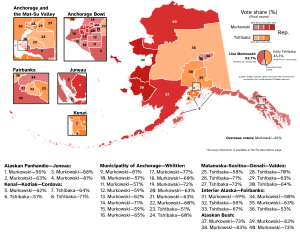
The 2022 United States Senate election in Alaska was held on November 8, 2022. Incumbent senator Lisa Murkowski won reelection[1] to a fourth full term, defeating fellow Republican Kelly Tshibaka and Democrat Patricia Chesbro.
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Murkowski: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Tshibaka: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
After the voter approval of Ballot Measure 2 during the 2020 Alaska elections, this was the first U.S. Senate election in Alaska to be held under a new election process. All candidates ran in a nonpartisan blanket top-four primary on August 16, 2022,[2] and the top four candidates advanced to the general election, where voters will utilize ranked-choice voting.[3]
Murkowski was appointed to the Senate in 2002 by her father, Frank Murkowski, who served as a U.S. senator from Alaska from 1981 until he was elected governor of Alaska. Murkowski has won three Senate elections since then, including a notable write-in campaign in the 2010 election, although she has never won an election with an outright majority of the vote.[4][5][6]
Murkowski was the only Republican senator running for reelection in 2022 who voted to convict former president Donald Trump in his second impeachment trial in 2021. On March 16, 2021, the Alaska Republican Party voted to censure Murkowski and announced that it would recruit a Republican challenger in the 2022 election cycle.[7][8] Following Murkowski's opposition to some of Trump's initiatives and her vote to convict him, Trump endorsed Tshibaka and campaigned against Murkowski.[9][10] The Alaska Republican Party endorsed Tshibaka; Republican Senate leader Mitch McConnell and the National Republican Senatorial Committee supported Murkowski.[11]
In addition to Murkowski and Tshibaka, Democrat Pat Chesbro and Republican Buzz Kelley also advanced to the general election. On September 13, Kelley suspended his campaign and endorsed Tshibaka.[12] Murkowski received a plurality of first-place votes, but because no candidate received a majority of the votes in the first round, the instant runoff was triggered. Murkowski won reelection in the third and final round, winning most of the second-choice votes from Chesbro's voters.[13] Since Murkowski won her three previous elections to the U.S. Senate (2004, 2010, and 2016) without a majority of the vote, this election became the fourth election in which she did not receive a majority of the vote in the first round (the other three elections did not employ ranked choice voting with multiple rounds). Murkowski thus holds the record for the most number of elections won by a U.S. Senator without winning a majority of the votes.
Primary election edit
Republican Party edit
Advanced to general edit
- Lisa Murkowski, incumbent U.S. senator[14]
- Kelly Tshibaka, former commissioner of the Alaska Department of Administration[15]
Withdrew after advancing to general edit
Eliminated in primary edit
- Sam Merrill, businessman[16]
- Pat Nolin, mechanic[16]
- John Schiess, perennial candidate[18]
- Kendall L. Shorkey[18]
- Karl Speights, retired U.S. Air Force officer and advisor to Donald Trump's 2020 presidential campaign[19]
Disqualified edit
- Sam Little, musician, truck driver, National Guard veteran and candidate for governor of Alaska in 2010[19]
Declined edit
- Mike Dunleavy, governor of Alaska[20] (ran for re-election)[21]
- Sarah Palin, former governor of Alaska and nominee for vice president of the United States in 2008 (ran for U.S. House)[22][23]
- Bob Lochner, mechanic and candidate for U.S. Senate in 2016[24]
