [126] Hezbollah: [126] [128] Russia: soldiers killed & 266–284 PMCs killed [129] Other non-Syrian fighters: [126] IRGC -led)[130] [131] Total:
Syrian Interim Government Syrian Salvation Government: [j] [126] [127]
Turkey: killed (2016–20 incursions )[132]
Islamic State: [126]
NES: [126] PKK [31]
CJTF–OIR :[133]
^ Formed in January 2017 as a merger between Jaysh al-Ahrar (a faction of Ahrar al-Sham ), Ansar al-Din Front , Jaysh al-Sunna , Jabhat Fatah al-Sham (successor of Al-Nusra Front) and Liwa al-Haqq .
^ Iraq's involvement was coordinated with the Syrian gov. & limited to airstrikes against ISIL.[1] [2]
^ Since early 2013, the FSA has been decentralized. Its name is arbitrarily used by various opposition fighters
^ Turkey provided arms support to rebels since 2011 & fought alongside the SNA against SDF, IS and Syrian government since August 2016
^ a b Sep.–Nov. 2016: U.S. supported the SNA in Aleppo governorate against IS[8] [9] purposely attacked the Syrian gov. 10 times, & in Sep. 2016 it accidentally hit a Syrian base , killing ≥100 SAA soldiers. Syria maintains this as intentional.[10]
^ a b al-Nusra Front , one of the predecessor organisations of HTS and IS (ISI ); were allied al-Qaeda branches until April 2013. Al-Nusra Front rejected an ISI-proposed merger into ISIL & al-Qaeda cut all affiliation with ISIL in February 2014. Predecessors of Ahrar al-Sham (Syrian Liberation Front ) & HTS (al-Nusra Front ), were allied under the Army of Conquest (Mar. 2015 – Jan. 2017).
^ HTS was formed on 28 January 2017 as a merger between Jabhat Fateh al-Sham, the Ansar al-Din Front, Jaysh al-Sunna, Liwa al-Haqq, and the Nour al-Din al-Zenki Movement. HTS describes itself as a new independent Islamist entity free from the previous factions and distanced itself from Al-Qaeda, disavowing any ties to it:[12] [13]
^ Israel provided arms to 12 unnamed rebel groups solely against Iran and ISIS.[38] [39]
^ Formed in January 2017 as a merger between Ansar al-Din Front , Jaysh al-Sunna , Jabhat Fatah al-Sham (successor of Al-Nusra Front), Liwa al-Haqq and elements of Ahrar al-Sham
^ Number incl. all anti-government forces, except ISIL and SDF, which are listed in their separate columns.