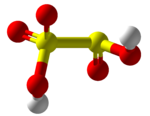
Disulfurous acid, metabisulfurous acid or pyrosulfurous acid is an oxoacid of sulfur with the formula H2S2O5. Its structure is HO−S(=O)2−S(=O)−OH. The salts of disulfurous acid are called disulfites or metabisulfites. Disulfurous acid is, like sulfurous acid (H2SO3), a phantom acid, which does not exist in the free state.[2] In contrast to disulfate (S2O2−7), disulfite has two directly connected sulfur atoms. The oxidation state of the sulfur atom bonded to three oxygen atoms is +5 and its valence is 6, while that of the other sulfur is +3 and 4 respectively.

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
disulfurous acid[1]
| |||
| Other names
pyrosulfurous acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2S2O5 | |||
| Molar mass | 146.13 g·mol−1 | ||
| Conjugate base | Disulfite | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||

References edit
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2005). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005). Cambridge (UK): RSC–IUPAC. ISBN 0-85404-438-8. p. 130. Electronic version.
- ^ Holleman, Wiberg (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. pp. 537–540. ISBN 9780123526519.