Democratic Party edit
Advanced to general edit
Eliminated in primary edit
- Edgar Blatchford, professor, former mayor of Seward, and candidate for U.S. Senate in 2016 and 2020[27]
- Ivan R. Taylor[28]
Withdrew edit
- Elvi Gray-Jackson, state senator for District I and former Anchorage Assembly member (ran for re-election)[29][30][31]
Libertarian Party edit
Eliminated in primary edit
- Sean Thorne, veteran[32]
Alaskan Independence Party edit
Eliminated in primary edit
- Dustin Darden, city maintenance worker and perennial candidate[19]
- Joe Stephens[33]
Declined edit
- John Howe, machinist and nominee for U.S. Senate in 2020 (ran for governor)[27]
Independents edit
Eliminated in primary edit
- Dave Darden, perennial candidate[33]
- Shoshana Gungurstein, businesswoman
- Sid Hill, political gadfly and candidate for U.S. Senate in 2014[33]
- Jeremy Keller, television personality[18]
- Huhnkie Lee, attorney, army veteran and Republican candidate for Alaska Senate in 2020[19]
Declined edit
- Al Gross, orthopedic surgeon, commercial fisherman, son of former Alaska Attorney General Avrum Gross, and candidate for U.S. Senate in 2020 (ran for U.S. House)[34][35]
Results edit
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Lisa Murkowski (incumbent) | 85,794 | 45.05% | |
| Republican | Kelly Tshibaka | 73,414 | 38.55% | |
| Democratic | Patricia Chesbro | 12,989 | 6.82% | |
| Republican | Buzz Kelley | 4,055 | 2.13% | |
| Republican | Pat Nolin | 2,004 | 1.05% | |
| Democratic | Edgar Blatchford | 1,981 | 1.04% | |
| Democratic | Ivan R. Taylor | 1,897 | 1.00% | |
| Republican | Sam Merrill | 1,529 | 0.80% | |
| Libertarian | Sean Thorne | 1,399 | 0.73% | |
| Independent | Shoshana Gungurstein | 853 | 0.45% | |
| Independence | Joe Stephens | 805 | 0.42% | |
| Republican | John Schiess | 734 | 0.39% | |
| Independence | Dustin Darden | 649 | 0.34% | |
| Republican | Kendall L. Shorkey | 627 | 0.33% | |
| Republican | Karl Speights | 613 | 0.32% | |
| Independent | Jeremy Keller | 405 | 0.21% | |
| Independent | Sid Hill | 274 | 0.14% | |
| Independent | Huhnkie Lee | 238 | 0.12% | |
| Independent | Dave Darden | 198 | 0.10% | |
| Total votes | 190,458 | 100.0% | ||
General election edit
Predictions edit
| Source | Ranking | As of |
|---|---|---|
| The Cook Political Report[37] | Solid R | March 4, 2022 |
| Inside Elections[38] | Solid R | April 1, 2022 |
| Sabato's Crystal Ball[39] | Safe R | March 1, 2022 |
| Politico[40] | Solid R | September 5, 2022 |
| RCP[41] | Safe R | September 15, 2022 |
| Fox News[42] | Solid R | May 12, 2022 |
| DDHQ[43] | Solid R | July 20, 2022 |
| FiveThirtyEight[44] | Solid R | October 24, 2022 |
| The Economist[45] | Safe R | September 7, 2022 |
Debates and forums edit
| No. | Date | Host | Link | Participants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P Participant A Absent N Non-invitee I Invitee W Withdrawn | |||||||
| Lisa Murkowski | Kelly Tshibaka | Patricia Chesbro | Buzz Kelley | ||||
| 1 | September 1, 2022 | Denaʼina Civic and Convention Center Alaska Oil and Gas Association Anchorage Daily News |
Youtube | P | P | P | A |
| 2 | October 10, 2022 | Anchorage Chamber of Commerce | Youtube | P | P | P | W |
Endorsements edit
- Organizations
- Alaska Democratic Party[46]
- The Alaska Center[47]
- Executive branch officials
- George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States (2001–2009)[48]
- Governors
- Larry Hogan, Governor of Maryland (2015–2023)[49]
- Bill Walker, Governor of Alaska (2014–2018) (Independent)[50]
- U.S. Senators
- John Barrasso, U.S. Senator from Wyoming (2007–present)[51]
- Susan Collins, U.S. Senator from Maine (1997–present)[52]
- Joni Ernst, U.S. Senator from Iowa (2015–present)[52]
- John Thune, U.S. Senator from South Dakota (2005–present), Senate Minority Whip (2021–present), and former Senate Majority Whip (2019–2021)[53]
- Joe Manchin, U.S. Senator from West Virginia (2010–present) (Democratic)[54]
- Mitch McConnell, U.S Senator from Kentucky (1985–present), Senate Minority Leader (2021–present, 2007–2015), and former Senate Majority Leader (2015–2021)[55]
- Rick Scott, U.S. Senator from Florida (2019–present)[56]
- Dan Sullivan, U.S. Senator from Alaska (2015–present)[57]
- John Cornyn, U.S. Senator from Texas (2002–present)[58]
- Tim Scott, U.S. Senator from South Carolina (2013–present)[59]
- Angus King, U.S. Senator from Maine (2013–present) (Independent)[58]
- Kyrsten Sinema, U.S. Senator from Arizona (2019–present) (Democratic)[58]
- Mark Warner, U.S. Senator from Virginia (2009–present) (Democratic)[58]
- Jeanne Shaheen, U.S. Senator from New Hampshire (2009–present) (Democratic)[58]
- U.S. Representatives
- Adam Kinzinger, U.S. representative from Illinois's 16th congressional district; formerly 17th district (2011–2023)[60]
- Mary Peltola, U.S. representative from Alaska's at-large congressional district (2022–present) (Democratic)[61]
- State Legislators
- Gary Stevens, state senator[62]
- Bryce Edgmon, state representative (Independent)[62]
- Dan Ortiz, state representative (Independent)[62]
- Zack Fields, state representative (Democratic)[62]
- Natasha von Imhof, state senator[63]
- Louise Stutes, state representative, Speaker of the Alaska House of Representatives[63]
- Adam Wool, state representative (Democratic)[63]
- Neal Foster, state representative (Democratic)[63]
- Newspapers
- Organizations
- Citizens for Responsible Energy Solutions[65]
- National Republican Senatorial Committee[56]
- National Education Association – Alaska[66]
- Renew America Movement[67]
- Pro-Israel America[68]
- Forward Party[69]
- Alaska Federation of Natives[70]
- Log Cabin Republicans[71]
- American Israel Public Affairs Committee[64]
- American Conservation Coalition[64]
- ClearPath Action Fund[64]
- United Fishermen of Alaska[64]
- ANCSA Regional Association[64]
- United States Chamber of Commerce[72]
- Labor unions
- Alaska AFL–CIO[73]
- Laborers' International Union of North America[64]
- International Longshore and Warehouse Union – Alaska[64]
- Alaska Professional Firefighters Association[64]
- Alaska Teamsters Local 959[64]
- Carpenters Local Union 1281[64]
- Inlandboatmen's Union of the Pacific – Alaska[64]
- Executive branch officials
- Donald Trump, 45th President of the United States (2017–2021)[74]
- Governors
- Kristi Noem, Governor of South Dakota (2019–present)[75]
- Sarah Palin, Governor of Alaska (2006–2009), candidate for Alaska's at-large congressional district in 2022 and nominee for Vice President of the United States in 2008[76]
- Local officials
- Edgar Blatchford, former mayor of Seward (1999–2003), candidate for the U.S. Senate in 2016, 2022 and lieutenant governor in 2018 (Democratic)[77]
- Individuals
- Tuckerman Babcock, political strategist and former chair of the Alaska Republican Party (2016–2018)[78]
- Charlie Kirk, political activist and founder of Turning Point USA[79]
- Donald Trump Jr., businessman and son of former President Donald Trump[80]
- Buzz Kelley, candidate for the U.S. Senate in 2022 and retired mechanic[16][17]
- Organizations
- Alaska Republican Party[81]
- American Conservative Union[82]
- Campaign for Working Families[83]
- Family Research Council Action PAC[84]
- Maggie's List[85]
- Susan B. Anthony List[86]
- Oil and Gas Workers' Association[87]
- Alaska Outdoor Council PAC[88]
Polling edit
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[b] |
Margin of error |
RCV count |
Lisa Murkowski (R) |
Kelly Tshibaka (R) |
Pat Chesbro (D) |
Buzz Kelley (R) |
Undecided / Not Ranked |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska Survey Research | October 19–22, 2022 | 1,276 (LV) | ±3.0% | ||||||
| 1 | 41% | 39% | 16% | 4% | — | ||||
| 2 | 42% | 41% | 17% | —[c] | — | ||||
| 3 | 56% | 44% | –[d] | — | |||||
| Alaska Survey Research | September 25–27, 2022 | 1,282 (LV) | ±3.0% | ||||||
| 1 | 41% | 39% | 16% | 4% | — | ||||
| 2 | 42% | 41% | 17% | —[c] | — | ||||
| 3 | 57% | 43% | –[d] | — | |||||
| Fabrizio Ward (R)/Impact Research (D)[A] | September 6–11, 2022 | 1,050 (LV) | [e] | N/A[f] | 35% | 43% | 13% | 1% | 7% U |
| 1 | 38% | 46% | 14% | 2% | 7% NR | ||||
| 2 | 38% | 47% | 14% | –[g] | 8% NR | ||||
| 3 | 50% | 50% | –[h] | 10% NR |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[b] |
Margin of error |
RCV count |
Pat Chesbro (D) |
Dustin Darden (AIP) |
Elvi Gray-Jackson (D) |
Al Gross (D/I) |
John Howe (AIP) |
Joe Miller (L) |
Lisa Murkowski (R) |
Sarah Palin (R) |
Kelly Tshibaka (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska Survey Research | July 2–5, 2022 | 1,201 (LV) | ± 2.9% | 1 | 17% | 5% | – | 35% | – | 43% | – | ||||
| 2 | 20% | – | 36% | 45% | |||||||||||
| 3 | – | 52% | 48% | ||||||||||||
| Cygnal (R)[B] | March 14–16, 2022 | 500 (LV) | ± 4.2% | 1 | – | 29% | – | 45% | 26% | – | |||||
| ? | 49% | – | 51% | – | |||||||||||
| Alaska Survey Research | October 22–27, 2021 | 969 (RV) | ± 3.2% | 1 | – | 22% | – | 35% | 20% | 23% | – | ||||
| 2 | 23% | 42% | – | 35% | |||||||||||
| 3 | – | 60% | 40% | ||||||||||||
| Alaska Survey Research | July 11–21, 2021 | 947 (LV) | ± 3.2% | 1 | – | 19% | – | 18% | 36% | – | 27% | – | |||
| 2 | 21% | – | 39% | 40% | |||||||||||
| 3 | – | 55% | 45% | ||||||||||||
| Change Research (D)[C] | May 22–25, 2021 | 1,023 (LV) | ± 3.1% | BA | – | 25% | 4% | – | 19% | – | 39% | 1%[i] | 12% | ||
| 3[j] | 46% | – | – | 54% | – | ||||||||||
Lisa Murkowski vs. Kelly Tshibaka
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[b] |
Margin of error |
Lisa Murkowski (R) |
Kelly Tshibaka (R) |
Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska Survey Research | April 16–21, 2022 | 1,208 (LV) | ± 2.9% | 55% | 45% | – |
Results edit
| Party | Candidate | First Choice | Round 1 | Round 2 | Round 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Transfer | Votes | % | Transfer | Votes | % | Transfer | Votes | % | ||||
| Republican | Lisa Murkowski (incumbent) | 113,495 | 43.37% | +623 | 114,118 | 43.39% | +1,641 | 115,759 | 44.49% | +20,571 | 136,330 | 53.70% | ||
| Republican | Kelly Tshibaka | 111,480 | 42.60% | +621 | 112,101 | 42.62% | +3,209 | 115,310 | 44.32% | +2,224 | 117,534 | 46.30% | ||
| Democratic | Pat Chesbro | 27,145 | 10.37% | +1,088 | 28,233 | 10.73% | +901 | 29,134 | 11.20% | −29,134 | Eliminated | |||
| Republican | Buzz Kelley (withdrew)[a] | 7,557 | 2.89% | +1,018 | 8,575 | 3.26% | −8,575 | Eliminated | ||||||
| Write-in | 2,028 | 0.77% | -2,028 | Eliminated | ||||||||||
| Total votes | 261,705 | 263,027 | 260,203 | 253,864 | ||||||||||
| Blank or inactive ballots | 3,770 | +2,824 | 6,594 | +6,339 | 12,933 | |||||||||
| Republican hold | ||||||||||||||
See also edit
Notes edit
- ^ a b Remained on the ballot because he withdrew after the deadline of 64 days ahead of the election.[17]
- ^ a b c Key:
A – all adults
RV – registered voters
LV – likely voters
V – unclear - ^ a b Kelley eliminated.
- ^ a b Chesbro eliminated.
- ^ The margin of sampling error for the 500 statewide sample is ±4.4%; for the 840 total sample of voters 50+ is ±3.3%.
- ^ Standard polling question.
- ^ Kelley eliminated. Vote transfer breakdown: 29% to Tshibaka and 71% not ranked further.
- ^ Chesbro eliminated. Vote transfer breakdown: 77% to Murkowski, 8% to Tshibaka, and 15% not ranked further.
- ^ Would not vote with 1%
- ^ Excluding undecided voters
Partisan clients
- ^ Poll sponsored by AARP
- ^ This poll was sponsored by Kelly Tshibaka's campaign
- ^ This poll was sponsored by 314 Action
References edit
- ^ Gomez, Henry J. "Sen. Lisa Murkowski wins re-election in Alaska, fending off Trump-backed challenge after a ranked-choice runoff", NBC News (November 23, 2022).
- ^ "Alaska Division of Elections, Primary Election Info". Archived from the original on May 4, 2022. Retrieved December 10, 2021.
- ^ Kitchenman, Andrew (November 18, 2020). "Alaska will have a new election system: Voters pass Ballot Measure 2". KTOO (FM). Archived from the original on November 18, 2020. Retrieved November 18, 2020.
- ^ Bolstad, Erika (January 5, 2011). "After primary loss, write-in win, legal battle, Murkowski sworn in". McClatchy. Archived from the original on March 1, 2020.
- ^ Khan, Huma (November 16, 2010). "Lisa Murkowski Makes History, Wins Alaska Senate Race But Joe Miller Not Conceding". ABC News. Archived from the original on April 19, 2022. Retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ^ "Miller Concedes Loss to Murkowski". CBS News. December 31, 2010. Archived from the original on April 19, 2022. Retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ^ Steinhauser, Paul (March 16, 2021). "Alaska GOP censures Murkowski, says it will recruit primary challenger". Fox News. Archived from the original on April 19, 2022. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ "Lisa Murkowski censured by Alaska Republicans for voting to convict Trump". The Guardian. Associated Press. March 16, 2021. Archived from the original on March 16, 2021. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ Desiderio, Andrew (June 4, 2020). "Trump vows to campaign against Murkowski after she backs Mattis". Politico. Archived from the original on April 19, 2022. Retrieved June 4, 2020.
- ^ Acosta, Jim; Pellish, Aaron (March 6, 2021). "Trump says he'll campaign against Murkowski in Alaska next year". CNN. Archived from the original on March 6, 2021. Retrieved March 6, 2021.
- ^ "Alaska GOP votes to censure McConnell over his support for Murkowski". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved November 13, 2022.
- ^ "Alaska Senate candidate drops out of race". The Hill. September 13, 2022. Retrieved September 26, 2022.
- ^ Cochrane, Emily (November 24, 2022). "Lisa Murkowski Wins Re-election in Alaska, Beating a Trump-Backed Rival". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 24, 2022.
- ^ "Alaska Sen. Lisa Murkowski to run in 2022; Trump backs rival". Associated Press. November 12, 2021. Archived from the original on April 12, 2022. Retrieved November 12, 2021.
- ^ Becky Bohrer (March 29, 2021). "Republican announces run for Murkowski's Alaska Senate seat". Associated Press. Archived from the original on April 18, 2022. Retrieved March 29, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "2022 Primary Candidate List". Alaska Division of Elections. Archived from the original on June 3, 2022. Retrieved June 1, 2022.
- ^ a b c "Alaska Senate candidate drops out of race". The Hill. September 13, 2022. Retrieved October 28, 2022.
- ^ a b c "Alaska Division of Elections Candidate List". April 25, 2022. Archived from the original on June 3, 2022. Retrieved April 25, 2021.
- ^ a b c d Thiessen, Mark (April 27, 2021). "Alaska candidate shadowed by anti-gay article, election post". Associated Press. Anchorage. Archived from the original on June 12, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
The state elections office says others who have registered for Senate include Dustin Darden with the Alaskan Independence Party, Huhnkie Lee, who is undeclared, and Republicans Samuel Little and Karl Speights.
- ^ Lottsfeldt, Jim (August 12, 2020). "It sure looks like Dunleavy is running for U.S. Senate in 2022". The Midnight Sun. Archived from the original on March 19, 2021. Retrieved October 30, 2020.
- ^ Brooks, James (August 13, 2021). "Alaska Gov. Mike Dunleavy will run for re-election in 2022". Anchorage Daily News. Archived from the original on April 16, 2022. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ "Sarah Palin Is Considering Running For Senate 'If God Wants Me To'—And Here We Go Again". Comic Sands. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on November 21, 2021. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ Ulloa, Jazmine; Peters, Jeremy W. (April 2, 2022). "Sarah Palin Announces She's Running for Congress in Alaska". The New York Times. Archived from the original on May 10, 2022. Retrieved May 8, 2022.
- ^ Kerry Picket (April 6, 2021). "Lisa Murkowski trails GOP challenger: Poll". Washington Examiner. Archived from the original on June 28, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ "A Mat-Su Democrat is running for U.S. Senate in Alaska, potentially scrambling the campaign". Archived from the original on May 20, 2022. Retrieved May 17, 2022.
- ^ "Chesbro For Alaska". Chesbro For Alaska. Archived from the original on June 24, 2022. Retrieved June 7, 2022.
- ^ a b "ALASKA STATEWIDE – SURVEY MEMORANDUM". www.politico.com. March 29, 2021. Archived from the original on April 14, 2021. Retrieved May 4, 2021.
- ^ "Taylor4Alaska.org". www.taylor4alaska.org. Archived from the original on May 18, 2022. Retrieved June 7, 2022.
- ^ Landfield, Jeff (July 27, 2021). "Democratic State Senator Elvi Gray-Jackson considering run for U.S. Senate". The Alaska Landmine. Archived from the original on February 10, 2022. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ "Anchorage state Sen. Elvi Gray-Jackson is 1st Democrat to enter race for U.S. Senate". Archived from the original on March 28, 2022. Retrieved February 10, 2022.
- ^ Democratic State Sen. Elvi Gray-Jackson makes it official: She is withdrawing from the Alaska U.S. Senate race in order to run for re-election to the Alaska Legislature. Archived March 25, 2022, at the Wayback Machine James Brooks on Twitter
- ^ "Sean Thorne FEC Statement of Candidacy". Archived from the original on December 23, 2021. Retrieved December 23, 2021.
- ^ a b c "Statewide campaign coffers are filling up". Juneau Empire. November 3, 2021. Archived from the original on March 5, 2022. Retrieved March 5, 2022.
- ^ Jacob Rubashkin (April 12, 2021). "Alaska Senate: Al Gross, 2020 Nominee, Considering Another Run". Inside Elections. Archived from the original on May 13, 2022. Retrieved April 12, 2021.
- ^ Matt Hickman (March 19, 2022). "Source: Gross running for Congressional seat vacated by Young's passing". Anchorage Press. Archived from the original on March 20, 2022. Retrieved March 21, 2022.
- ^ "August 16, 2022 Primary Election Summary Report - OFFICIAL RESULTS" (PDF). Alaska Division of Elections. September 2, 2022. Retrieved September 2, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Senate Race ratings". The Cook Political Report. Archived from the original on January 5, 2021. Retrieved January 14, 2021.
- ^ "Senate ratings". Inside Elections. Archived from the original on January 20, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "2022 Senate". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Archived from the original on February 1, 2021. Retrieved January 28, 2021.
- ^ "Alaska Senate Race 2022". Politico. April 1, 2022. Archived from the original on April 19, 2022. Retrieved April 19, 2022.
- ^ "Battle for the Senate 2022". RCP. January 10, 2022. Archived from the original on January 24, 2022. Retrieved January 11, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Election Forecast". Fox News. May 12, 2022. Archived from the original on May 12, 2022. Retrieved May 12, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Election Forecast". DDHQ. July 20, 2022. Archived from the original on January 6, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Election Forecast". FiveThirtyEight. June 30, 2022. Archived from the original on August 1, 2022. Retrieved June 30, 2022.
- ^ "Economist's 2022 Senate forecast". The Economist. September 7, 2022. Retrieved September 7, 2022.
- ^ Samuels, Iris (August 11, 2022). "In Alaska's U.S. Senate race, Murkowski and Tshibaka look ahead to November". Anchorage Daily News. Archived from the original on August 13, 2022. Retrieved August 16, 2022.
- ^ "Our Endorsed Candidates for Congress 2022". akcenter.org. July 20, 2022. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ Greenwood, Max (February 1, 2022). "Ex-President Bush backs two high-profile Republicans slammed by Trump". The Hill. Archived from the original on August 21, 2022. Retrieved February 1, 2022.
- ^ "Hogan to headline fundraiser for Murkowski in DC". The Hill. June 15, 2022. Archived from the original on August 1, 2022. Retrieved August 1, 2022.
- ^ "Bill Walker on Facebook". Facebook. November 3, 2022.
- ^ Niedzwiadek, Nick (March 7, 2021). "Sen. Barrasso backs Murkowski after Trump targets her". Politico. Archived from the original on March 12, 2021. Retrieved March 25, 2021.
- ^ a b Suzanne Downing (April 16, 2021). "Murkowski raises $380,687 in first quarter, as Tshibaka raises $214,844 in three days". Must Read Alaska. Archived from the original on June 2, 2021. Retrieved June 1, 2021.
- ^ "GOP senator accuses Trump allies of embracing 'cancel culture'". The American Independent. Associated Press. February 19, 2021. Archived from the original on July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 9, 2021.
- ^ Schnell, Mychael (February 6, 2022). "Manchin crosses party lines in officially endorsing Murkowski". The Hill. Archived from the original on February 6, 2022. Retrieved February 6, 2022.
- ^ Alex Rogers (March 30, 2021). "Republican Kelly Tshibaka launches Senate campaign against Lisa Murkowski". CNN. Archived from the original on April 10, 2021. Retrieved April 10, 2021.
- ^ a b Wang, Amy B. "Defying Trump, Rick Scott backs McConnell and Murkowski, tiptoes around false claims about election fraud". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on November 8, 2021. Retrieved November 8, 2021.
- ^ Ardrey, Taylor (March 28, 2021). "Alaska Sen. Dan Sullivan said he'll 'support' Sen. Lisa Murkowski's reelection". Business Insider. Archived from the original on March 28, 2021. Retrieved March 28, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "Democrats for Murkowski: Alaska Republican counts her fans across the aisle". POLITICO. POLITICO. July 18, 2022. Archived from the original on July 24, 2022. Retrieved July 25, 2022.
- ^ Olson, Tyler (August 4, 2022). "Tim Scott defends Murkowski endorsement amid blowback from the right: 'I like to win'". Fox News.
- ^ Montellaro, Zach (October 11, 2022). "Kinzinger endorses Dems in major governor, secretary of state races". Politico. Archived from the original on October 11, 2022. Retrieved October 11, 2022.
- ^ Caldwell, Leigh Ann (October 24, 2022). "Murkowski, Peltola cross party lines to endorse each other in tight Alaska races". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on October 24, 2022. Retrieved October 28, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Suzanne Downing (January 11, 2022). "Reps. Zack Fields, Bryce Edgmon, Dan Ortiz, and Sen. Gary Stevens endorse Murkowski". Archived from the original on January 25, 2022. Retrieved January 25, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Downing, Suzanne (February 8, 2022). "Lisa gets support from State Sen. von Imhof; Tshibaka brings in Alaska Outdoor Council endorsement for Senate". Must Read Alaska. Archived from the original on February 8, 2022. Retrieved February 11, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Endorsements - Lisa Murkowski for US Senate". lisamurkowski.com. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ "Citizens for Responsible Energy Solutions Announces Second Round of Congressional Endorsements for the 2022 Election Cycle". cresenergy.com. Citizens for Responsible Energy Solutions. May 4, 2022. Archived from the original on August 21, 2022. Retrieved June 7, 2022.
- ^ "Notes from the trail: Palin stumps in Georgia and Murkowski endorsed by NEA-Alaska". May 22, 2022. Archived from the original on May 22, 2022. Retrieved May 28, 2022.
- ^ "Anti-Trump Republicans endorsing vulnerable Democrats to prevent GOP takeover". The Hill. October 14, 2021. Archived from the original on October 19, 2021. Retrieved October 14, 2021.
- ^ "Endorsed Candidates". proisraelamerica.org. Archived from the original on December 20, 2021. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ "Endorsements". Forward Party.
- ^ "AFN endorses Peltola and Murkowski, citing accomplishments and commitments". alaskabeacon.com. October 23, 2022. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Endorsed Candidates".
- ^ Hall, Joelle; Bradley, Neil (October 18, 2022). "Opinion: Murkowski is a champion for workers and our economy". Anchorage Daily News. Retrieved December 19, 2022.
- ^ Brooks, James (June 23, 2022). "Alaska AFL-CIO endorses Walker, Murkowski, Peltola". Archived from the original on June 27, 2022. Retrieved June 27, 2022.
- ^ Axelrod, Tal (June 18, 2021). "Trump endorses Murkowski challenger". The Hill. Archived from the original on August 21, 2022. Retrieved June 18, 2021.
- ^ "Gov. Kristi Noem endorsing Kelly Tshibaka for Senate". May 12, 2022. Archived from the original on May 28, 2022. Retrieved May 28, 2022.
- ^ "Trump rallies his Alaska faithful against Murkowski, for Tshibaka and Palin". alaskapublic.org. July 9, 2022. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ "Trump-endorsed Kelly Tshibaka won on Wednesday the endorsement of Edgar Blatchford, a former U.S. Senate Democrat candidate and mayor of Seward". Twitter. September 7, 2022. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Surreal ValeCity (April 5, 2021). "Former Republican Chairmen endorse Kelly Tshibaka". www.surrealvalecity.com. Archived from the original on April 9, 2021. Retrieved April 7, 2021.
- ^ "Notes from the trail: Walker picks up new co-chairs". July 23, 2022. Archived from the original on July 25, 2022. Retrieved July 25, 2022.
- ^ Downing, Suzanne (August 6, 2021). "Donald Trump Jr. jumps in, supports Kelly Tshibaka for Senate". Must Read Alaska. Archived from the original on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ Celine Castronuovo (July 10, 2021). "Alaska GOP endorses Murkowski primary challenger". The Hill. Archived from the original on July 10, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ Bratton, Regina (September 29, 2021). "The Conservative Political Action Coalition (CPAC) today announced its endorsement Kelly Tshibaka for U.S. Senator of the State of Alaska". American Conservative Union. Archived from the original on June 26, 2022. Retrieved June 26, 2022.
- ^ "Endorsed Candidates". Campaign for Working Families. Archived from the original on November 30, 2020. Retrieved August 3, 2022.
- ^ "FRC Action PAC Endorses Kelly Tshibaka for U.S. Senate in Alaska". June 27, 2022. Archived from the original on August 13, 2022. Retrieved August 13, 2022.
- ^ Manchester, Julia (December 22, 2021). "Conservative women's group backing Murkowski challenger". The Hill. Archived from the original on December 22, 2021. Retrieved December 22, 2021.
- ^ "Tshibaka endorsed by leading national pro-life women's group". alaskawatchman.com. September 22, 2022. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ Downing, Suzanne (March 9, 2022). "Oil and Gas Workers Association endorses Tshibaka". Mustreadalaska.com. Archived from the original on March 12, 2022. Retrieved March 18, 2022.
- ^ "POLITICAL CANDIDATE SURVEY AND ENDORSEMENTS". alaskaoutdoorcouncil.org. June 30, 2022. Retrieved November 8, 2022.
- ^ "State of Alaska 2022 General Election RCV Detailed Report" (PDF). Alaska Division of Elections. November 30, 2022. Retrieved January 9, 2023.
- ^ "State of Alaska 2022 GENERAL ELECTION Election Summary Report" (PDF). Alaska Division of Elections. November 30, 2022. Retrieved January 8, 2023.
External links edit
Official campaign websites